©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2013; 19(41): 7097-7105
Published online Nov 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i41.7097
Published online Nov 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i41.7097
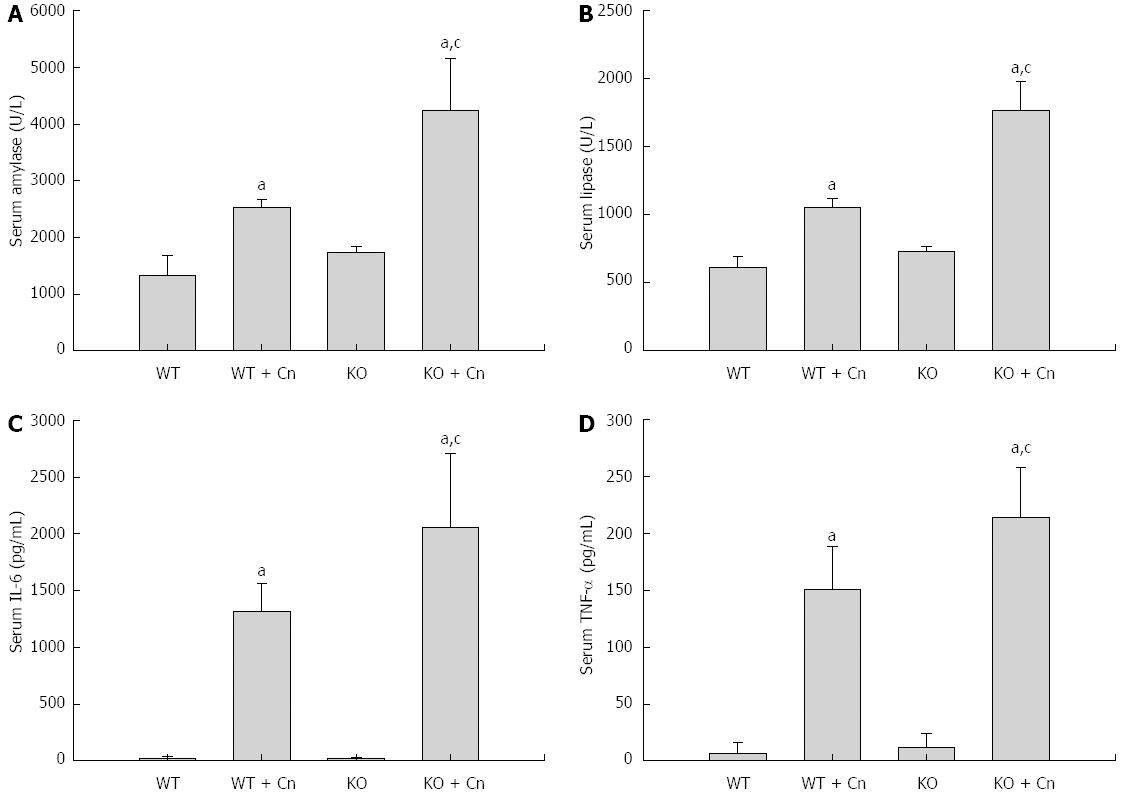
Figure 1 Mice deficient in C/EBP homologous protein displayed increased serum amylase, lipase, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α.
Acute pancreatitis was induced using cerulein (Cn) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in Chop-/- (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice. Serum levels of amylase (A), lipase (B), interleukin (IL)-6 (C), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (D), were detected 24 h (A-C) and 9 h (D) after induction of acute pancreatitis. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6). The data are normally distributed. aP < 0.05 compared with WT mice without pancreatitis; cP < 0.05 vs WT mice with pancreatitis.
