©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3590-3596
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3590
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3590
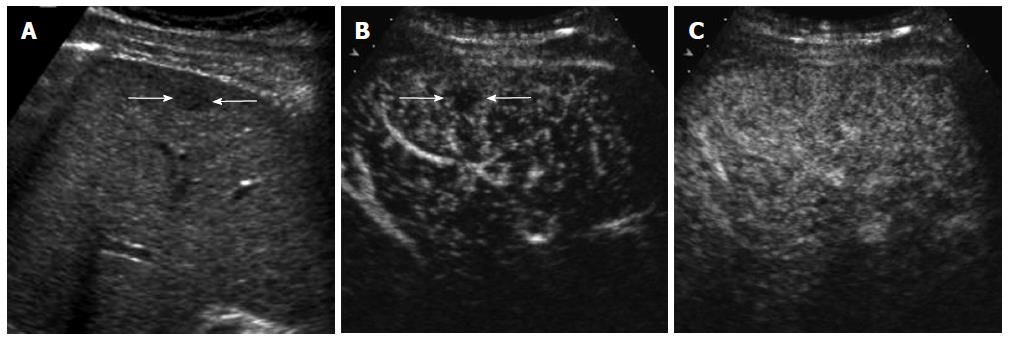
Figure 1 A 61-year-old man with hepatocellular carcinoma and renal failure.
A: Gray-scale ultrasound shows a hypoechoic mass (arrow) within the cirrhotic liver. There is a large amount of ascites surrounding the liver. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography or magnetic resonance scan could not be performed because of renal failure; B: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) image in the arterial phase shows hypervascularity of the mass (arrow) relative to the liver; C: The mass (arrow) shows washout in the portal venous phase. The diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma was made based on imaging findings of CEUS without biopsy.
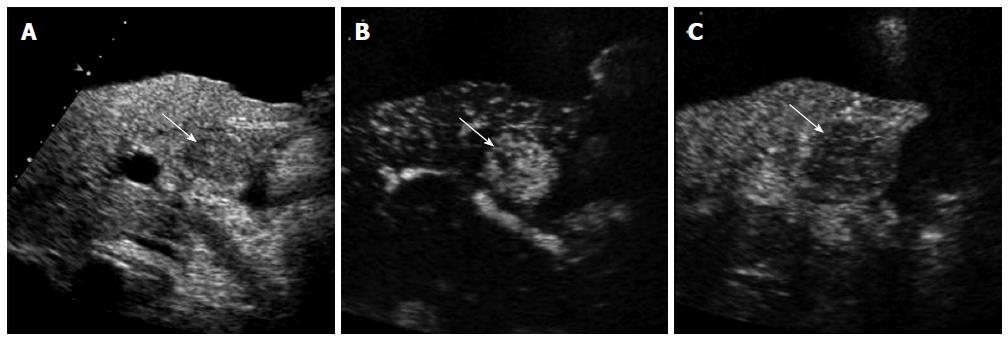
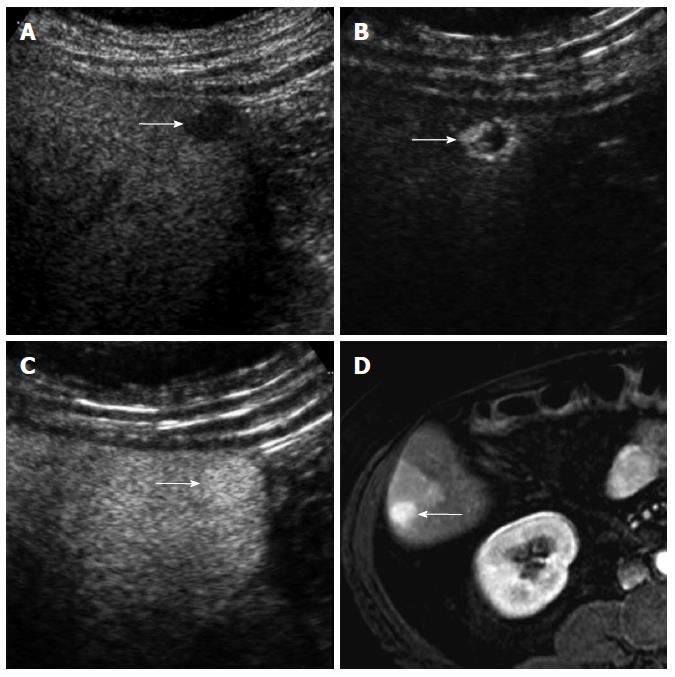
Figure 2 A 63-year-old man with moderately-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Computed tomography scan in the arterial phase shows a small exophytic nodule (arrow) which shows similar attenuation to the liver; B: The nodule (arrow) is slightly hypoattenuating to the liver in the delayed phase; C: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in the arterial phase clearly demonstrates hypervascularity of the nodule (arrow); D: CEUS in the portal venous phase shows washout of the nodule (arrow).
