Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2013; 19(30): 4973-4978
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4973
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4973
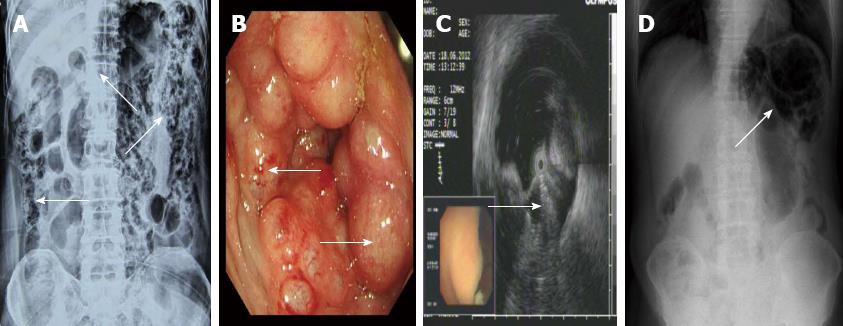
Figure 1 Imaging features of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis.
A: Barium enema study revealing multiple polypoid lesions with air shadows (arrow) and grape-like intramural gas in the whole colon; B: Colonoscopy revealing multiple round and smooth-surfaced elevated lesions (arrow) similar to submucosal tumors in the colon; C: Endoscopic ultrasonography revealing hyperechoic lesions and acoustic shadows in the submucosal layer (arrow); D: Plain radiography of the left upper quadrant abdomen revealing dilatation of the intestine and small linear, round radiolucent areas (arrow) on the clusters in the wall of the colon.
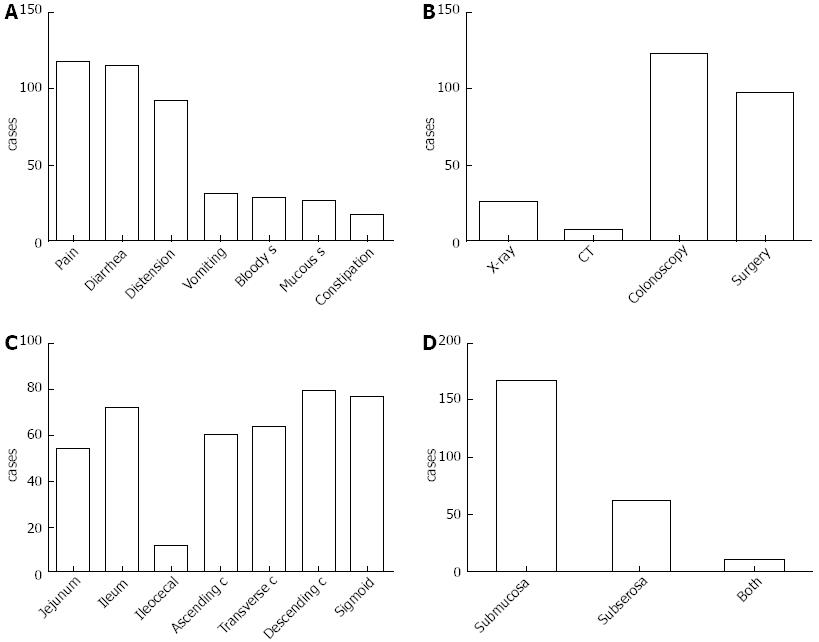
Figure 2 Clinical information of all 217 cases.
A: The chief complaints; B: The methods of diagnosis; C: The primary involved site; D: The localization of gas in the intestinal wall. S: Stool; C: Colon; CT: Computed tomography.
- Citation: Wu LL, Yang YS, Dou Y, Liu QS. A systematic analysis of pneumatosis cystoids intestinalis. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(30): 4973-4978
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i30/4973.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4973