©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2013; 19(22): 3528-3530
Published online Jun 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3528
Published online Jun 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3528
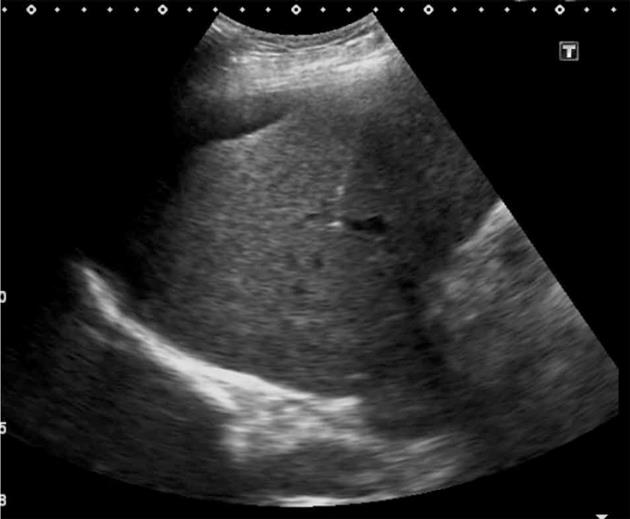
Figure 1 The right portal vein was punctured with a 22-gauge, 20-cm Chiba needle (Cook) close to the bifurcation of the main portal vein, with entry confirmed by aspiration of blood.
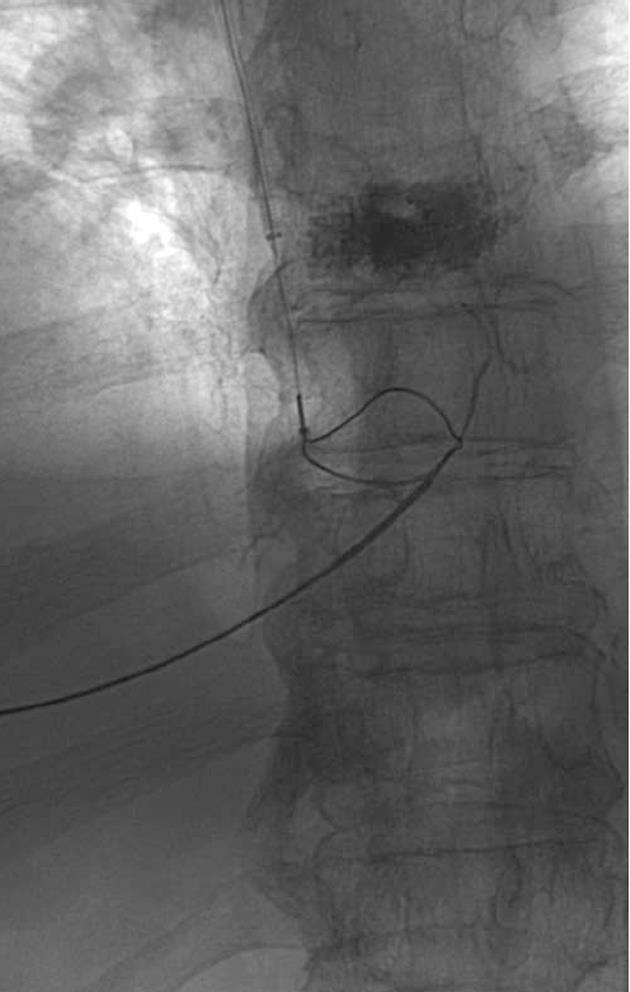
Figure 2 A 25-mm diameter Amplatz Gooseneck Snare (ev3 Inc) was used to snare the transhepatic wire, achieving through and through access.
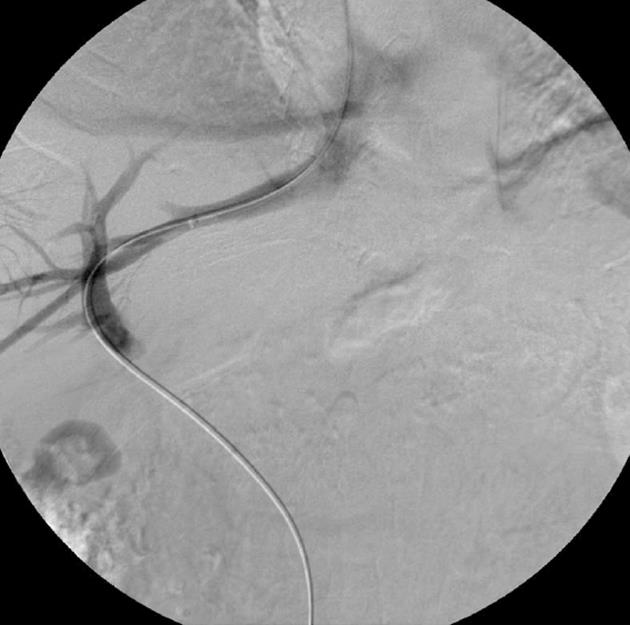
Figure 3 A 0.
035-inch, 260-cm long hydrophilic guidewire (Glidewire, Boston Scientific) and 5 Fr Berenstein catheter was then introduced through the transjugular sheath and manipulated into the main portal vein and then into the superior mesenteric vein.
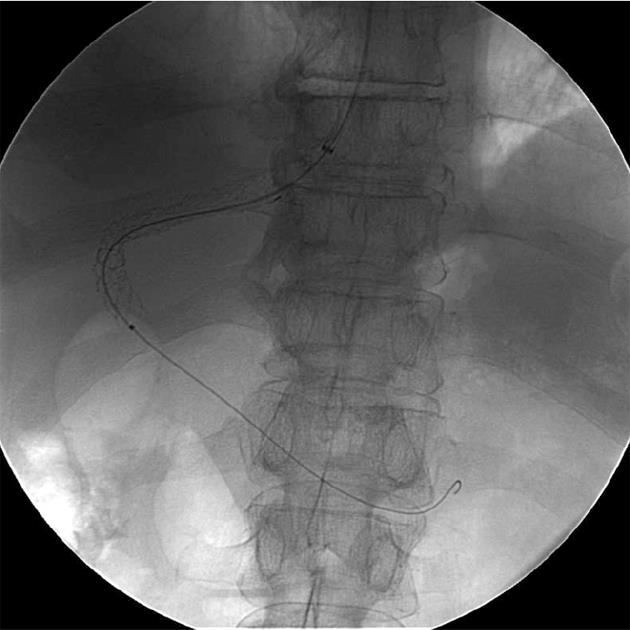
Figure 4 The procedure was completed as conventional transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with deployment of a 10 mm x 70 mm (Viatorr, WL Gore and Associates) transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt endoprosthesis stent.
- Citation: Leong S, Kok HK, Govender P, Torreggiani W. Reducing risk of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt using ultrasound guided single needle pass. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(22): 3528-3530
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i22/3528.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3528