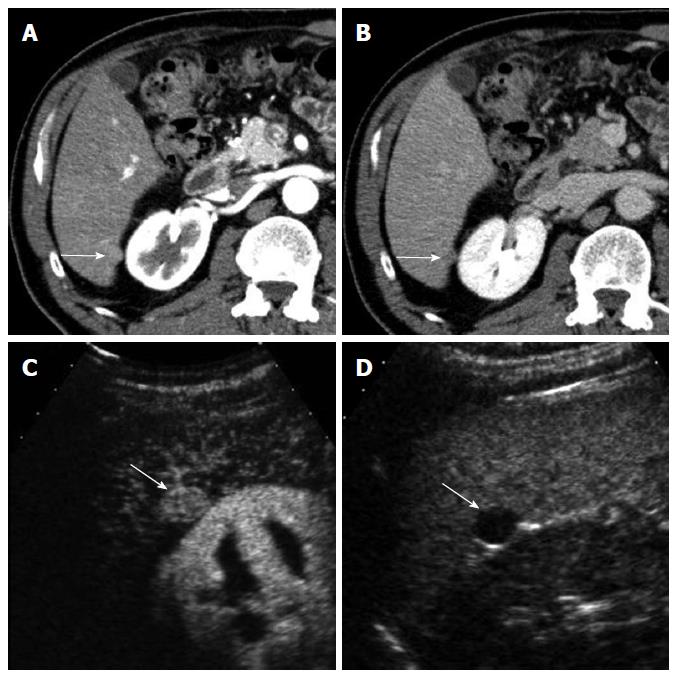
Figure 3 A 70-year-old man with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma detected during surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Gray-scale ultrasound shows a hypoechoic mass in the liver; B: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in the arterial phase obtained 14 s after contrast injection shows mild hypervascularity in the periphery of the mass (arrows); C: CEUS obtained at 19 s after contrast injection shows diffuse hypervascularity of the mass (arrows); D: The mass (arrows) shows rapid washout at 28 s after contrast injection. Biopsy revealed cholangiocarcinoma.
Figure 4 A 69-year-old man with well-differentiated hypovascular hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Gray-scale ultrasound shows an exophytic hypoechoic mass in the liver; B: The mass (arrows) is hypoechoic relative to the adjacent liver in the arterial phase of contrast-enhanced ultrasound; C: The mass (arrows) is isoechoic to the liver in the portal venous phase. Biopsy revealed well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma.
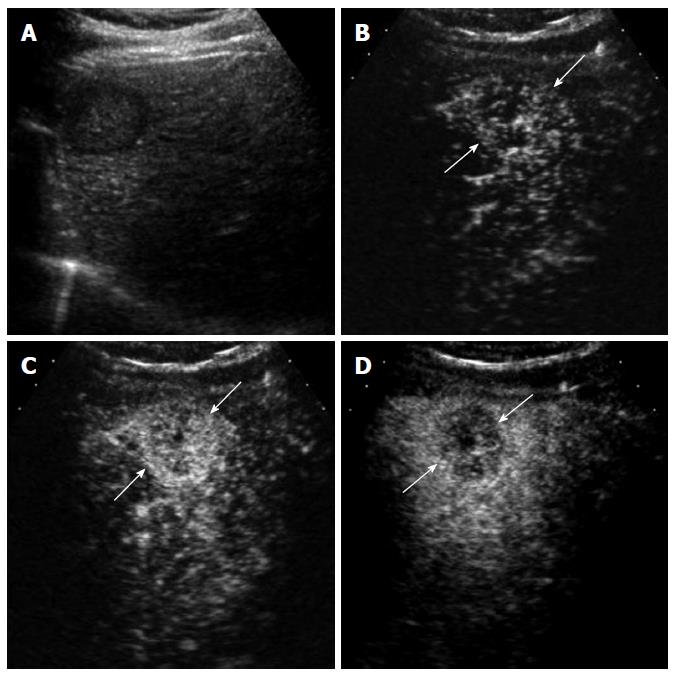
Figure 5 A 69-year-old man with dysplastic nodule.
A: Gray-scale ultrasound shows a small hypoechoic nodule (arrows) in the subcapsular portion of the liver; B: The nodule (arrows) is hypoechoic to the liver in the arterial phase of contrast-enhanced ultrasound; C: The nodule is isoechoic to the liver in the portal venous phase. Biopsy revealed low-grade dysplastic nodule.
Figure 6 A 53-year-old woman with hemangioma.
A: Gray-scale ultrasound shows a hypoechoic nodule (arrow) in the subcapsular portion of the liver; B: There is a peripheral strong hyperenhancement (arrows) in the arterial phase of contrast-enhanced ultrasound; C: The nodule (arrow) is homogeneously hyperechoic to the liver in the portal venous phase; D: The nodule (arrow) is homogeneously hyperintense to the liver without the appearance of peripheral enhancement in the arterial phase of contrast-enhanced T1-weighed magnetic resonance image.
