©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2013; 19(31): 5085-5093
Published online Aug 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i31.5085
Published online Aug 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i31.5085
Figure 1 The molecular structure of radix curcumae-derived diterpenoid C.
Originated from Huang et al[9], with permission.
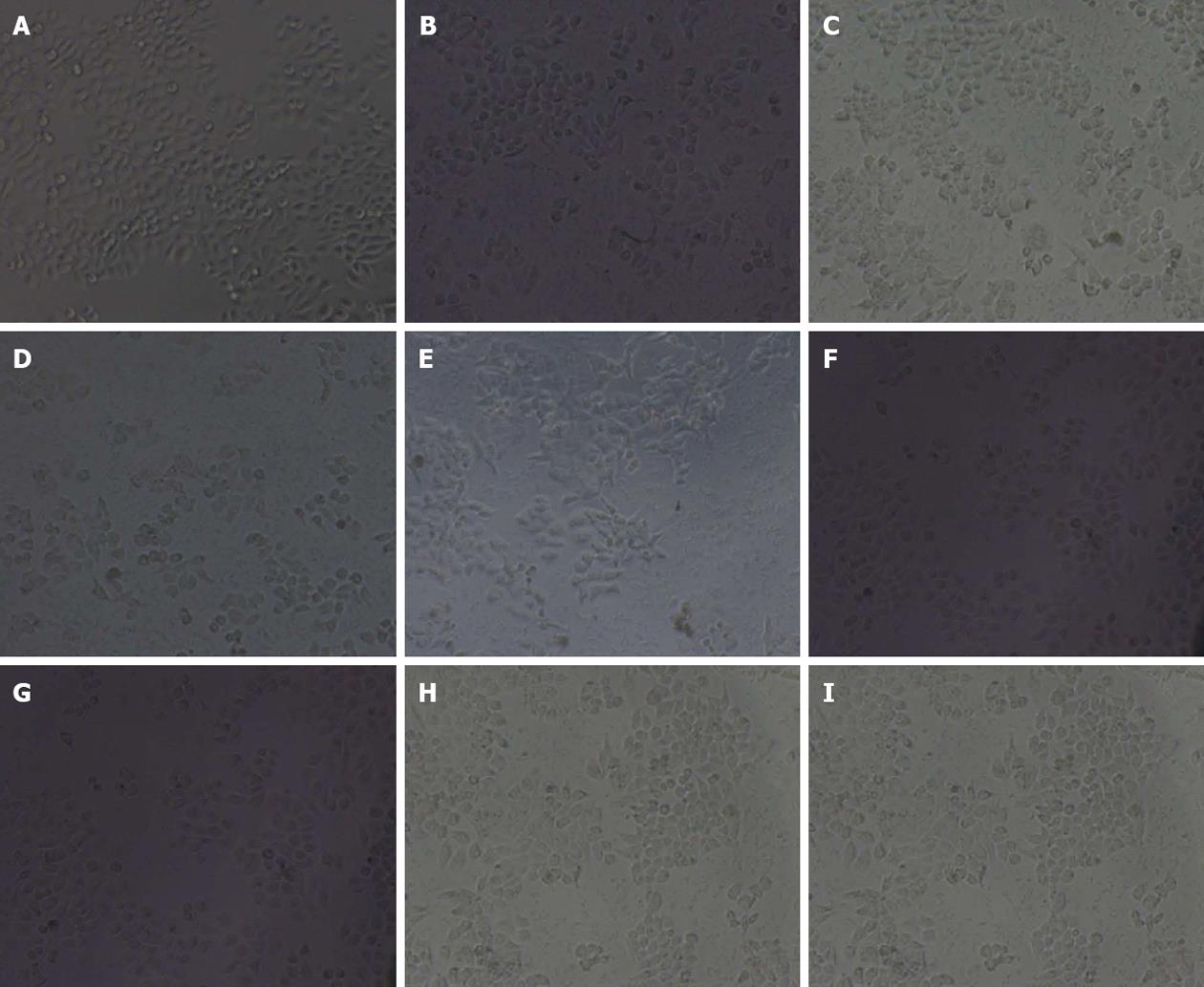
Figure 2 Gastric epithelium cell line cell morphology (× 200).
