©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2013; 19(31): 5182-5186
Published online Aug 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i31.5182
Published online Aug 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i31.5182
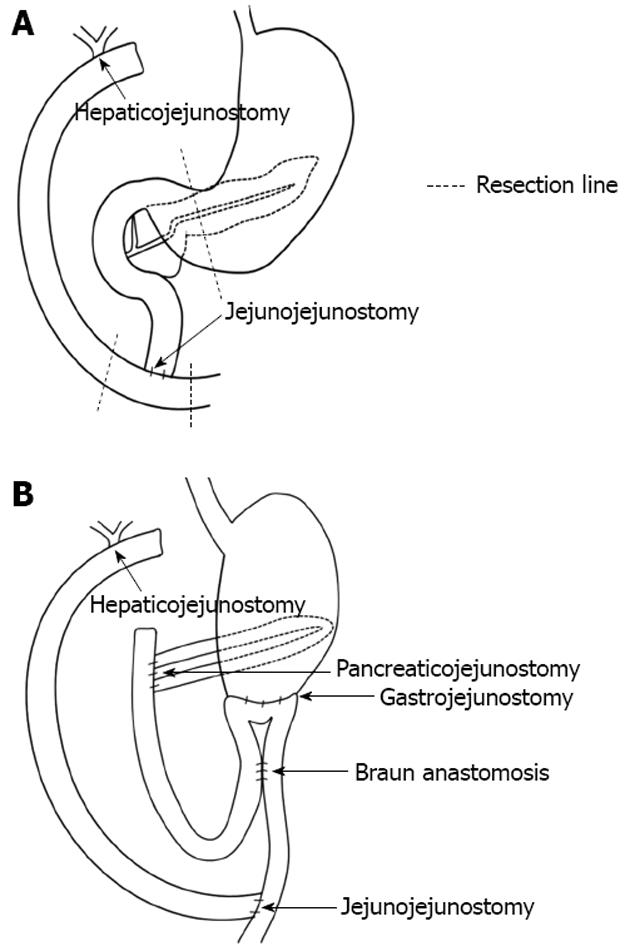
Figure 1 Re-construction after subtotal stomach-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy.
A: Before the operation (after excision of extrahepatic bile duct and Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy; B: After the operation, pancreaticojejunostomy and gastrojejunostomy were performed. Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy was re-established.
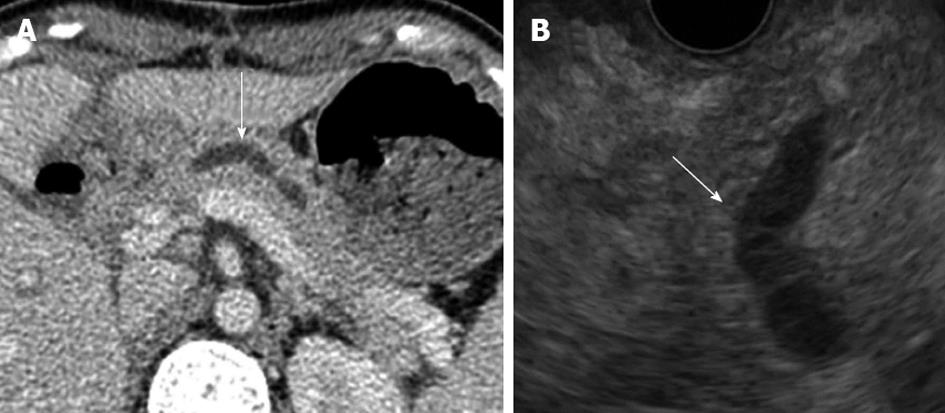
Figure 2 Computed tomography (A) and and endoscopic ultrasonography (B) revealed a dilated pancreatic duct (white arrows).
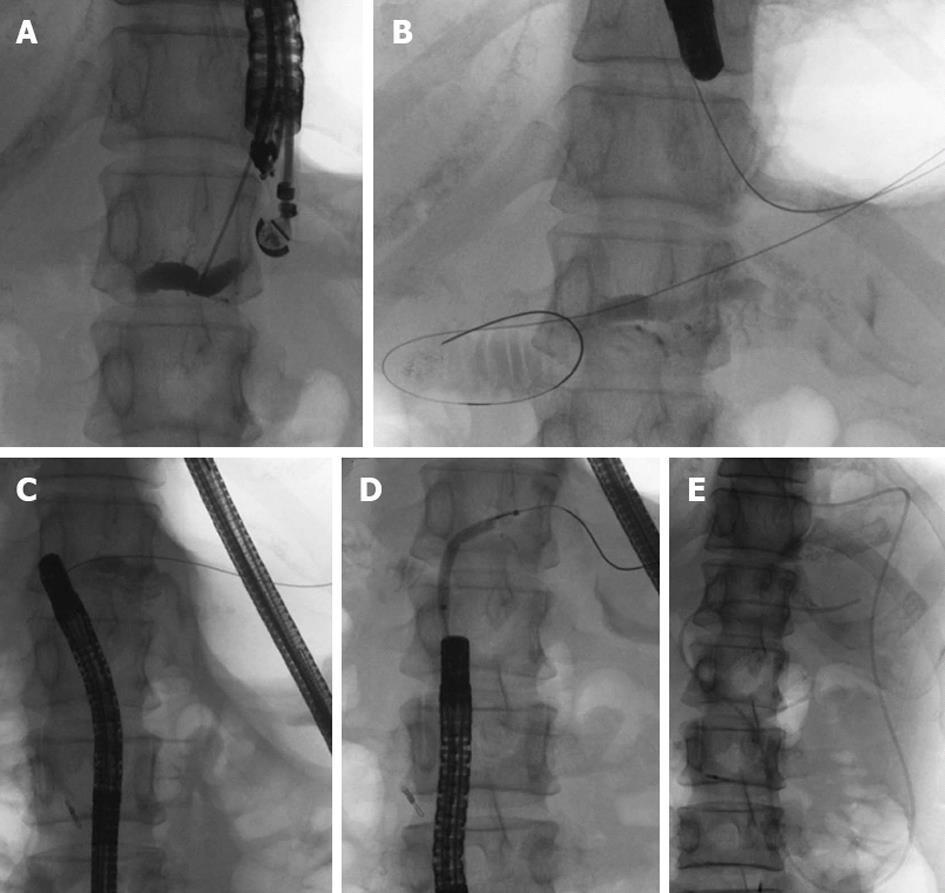
Figure 3 Pancreatic duct drainage procedures using endoscopic ultrasonograph-guided rendezvous technique.
A: Pancreatic duct puncture and pancreatography using endoscopic ultrasonography; B: Introducing the guidewire into the jejunum through the pancreatic duct and the stenotic anastomosis; C: After exchanging echoendoscope for oblique-viewing endoscope, the guidewire was withdrawn into the working channel; D: Balloon dilatation of the stenotic anastomosis; E: Placement of an endoscopic naso-pancreatic drainage tube.
- Citation: Takikawa T, Kanno A, Masamune A, Hamada S, Nakano E, Miura S, Ariga H, Unno J, Kume K, Kikuta K, Hirota M, Yoshida H, Katayose Y, Unno M, Shimosegawa T. Pancreatic duct drainage using EUS-guided rendezvous technique for stenotic pancreaticojejunostomy. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(31): 5182-5186
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i31/5182.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i31.5182