©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2013; 19(47): 9111-9118
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9111
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9111
Figure 1 Flow chart of study selection and risk of bias summary.
A: Flow chart of study selection; B: Risk of bias summary.
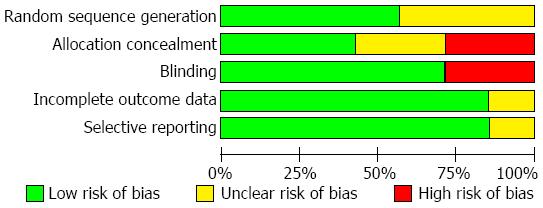
Figure 2 Risk of bias in trials.
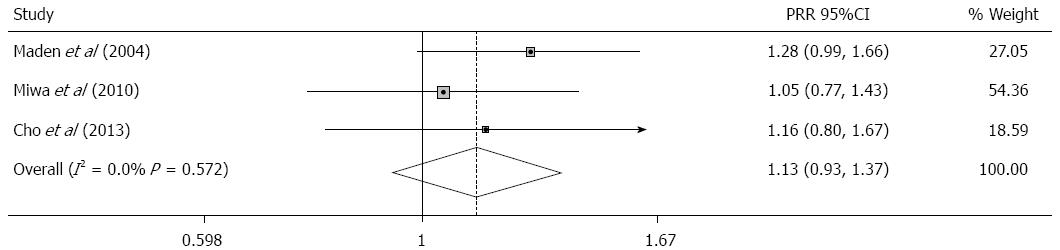
Figure 3 Meta-analysis of three trials that used mosapride as combined therapy with proton pump inhibitor compared with placebo in gastroesophageal reflux disease, a fixed-effects model was used and pooled relative rate was the measure of effect size.
I2, total variation across studies that is attributable to heterogeneity rather than to chance; PRR: Pooled relative rate.
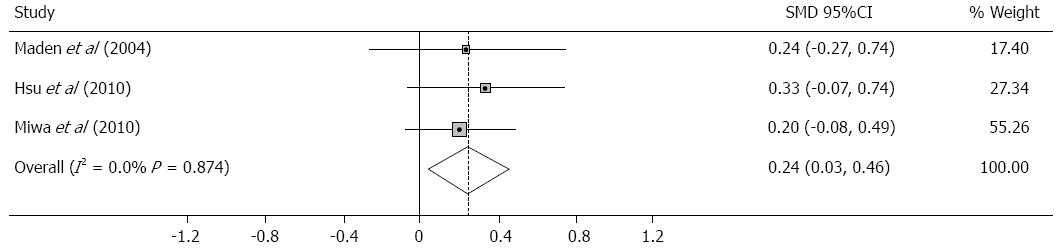
Figure 4 Meta-analysis of three trials that used mosapride as combined therapy with proton pump inhibitor compared with placebo in gastroesophageal reflux disease, a fixed-effects model was used and Hedges’g was the measure of effect size.
I2, total variation across studies that is attributable to heterogeneity rather than to chance; SMD: Standardized mean difference.
- Citation: Liu Q, Feng CC, Wang EM, Yan XJ, Chen SL. Efficacy of mosapride plus proton pump inhibitors for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: A systematic review. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(47): 9111-9118
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i47/9111.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9111