©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2013; 19(19): 2894-2903
Published online May 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2894
Published online May 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2894
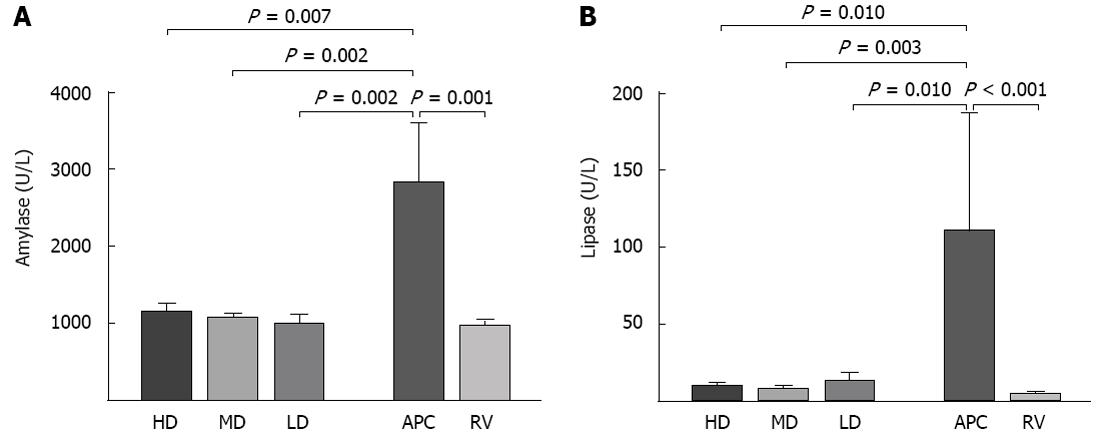
Figure 1 Plasma amylase (A) and lipase (B) activities.
Columns show the mean and the error bars represent SEM. All groups are compared with the acute pancreatitis control (APC) group and the statistical significance is expressed as a vertical P value over the column. LD: Low-dose; MD: Medium-dose; HD: High-dose; RV: Reference values.
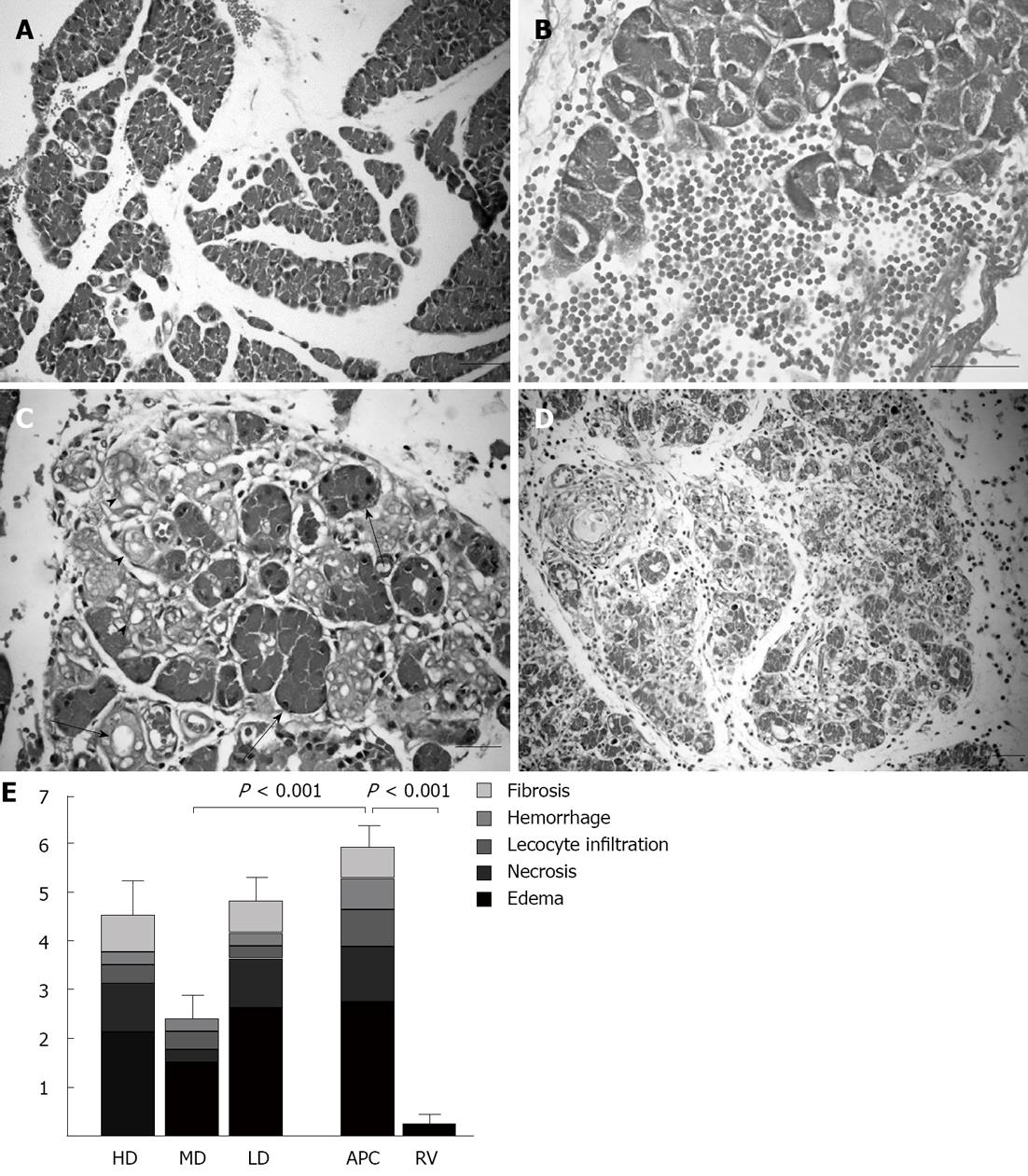
Figure 2 Histopathological alterations in rat pancreas caused by cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis and histopathological scores.
A: Pancreatic acini were separated because of interlobular edema in cerulein treated animals (bar = 100 μm); B: Occasionally mild hemorrhages were observed (bar = 50 μm); C: Several acinar cells lost their zymogen granules (arrows) and ductus-like structures (arrowheads) occurred (bar = 50 μm); D: In some animals, leucocyte, fibrocyte and fibroblast infiltrations and collagen bands were detected (bar = 200 μm); E: Histopathological scores of each group are shown as stacked columns representing means. The whole column corresponds to the mean of the total score and the error bars represent the SEM of the total score. All groups are compared with the APC group and the statistical significance is expressed as a vertical P value over the column. HD: High-dose; MD: Medium-dose; LD: Low-dose; APC: Acute pancreatitis control; RV: Reference values.
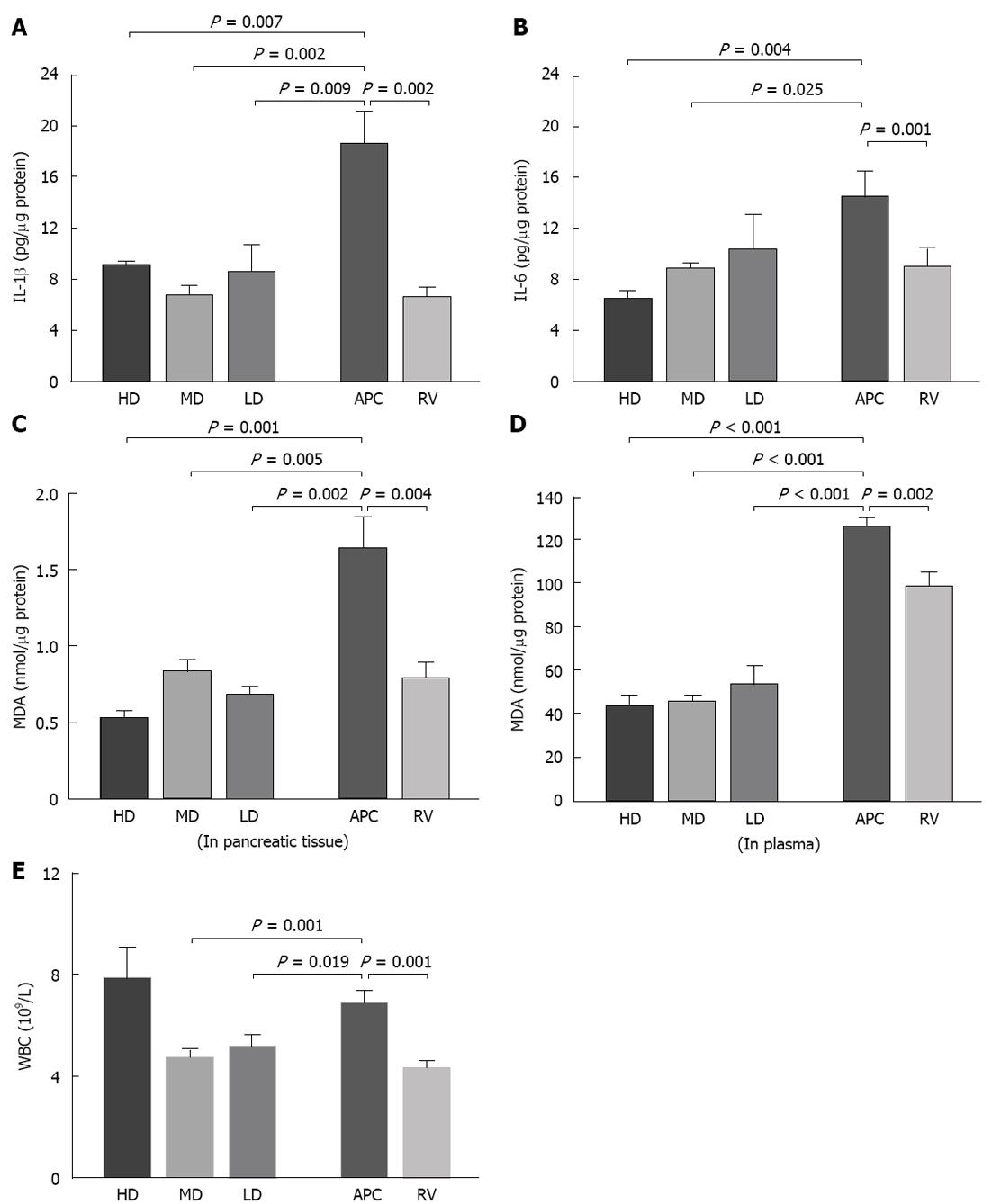
Figure 3 Cytokine levels, lipid peroxidation and white blood cells.
A: Cerulein induced acute pancreatitis (AP) caused a marked elevation of interleukin (IL)-1β level in pancreatic tissue compared to that of the reference values (RV) group (18.81 ± 2.55 and 6.65 ± 0.24 pg/μg, respectively, P = 0.002); B: This elevation was suppressed significantly by acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) in all treatment groups. A similar increase was observed in the pancreatic IL-6 level. However, this time, the low-dose seemed to be ineffective against it, while medium- and high-dose ASA pretreatments suppressed the IL-6 elevation. There was no statistical difference between the groups regarding the tumor necrosis factor-α and nuclear factor-κB levels; C, D: Cerulein induced AP increased malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in both pancreatic tissue and plasma compared to that of the RV group; E: Cerulein induced AP increased the peripheral white blood cell (WBC) count significantly compared to the RV group. HD: High-dose; MD: Medium-dose; LD: Low-dose; APC: Acute pancreatitis control.
- Citation: Akyazi I, Eraslan E, Gülçubuk A, Ekiz EE, Çırakli ZL, Haktanir D, Bala DA, Özkurt M, Matur E, Özcan M. Long-term aspirin pretreatment in the prevention of cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(19): 2894-2903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i19/2894.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2894