©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2013; 19(19): 2904-2912
Published online May 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2904
Published online May 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2904
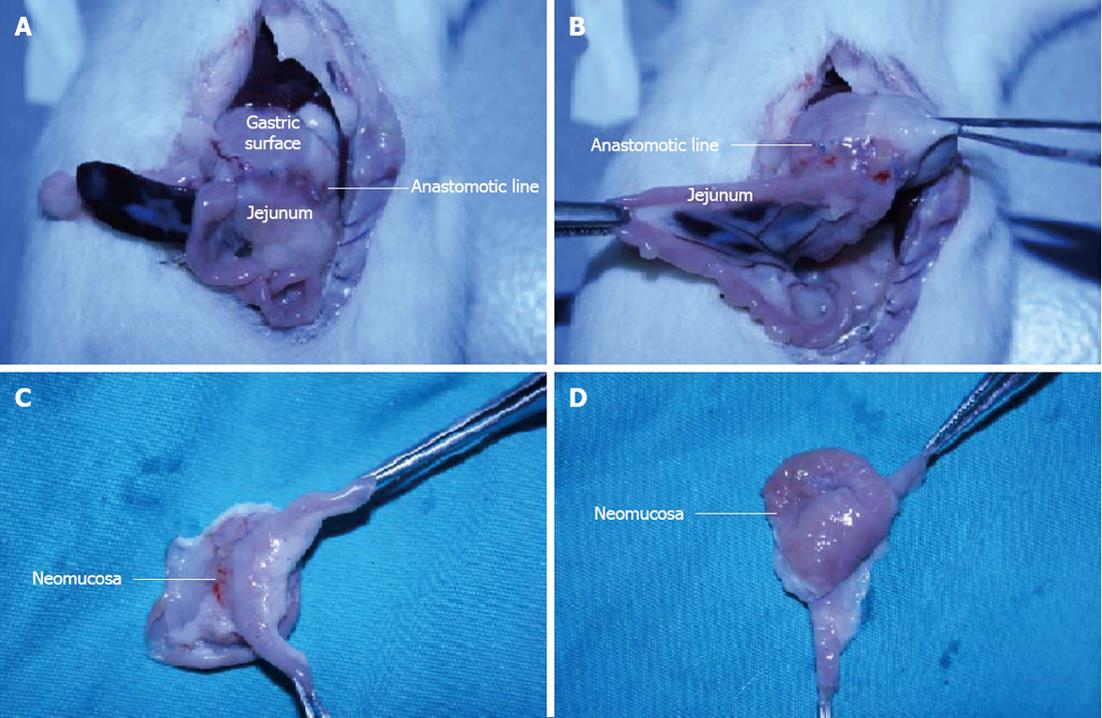
Figure 1 Surgical procedure and histopathological assessment.
A, B: Anastomotic line is shown between the gastric surface and jejunum, C: Outer surface of the neomucosa formation is shown with the jejunal segment; D: Inner surface of the neomucosa is shown, and the neomucosa has a typical small intestinal phenotype.
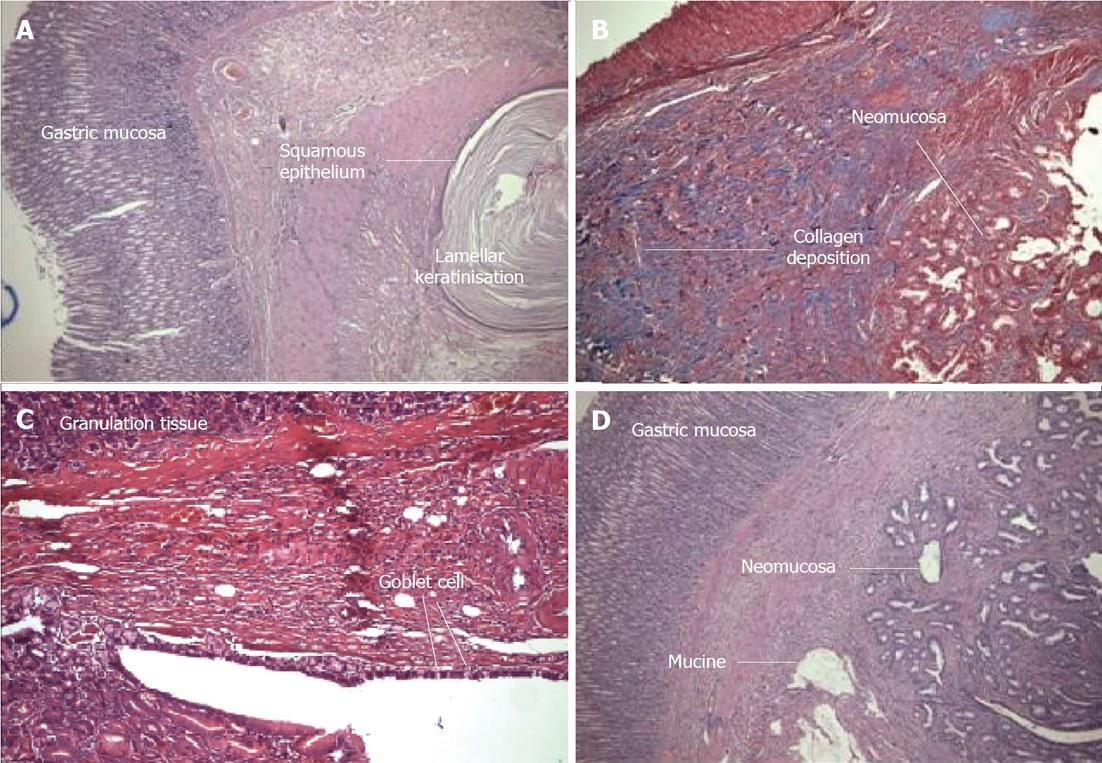
Figure 2 Histological and morphologic evaluation.