In bland group, gastric epithelium cell line (GES-1) cells were polygon-shaped or spindle-shape with pseudopodia and island-like growth. Cells gradually were adherent. With prolonged incubation time, the number and density of cells were increased with a few floating cells (A). In the GES-1 cells treated with Helicobacter pylori for 12 (B), 24 (C), 48 (D) and 72 (E), cells became round; adherent cells were decreased and floating cells were increased; fragments occurred around cells; cell junction was reduced; the boundaries between cell nucleus and cytoplasm were obscure, and nucleus-cytoplasm fusion was seen. In the GES-1 cells treated with radix curcumae-derived diterpenoid C (5, 10, 20 μg/mL), adherent cells increased and cell morphology gradually recovered at 24 h (F-I, respectively). Amoxicillin had no marked effects on cell morphology.
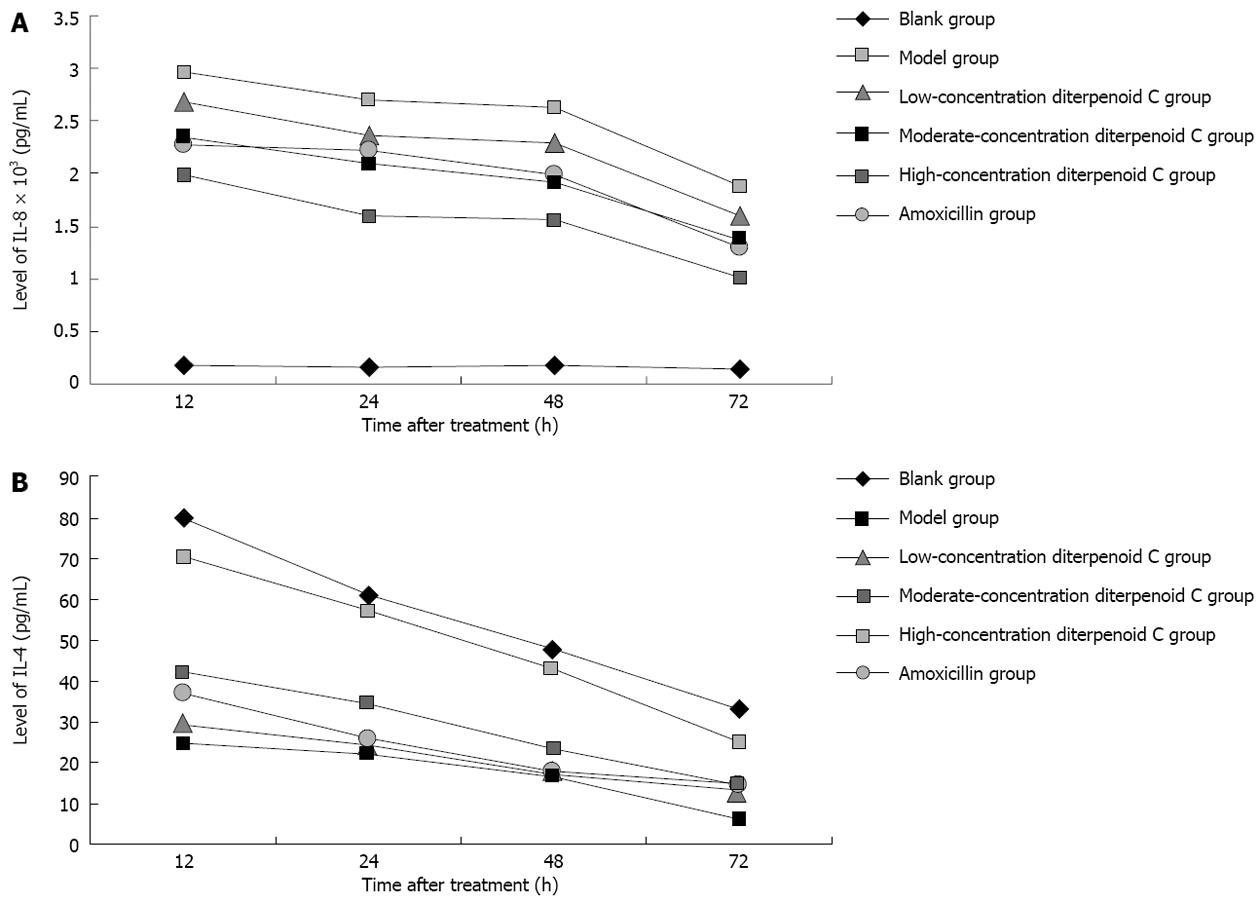
Figure 3 Effects of radix curcumae-derived diterpenoid C on Helicobacter pylori-induced human gastric epithelium cell line cell inflammation.
