©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2014; 20(10): 2725-2730
Published online Mar 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2725
Published online Mar 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2725
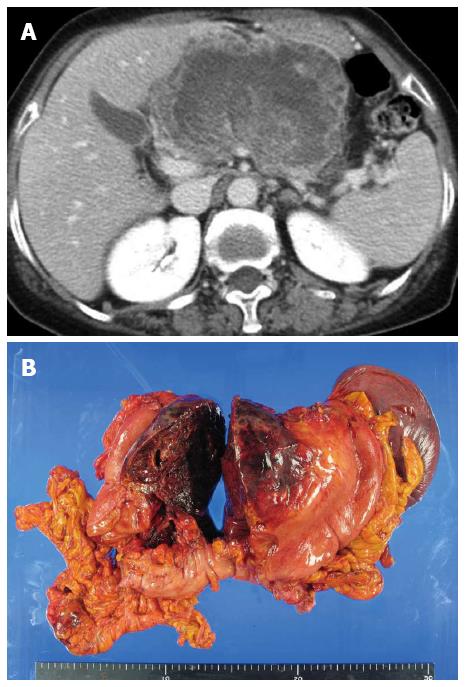
Figure 1 Huge undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells.
A: Computed tomography scans revealed the tumor occupying the lesser sac; B: Tumor arose from the pancreas body and invaded directly the stomach wall and transverse mesocolon.
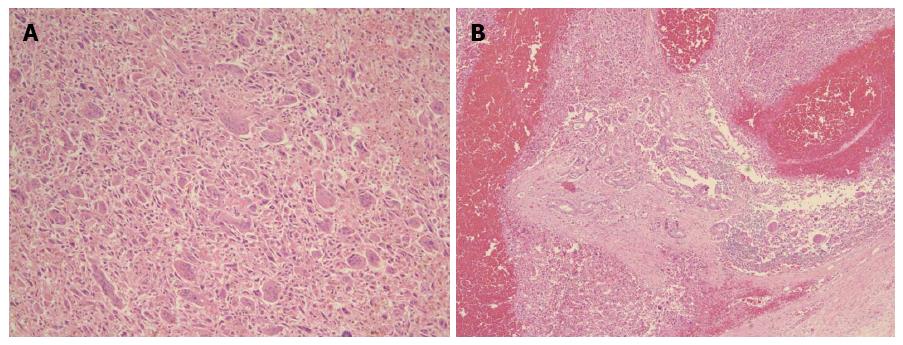
Figure 2 Histopathological characteristics.
A: Tumor was composed of highly pleomorphic neoplastic cells and non-neoplastic osteoclast-like giant cells. Hematoxylin and eosin (H and E), × 100; B: Ductal adenocarcinoma component was also found in some areas. H and E, × 40.
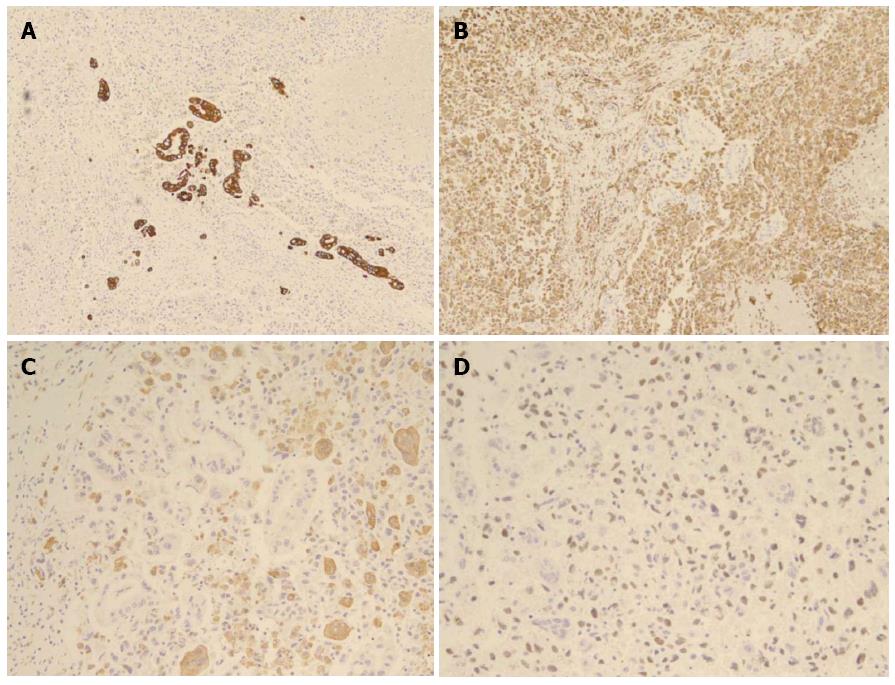
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining.
A: Reactivity with cytokeratin in ductal adenocarcinoma component; B: Reactivity with vimentin in pleomorphic neoplastic cells; C: Reactivity with CD68 in osteoclast-like giant cells; D: Reactivity with p53 in tumor cells.
- Citation: Jo S. Huge undifferentiated carcinoma of the pancreas with osteoclast-like giant cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(10): 2725-2730
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i10/2725.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2725