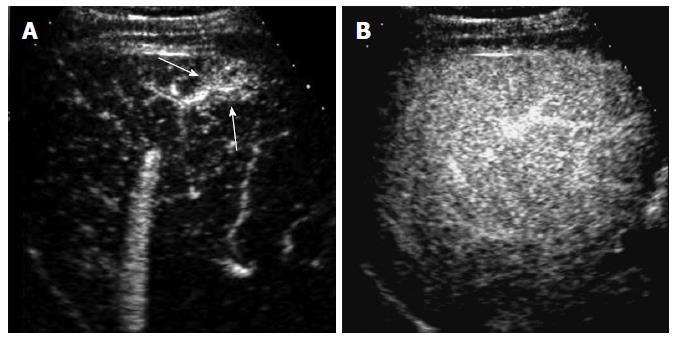
Figure 7 A 65-year-old man with nontumorous arterioportal shunt.
A: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the arterial phase shows a wedge-shaped hypervascular lesion (arrows) in the subcapsular portion of the liver; B: The lesion is not visualized in the portal venous phase due to isoechogenicity to the liver.
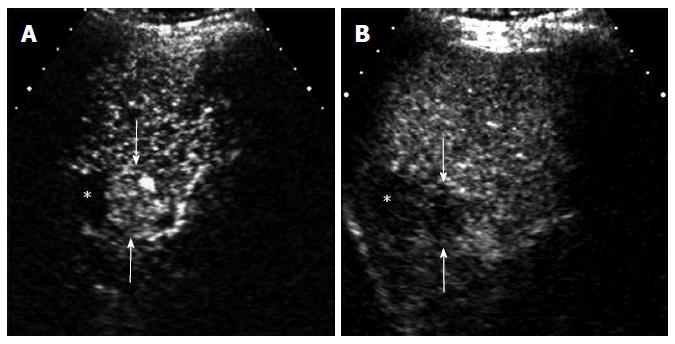
Figure 8 A 70-year-old man with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation.
A: There is a focal nodular hypervascular lesion (arrows) adjacent to an ablation zone (*) in the arterial phase of contrast-enhanced ultrasound; B: The lesion (arrows) shows washout in the portal venous phase.
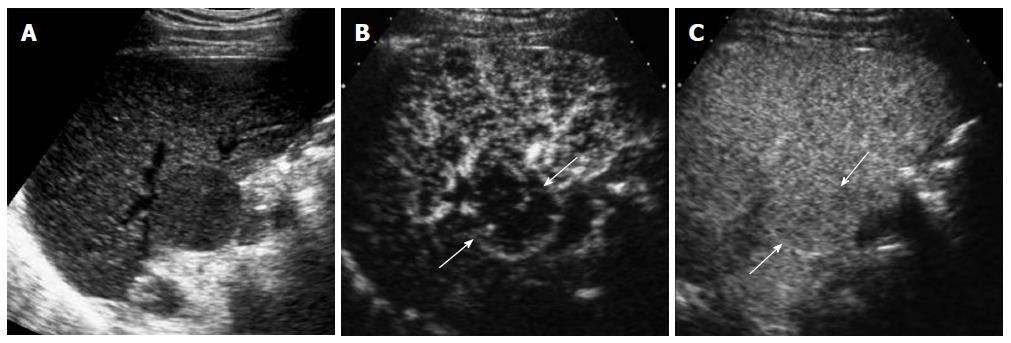
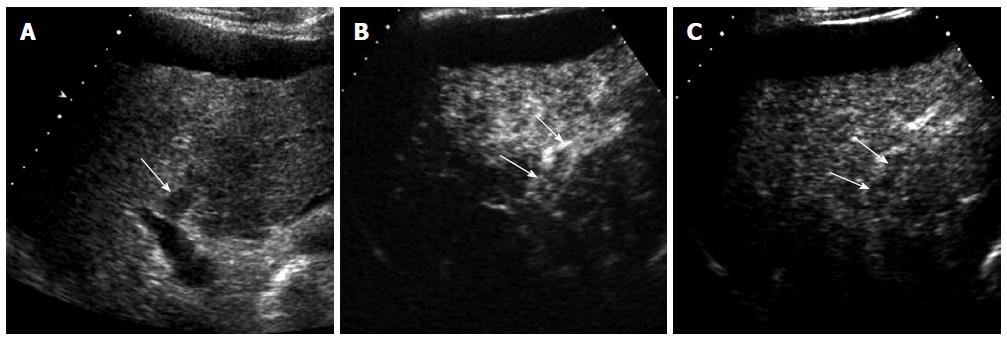
Figure 9 A 73-year-old man with malignant portal vein thrombosis associated with hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Gray-scale ultrasound shows a hypoechoic thrombus (arrow) within the anterior segmental branch of the right portal vein; B: The thrombus (arrows) is heterogeneously enhancing in the arterial phase of contrast-enhanced ultrasound; C: The thrombus (arrows) is hypoechoic relative to the liver in the portal venous phase.
- Citation: Kim TK, Jang HJ. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the diagnosis of nodules in liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3590-3596
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3590.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3590