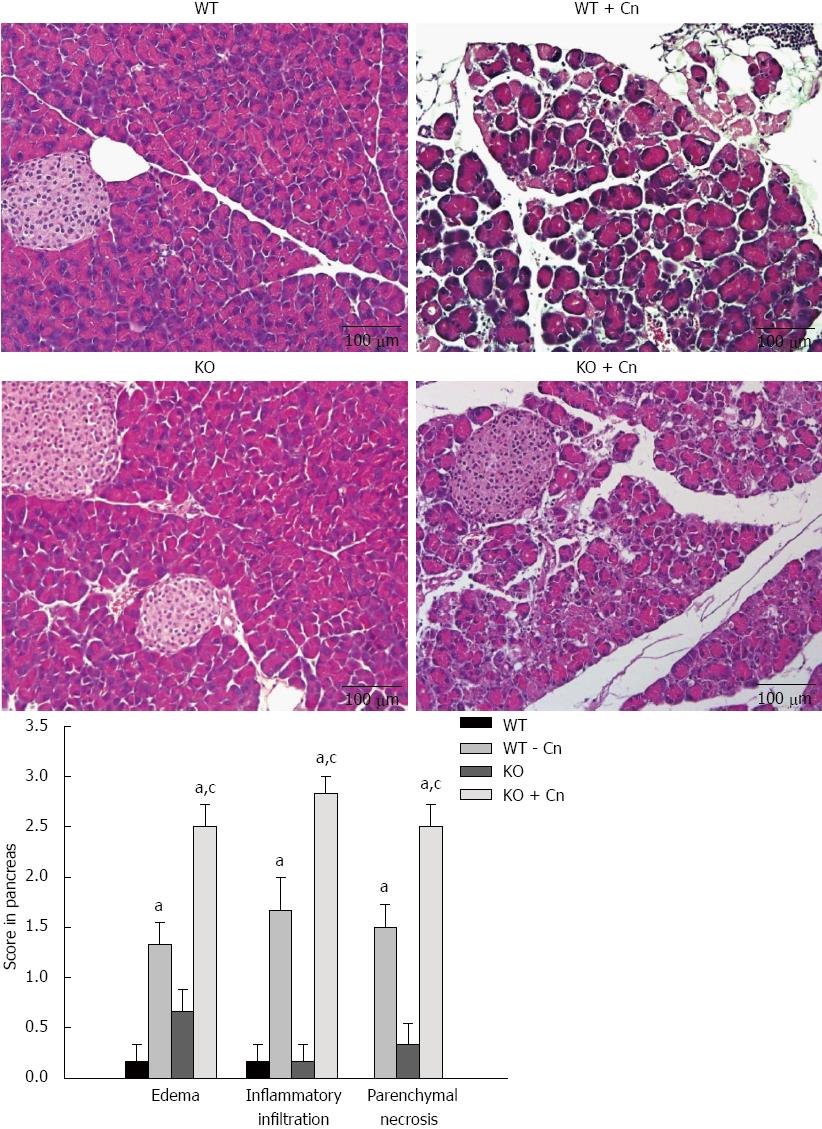
Figure 2 Experimental acute pancreatitis in Chop-/- mice.
Acute pancreatitis was induced using cerulein (Cn) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in Chop-/- (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice. Histological examination was performed 24 h after induction of acute pancreatitis. Representative histological changes in pancreatic sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin are shown. Scale bar = 100 μm. Pathological changes in the pancreas were scored. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4). The data are normally distributed. aP < 0.05 vs WT mice without pancreatitis; cP < 0.050 vs WT mice with pancreatitis.
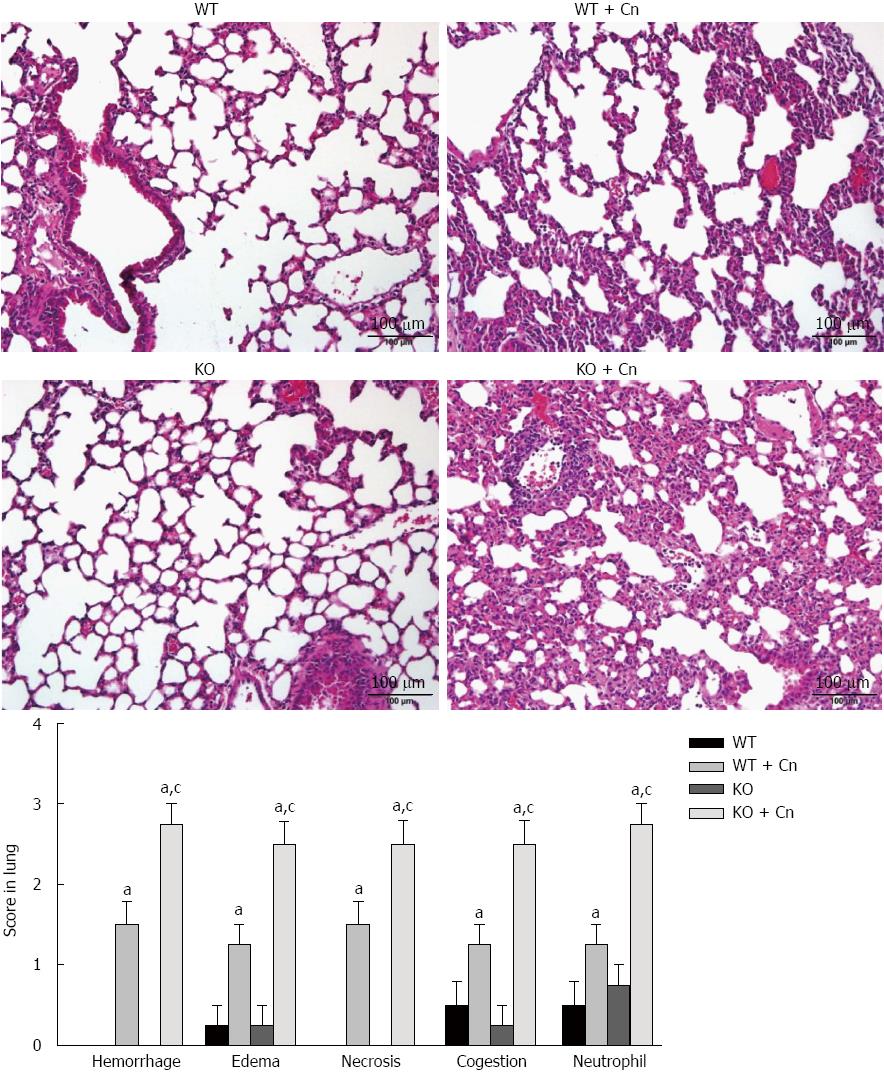
Figure 3 Experimental acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury in Chop-/- mice.
