©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2013; 19(43): 7661-7670
Published online Nov 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7661
Published online Nov 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7661
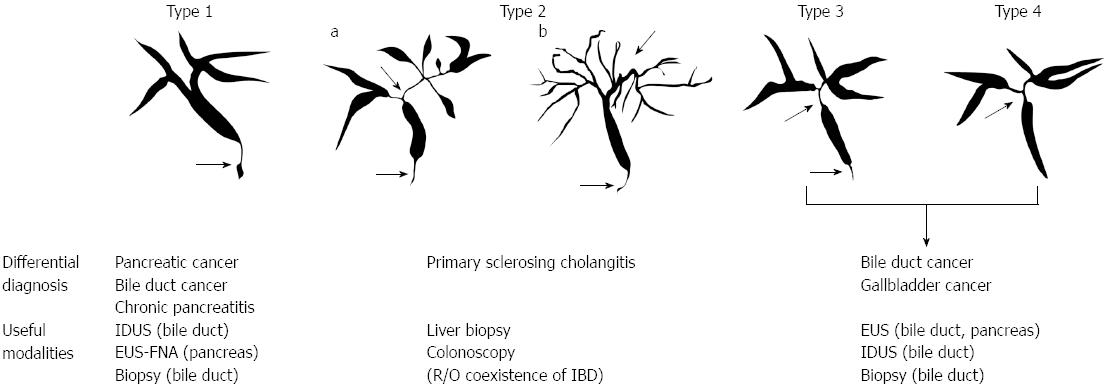
Figure 1 Cholangiographic classification of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and differential diagnosis.
Stenosis is located only in the lower part of the common bile duct in type 1; stenosis is diffusely distributed in the intra-and extra-hepatic bile ducts in type 2. Type 2 is further subdivided into two. Extended narrowing of the intrahepatic bile ducts with prestenotic dilation is widely distributed in type 2a. Narrowing of the intrahepatic bile ducts without prestenotic dilation and reduced bile duct branches are widely distributed in type 2b; stenosis is detected in both the hilar hepatic lesions and the lower part of the common bile ducts in type 3; strictures of the bile duct are detected only in the hilar hepatic lesions in type 4. IDUS: Intraductal ultrasonography; EUS-FNA: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease.
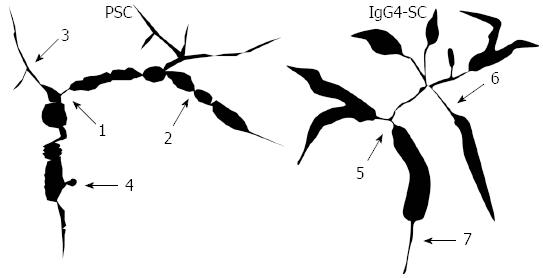
Figure 2 Schematic illustration of comparison of cholangiographic (primary sclerosing cholangitis vs IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis) findings[28].