A: The changes in the level of interleukin (IL)-8 in cell supernatant; B: The changes in the level of IL-4 in cell supernatant.
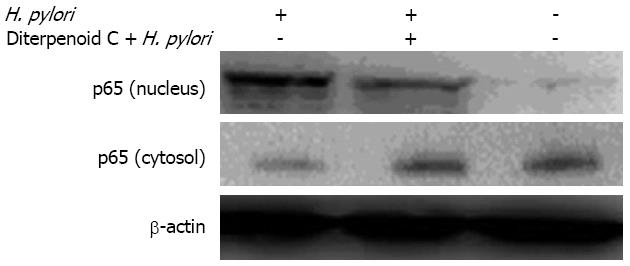
Figure 4 Effects of radix curcumae-derived diterpenoid C on nucleic localization of nuclear factor kappa B p65.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
Figure 5 Effects of radix curcumae-derived diterpenoid C on IkBα degradation caused by Helicobacter pylori.
A: After gastric epithelium cell line cells were respectively treated with Helicobacter pylori for 0, 15, 30, 60 and 90 min, cytoplasm was isolated to be used for determination of IkBα degradation with Western blotting; B: Helicobacter pylori for 0, 5, 15 and 30 min; C: Diterpenoid C + Helicobacter pylori for 0, 5, 15 and 30 min.
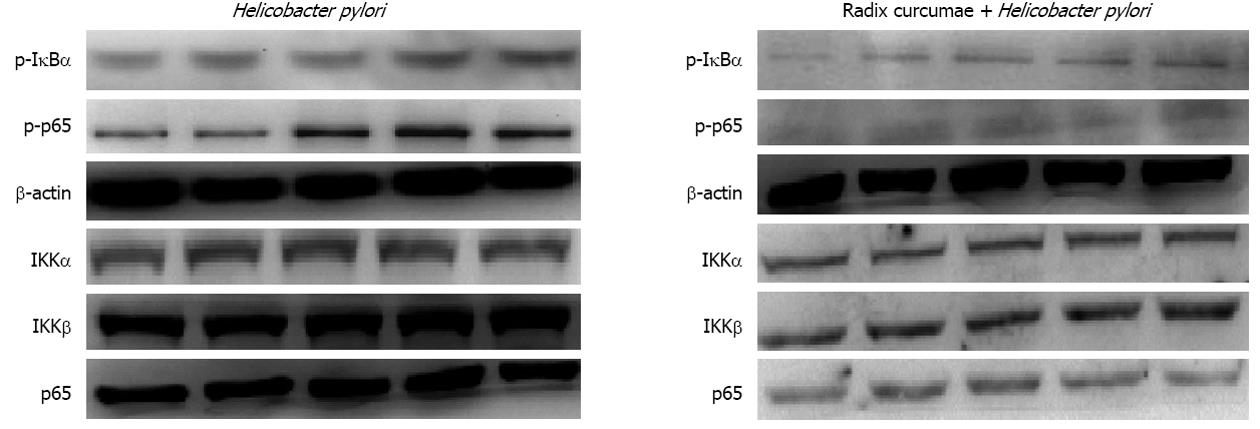
Figure 6 Effects of radix curcumae-derived diterpenoid C on the expression of nuclear factor kappa B proteins.
p-IκBα: Phosphorylated IκBα; IKK: IκB kinase.
-
Citation: Huang X, Lv B, Zhang S, Dai Q, Chen BB, Meng LN. Effects of radix curcumae-derived diterpenoid C on
Helicobacter pylori -induced inflammation and nuclear factor kappa B signal pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(31): 5085-5093 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i31/5085.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i31.5085