A: Unexpected neomucosal formation. The gastric corpus mucosa can be seen. The squamous epithelium and lamellar keratinization formed from the anastomosis [Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) × 100] (Group 3); B: Granulation tissue and newly formed neomucosa. The blue area is connective tissue (Masson Trichrome × 100) (Group 4); C: In the gastric mucosa of the large granulation tissue, newly formed goblet cells can be seen (HE × 100) (Group 4); D: The left side shows the gastric mucosa, and the right side shows newly formed neomucosa that contains mucin. The granulation tissue is reduced (HE × 100) (Group 4).
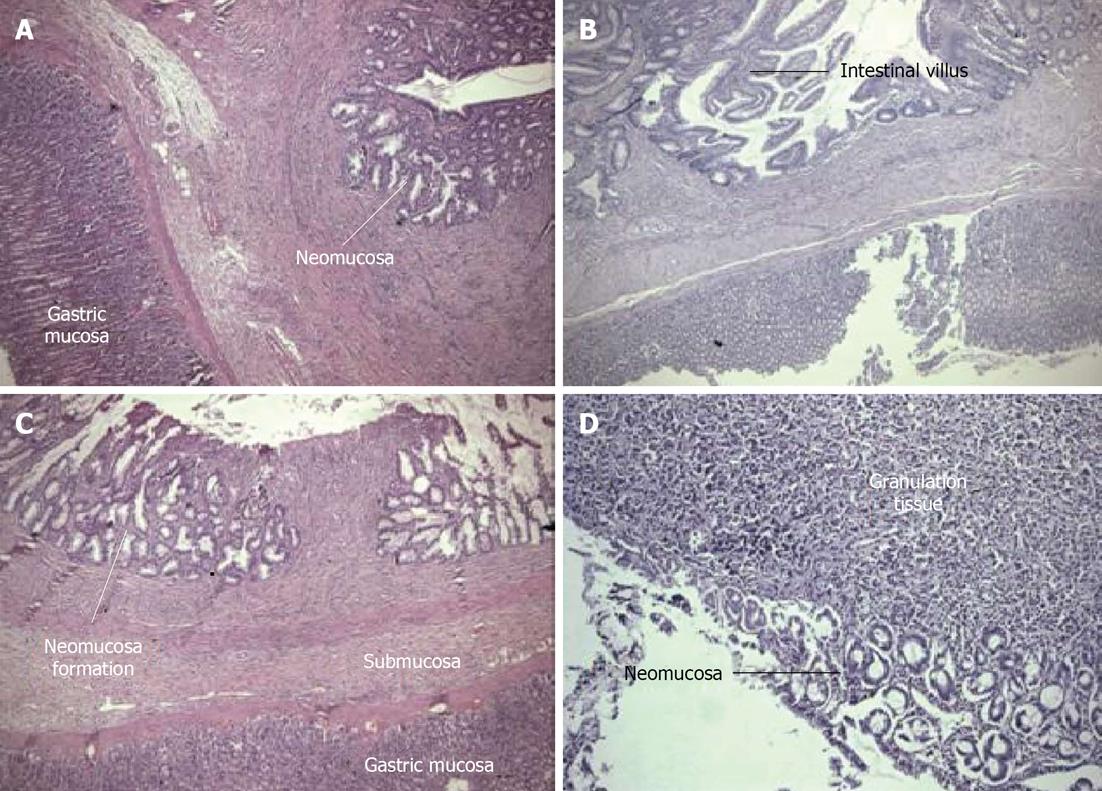
Figure 3 There were significant differences in the villus density in all of the groups compared with the control group.
A: Gastric corpus mucosa on the left, newly formed thin neomucosa on the right. The muscularispropria has not yet formed. The granulation tissue regressed [Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) × 100] (Group 3); B: Neomucosa formation is observed at the bottom of the gastric mucosa (HE × 125) (Group 4); C: The granulation tissue is in the middle, with newly formed neomucosa on either side. At the bottom, the stomach tissue is visible (HE x 100) (Group 2); D: The early development of the mucosal layer and granulation tissue (HE x 125) (Group 1).
- Citation: Adas G, Adas M, Arikan S, Sarvan AK, Toklu AS, Mert S, Barut G, Kamali S, Koc B, Tutal F. Effect of growth hormone, hyperbaric oxygen and combined therapy on the gastric serosa. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(19): 2904-2912
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i19/2904.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2904