The schematic comparison of cholangiographic findings between IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (SC) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). IgG4-related SC displays segmental and long strictures and stricture of the lower common bile duct, whereas PSC displays band-like strictures (1-2 mm), beaded appearance (short and annular stricture alternating with normal or minimally dilated segments), pruned-tree appearance (diminished arbolization of intrahepatic duct and pruning), and diverticulum-like outpouching (outpouchings resembling diverticula, often protruding between adjacent strictures). 1: Band-like stricture; 2: Beaded appearance; 3: Pruned-tree appearance; 4: Dverticulum-like outpouching; 5: Segmental stricture; 6: Long stricture with prestenotic dilation; 7: Stricture of lower common bile duct.
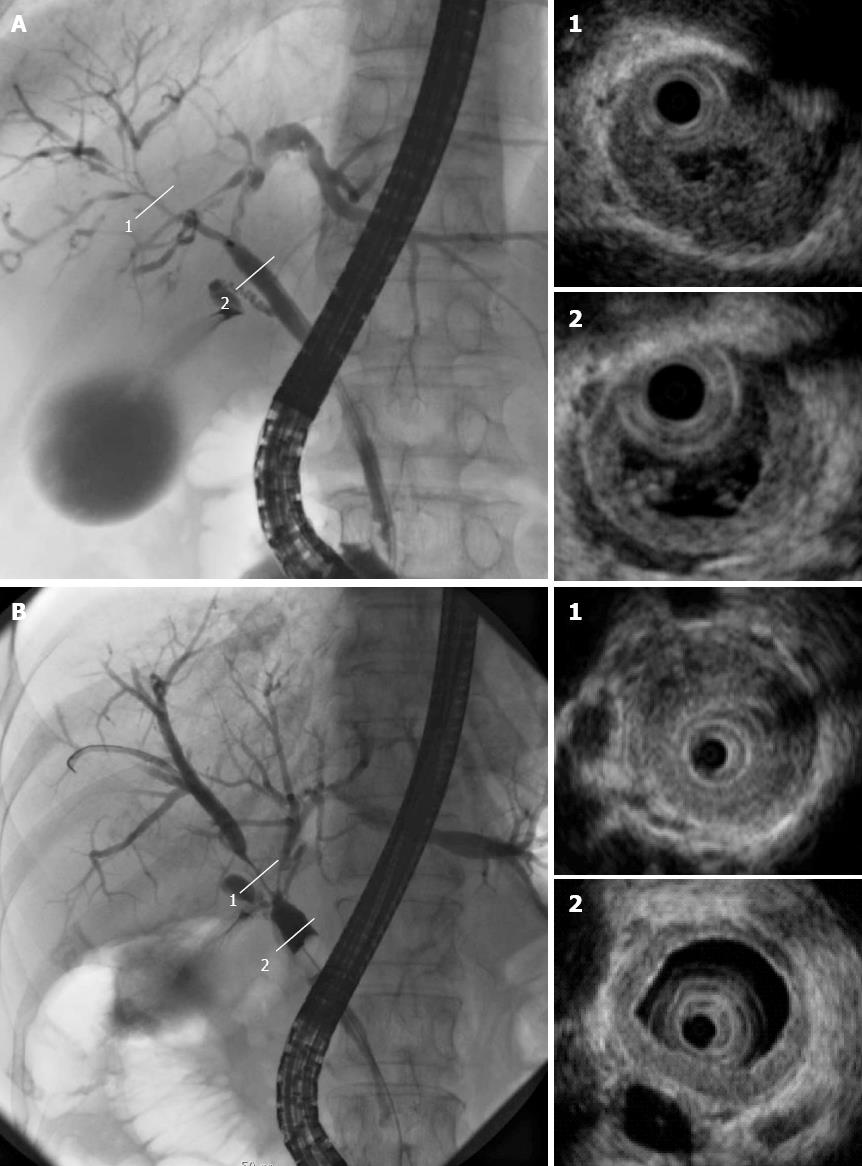
Figure 3 Cholangiogram displaying stenosis in the intrahepatic ducts (A-1) and hilar hepatic lesions (B-1); intraductal ultrasonography revealing bile duct wall thickening in areas with stenosis (1) and without (2).
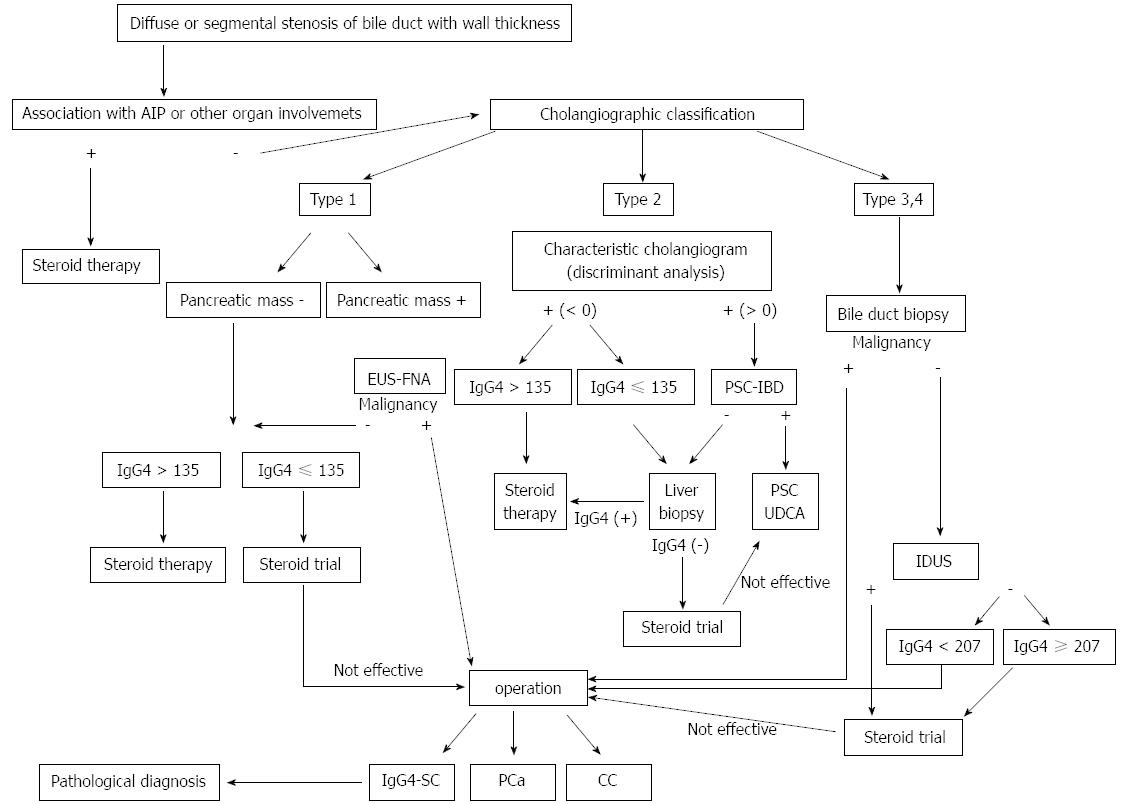
Figure 4 Algorithm for management of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (cited from [22]).
CC: Cholangiocarcinoma; PSC: Primary sclerosing cholangitis; IgG4-SC: IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis; IDUS: Intraductal ultrasonography; EUS-FNA: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; UDCA: Ursodeoxycholic acid.
- Citation: Nakazawa T, Naitoh I, Hayashi K, Miyabe K, Simizu S, Joh T. Diagnosis of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(43): 7661-7670
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i43/7661.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7661