©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2012; 18(42): 6148-6154
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6148
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6148
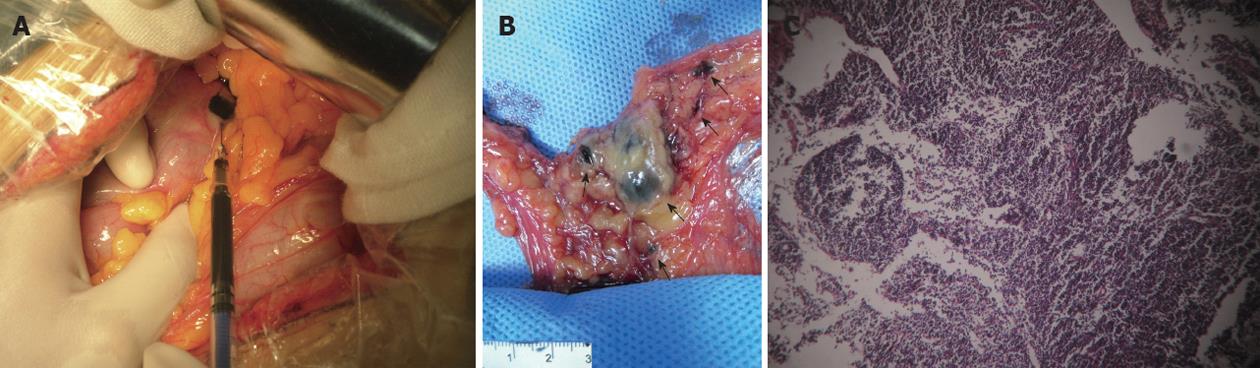
Figure 1 Activated carbon nanoparticles suspension in vivo is effective as a tracer in colorectal cancer lymph node detection.
A: Subserosal injection of activated carbon nanoparticles suspension (ACNS) into a 4-quadrant region around the mass; B: Lymph nodes can easily be identified from the mesenteric adipose tissues, arrow points to the black dyed lymph nodes; C: ACNS migrating to the lymph node (hematoxylin and eosin, ×100).
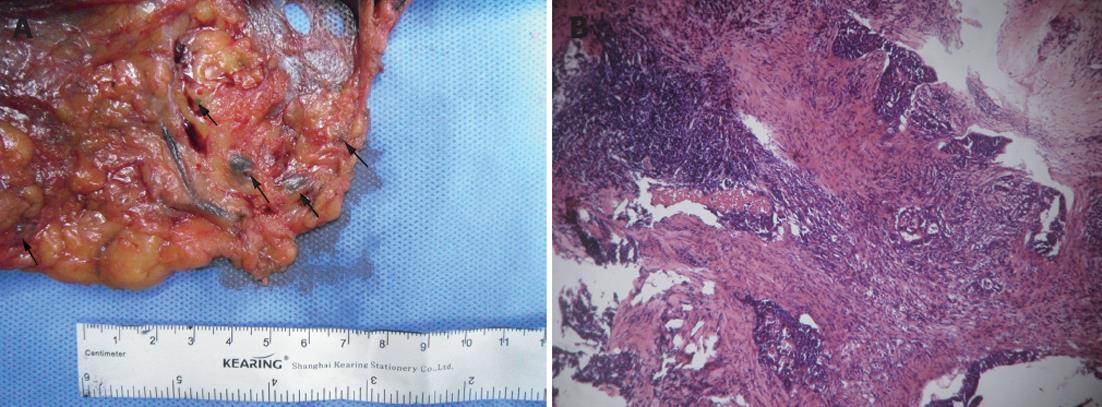
Figure 2 Methylene blue in vitro used as a tracer in colorectal cancer lymph node detection.
A: The main artery of the specimen was isolated and methylene blue (MB) was injected into the vessel. Lymph nodes can easily be identified, arrow points to the blue dyed lymph nodes; B: MB migrating to the lymph node (hematoxylin and eosin, ×100).
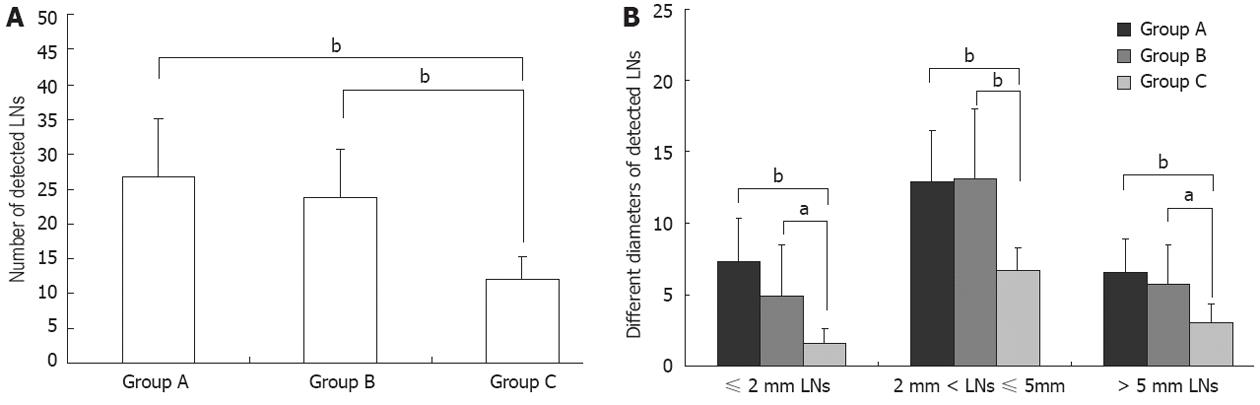
Figure 3 Lymph nodes detected in the three groups.
A: The mean number of lymph nodes detected; B: Distribution of lymph node diameters. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs group A. LN: Lymph node.
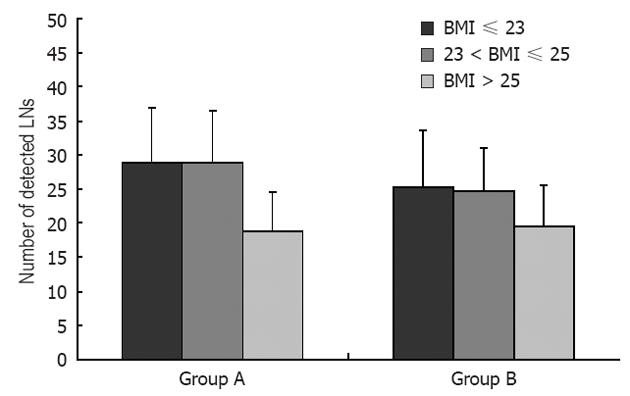
Figure 4 Body mass index as an influencing factor in the two different staining methods.
LN: Lymph node; BMI: Body mass index.
-
Citation: Cai HK, He HF, Tian W, Zhou MQ, Hu Y, Deng YC. Colorectal cancer lymph node staining by activated carbon nanoparticles suspension
in vivo or methylene bluein vitro . World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(42): 6148-6154 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i42/6148.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6148