Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2013; 19(10): 1657-1660
Published online Mar 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i10.1657
Published online Mar 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i10.1657
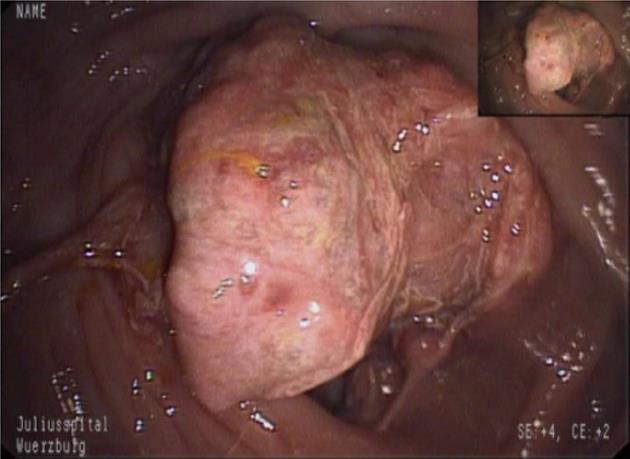
Figure 1 Endoscopic aspect of a soft and friable perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the cecum.
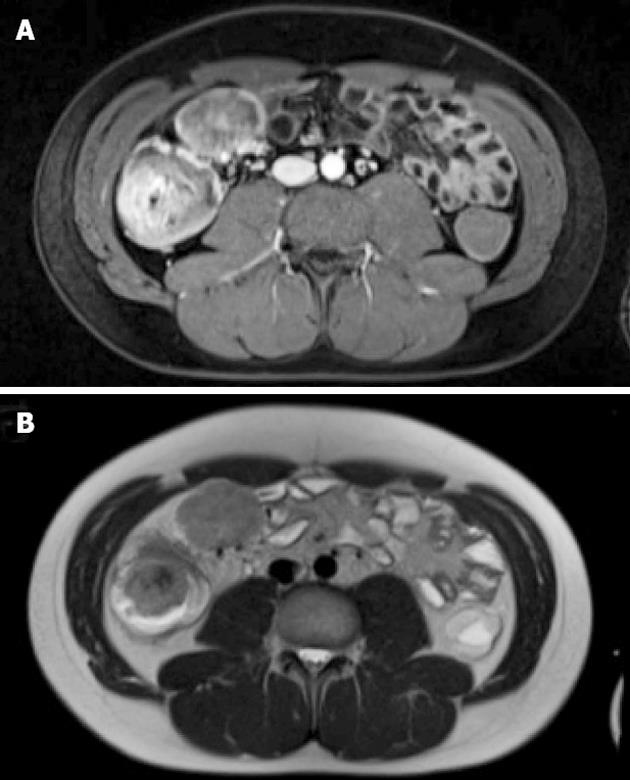
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging of cecal perivascular epithelioid cell tumor and mesenteric lymph node metastasis.
A: T2-weighted image; B: T1-weighted image after iv administration of contrast medium.
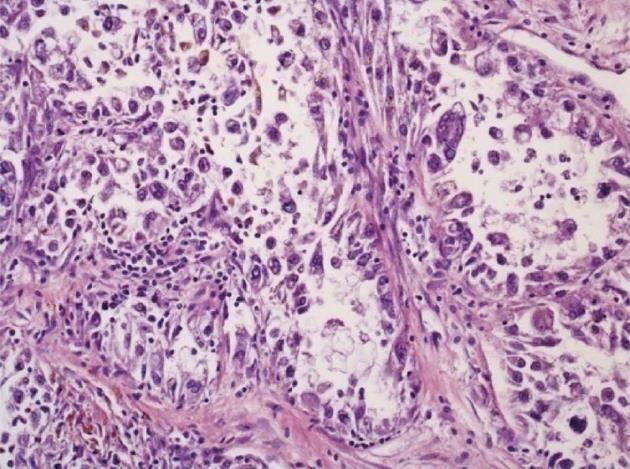
Figure 3 Histologic section of the primary tumor in the cecum.
A representative part of the tumor shows epithelioid tumor cells. The cytoplasm exhibits both clear and granular eosinophilic parts. The tumor cells are arranged in large nodules with necrotic debris in the central parts. In the lower left corner, a cytoplasmic brown pigment is seen that upon ultrastructural evaluation turned out to be melanin pigment and melanosomes. There are narrow stalks of collagen-rich stroma with a scant lymphocytic infiltrate (Hematoxylin and eosin, magnification 200 ×).
- Citation: Scheppach W, Reissmann N, Sprinz T, Schippers E, Schoettker B, Mueller JG. PEComa of the colon resistant to sirolimus but responsive to doxorubicin/ifosfamide. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(10): 1657-1660
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i10/1657.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i10.1657