©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2012; 18(38): 5389-5396
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5389
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5389
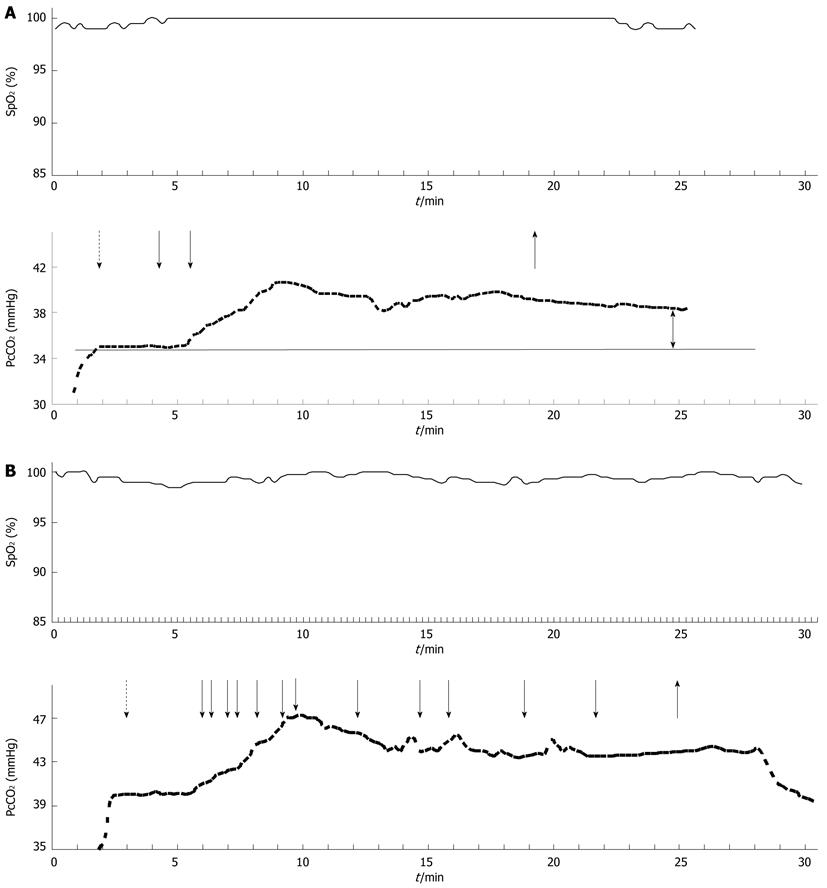
Figure 1 A typical course of oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximetry and transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension following administration of alfentanil (dashed arrow) and midazolam (A) or propofol (B) (solid arrows as indicated).
The upright arrow indicates the end of the procedure. The double arrow highlights the difference after termination of the procedure.
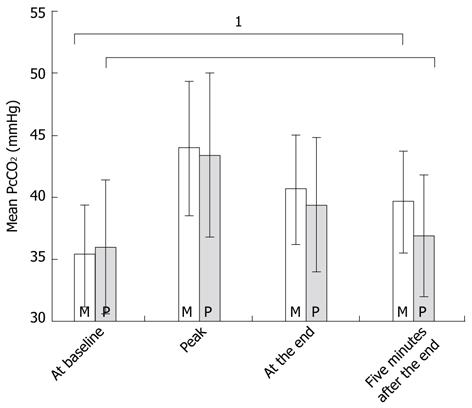
Figure 2 Mean transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension values in mmHg (± SD) at four distinct time points during colonoscopies according to sedative use (for the whole group).
1A significant difference in the transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension values measured five minutes after the end of the procedure when compared with the baseline values. M: Midazolam; P: Propofol.
- Citation: Heuss LT, Sugandha SP, Beglinger C. Carbon dioxide accumulation during analgosedated colonoscopy: Comparison of propofol and midazolam. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(38): 5389-5396
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i38/5389.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5389