©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2013; 19(18): 2740-2751
Published online May 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i18.2740
Published online May 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i18.2740
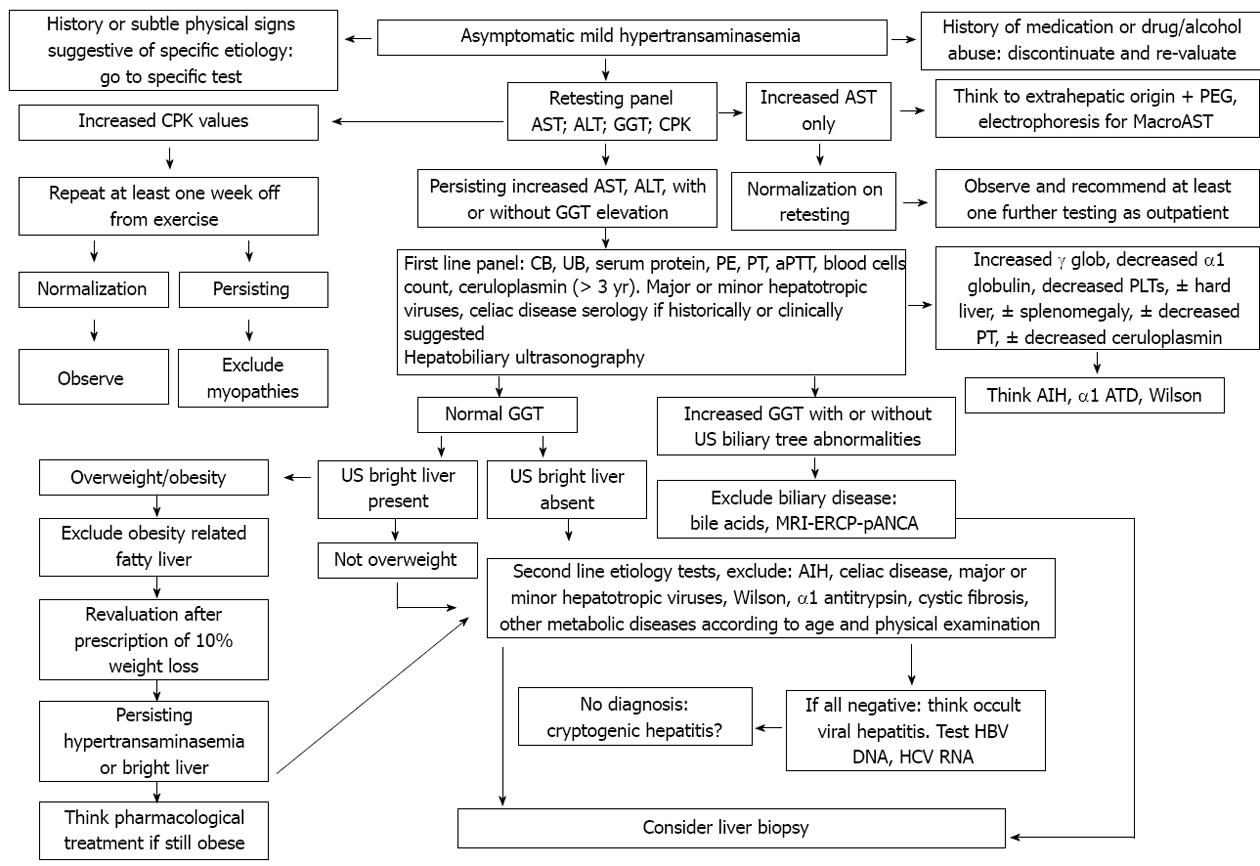
Figure 1 Diagnostic algorithm for the diagnosis of pediatric mild chronic asymptomatic hypertransaminasemia.
Modified from the reference of 28. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; CB: Conjugated bilirubin; UB: Unconjugated bilirubin; CPK: Creatine kinase; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transferase; PE: Pulmonary embolism; PEG: Polyethylene glycol; PT: Prothrombin time; PTT: Partial thromboplastin time; US: Ultrasound; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; pANCA: Perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis; α1 ATD: α1-antitrypsin deficiency.
- Citation: Vajro P, Maddaluno S, Veropalumbo C. Persistent hypertransaminasemia in asymptomatic children: A stepwise approach. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(18): 2740-2751
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i18/2740.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i18.2740