Acute pancreatitis was induced using cerulein (Cn) and lipopolysaccharide in Chop-/- (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice. Histological examination was performed 24 h after induction of acute pancreatitis. Representative histological changes in lung sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin are shown. Scale bar = 100 μm. Pathological changes in lungs were scored. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4). The data are normally distributed. aP < 0.050 vs WT mice without pancreatitis; cP < 0.05 vs WT mice with pancreatitis.
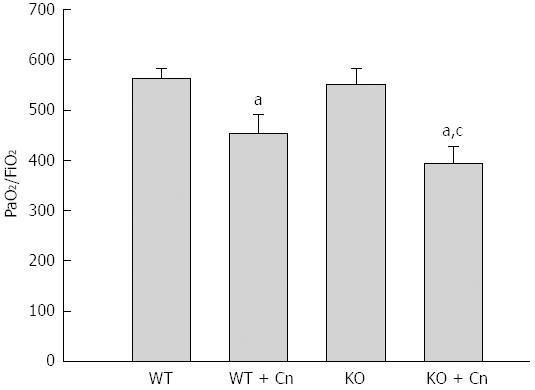
Figure 4 The PaO2/FiO2 ratio in Chop-/- mice with acute pancreatitis.
Acute pancreatitis was induced by using cerulein (Cn) and lipopolysaccharide in Chop-/- (KO) mice and wild-type (WT) mice. The PaO2/FiO2 ratio was detected 24 h after induction of acute pancreatitis in mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6). The data are normally distributed. aP < 0.05 vs wild type mice without pancreatitis;. cP < 0.05 vs wild type mice with pancreatitis.
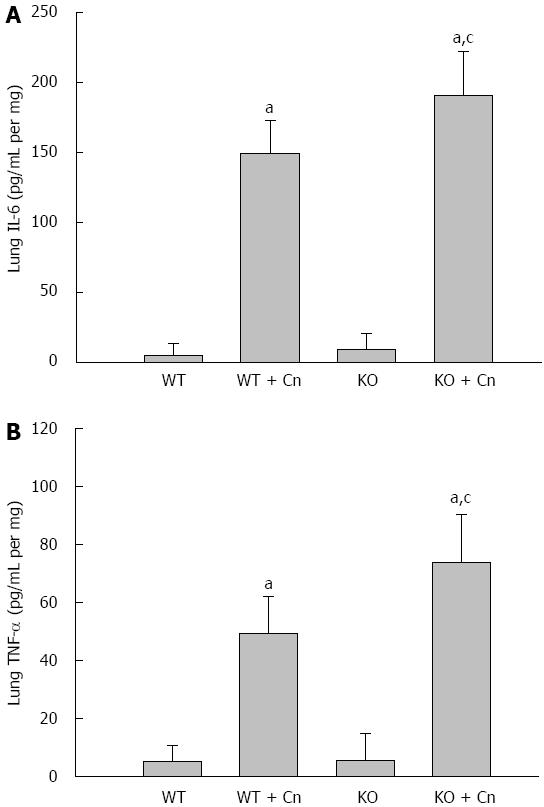
Figure 5 Mice deficient in C/EBP homologous protein displayed increased interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α in the lungs.
Levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (A), and interleukin (IL)-6 (B) were detected 9 h (A) and 24 h (B) after induction of acute pancreatitis in Chop-/- and wild-type (WT) mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6). The data are normally distributed. aP < 0.050 vs WT mice without pancreatitis; cP < 0.05 vs WT mice with pancreatitis.
