©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2014; 20(12): 3180-3190
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3180
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3180
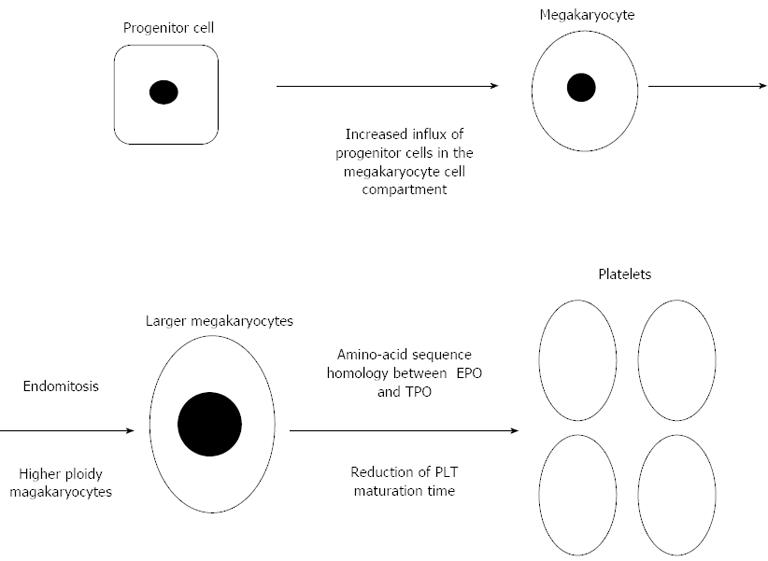
Figure 1 Possible iron deficiency mechanisms affecting platelet count in inflammatory bowel disease.
PLT: Platelets; TPO: Thrombopoietin; EPO: Erythropoietin.
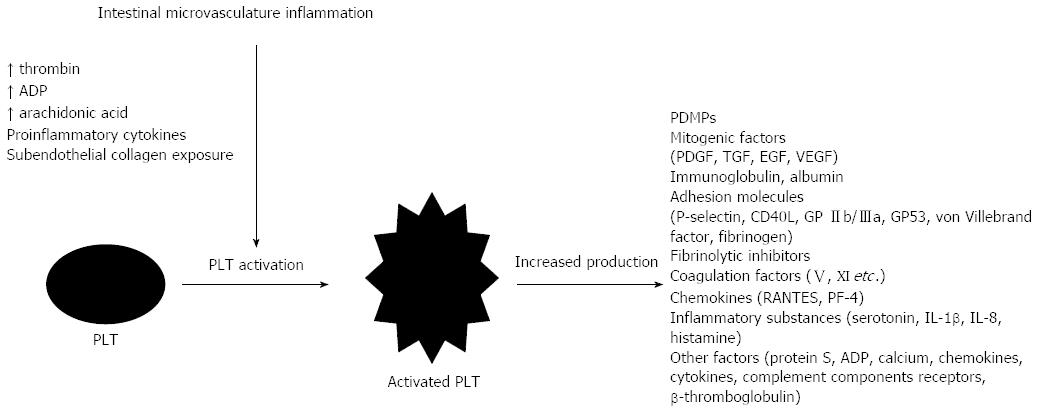
Figure 2 Factors affecting platelet function and platelet products in inflammatory bowel disease.
PLT: Platelets; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; PDMP: Platelet-derived microparticles; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PF-4: Platelet factor-4; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Voudoukis E, Karmiris K, Koutroubakis IE. Multipotent role of platelets in inflammatory bowel diseases: A clinical approach. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(12): 3180-3190
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i12/3180.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3180