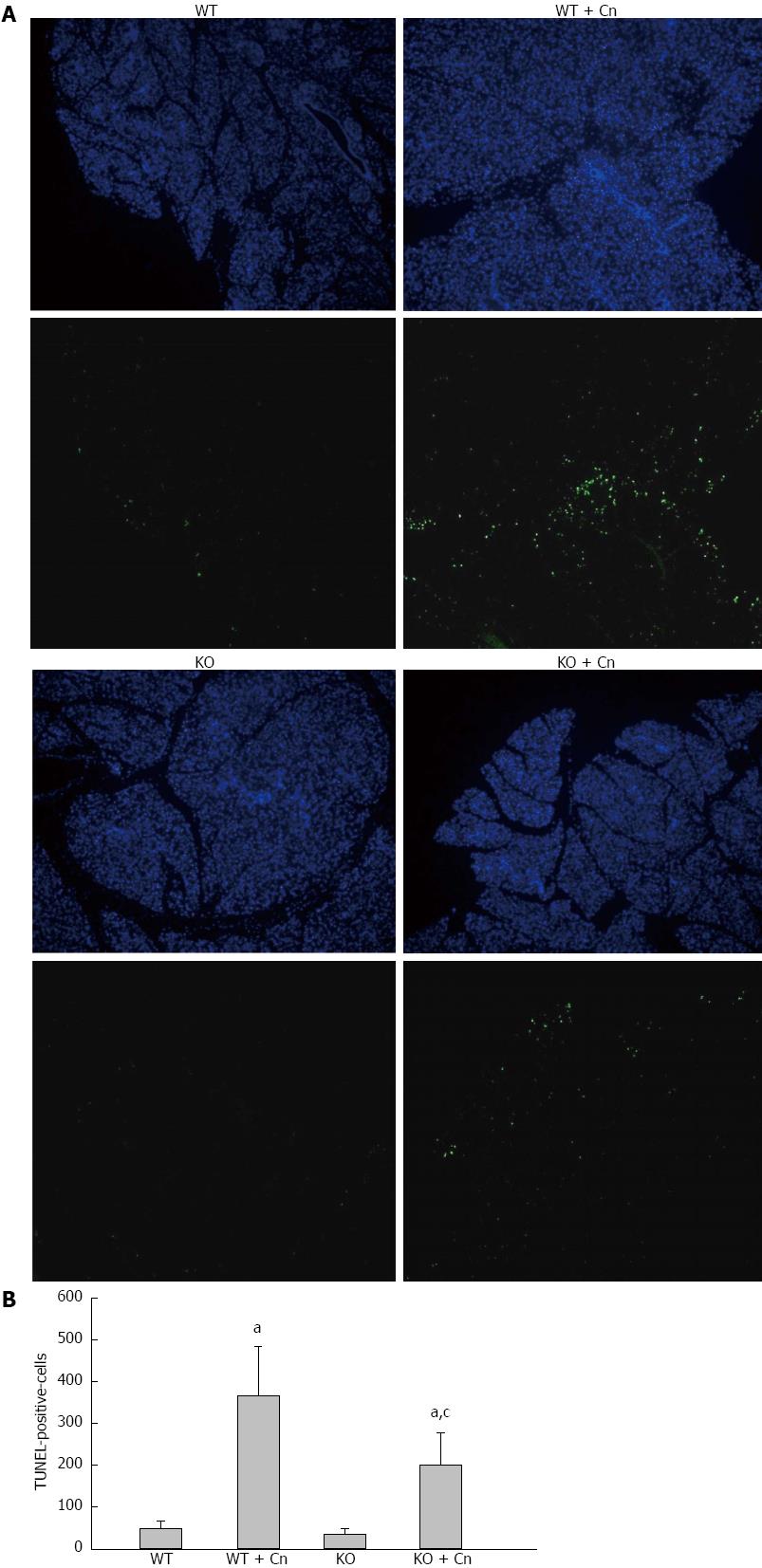
Figure 6 Mice deficient in C/EBP homologous protein displayed decreased apoptosis in the pancreas after induction of acute pancreatitis.
Acute pancreatitis was induced using cerulein (Cn) and lipopolysaccharide in Chop-/- (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice. We performed transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick-end labeling (TUNEL) analysis 9 h after induction of acute pancreatitis. Results indicated the presence of TUNEL-positive cells (A, B) in the pancreas. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6). The data are normally distributed. aP < 0.050 vs WT mice without pancreatitis; cP = 0.016 vs WT mice with pancreatitis.
- Citation: Weng TI, Wu HY, Chen BL, Jhuang JY, Huang KH, Chiang CK, Liu SH. C/EBP homologous protein deficiency aggravates acute pancreatitis and associated lung injury. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(41): 7097-7105
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i41/7097.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i41.7097