©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2012; 18(38): 5369-5376
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5369
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5369
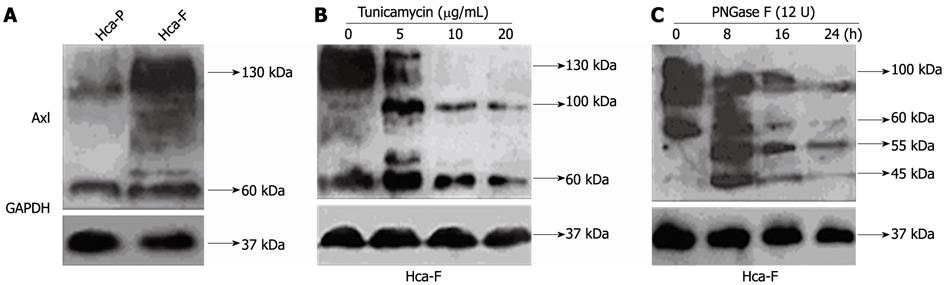
Figure 1 Expression profile of Axl glycoprotein in mouse hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.
A: Axl glycoprotein levels by Western blotting analysis in Hca-P and Hca-F cell lines. Relative signal intensities of Axl protein were compared with GAPDH by LabWorks (TM ver4.6, UVP; BioImaging Systems), (aP < 0.05 vs untreated Hca-F cells); B: Hca-F cells were treated with 0 μg/mL, 5 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL, and 20 μg/mL tunicamycin for 12 h. Total protein extracts were loaded for each sample; C: Hca-F cell protein was deglycosylated with 12 units of PNGase F in lysis buffer. Probes were incubated at 37 °C in a time-dependent manner (0 h, 8 h, 16 h, 24 h). Protein was separated on a gel for Western blotting Analysis. After sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, proteins were transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane, and were detected by rabbit anti-mouse Axl polyclonal antibody. GAPDH blotting was used as the control. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
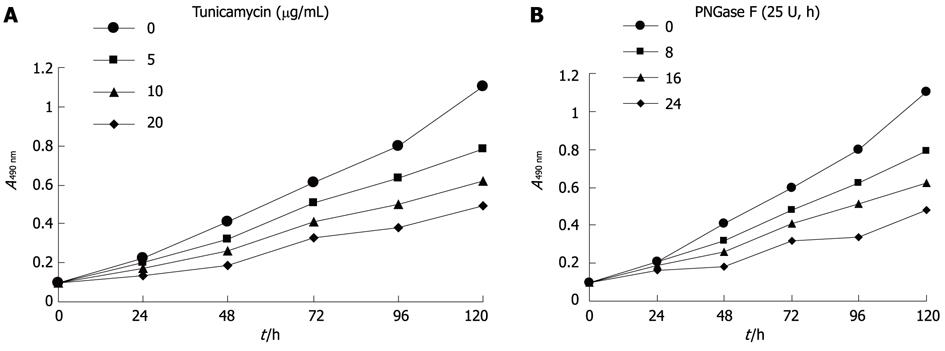
Figure 2 Axl deglycosylation effects on cell proliferation in vitro.
Hca-F cells were exposed to tunicamycin or PNGase F and harvested at 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, 96 h, and 120 h. Cell proliferation was measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. Decreased proliferative ability was detected in cells treated with tunicamycin (A) or PNGase F (B), compared with untreated Hca-F cells. Data was obtained in triplicate.
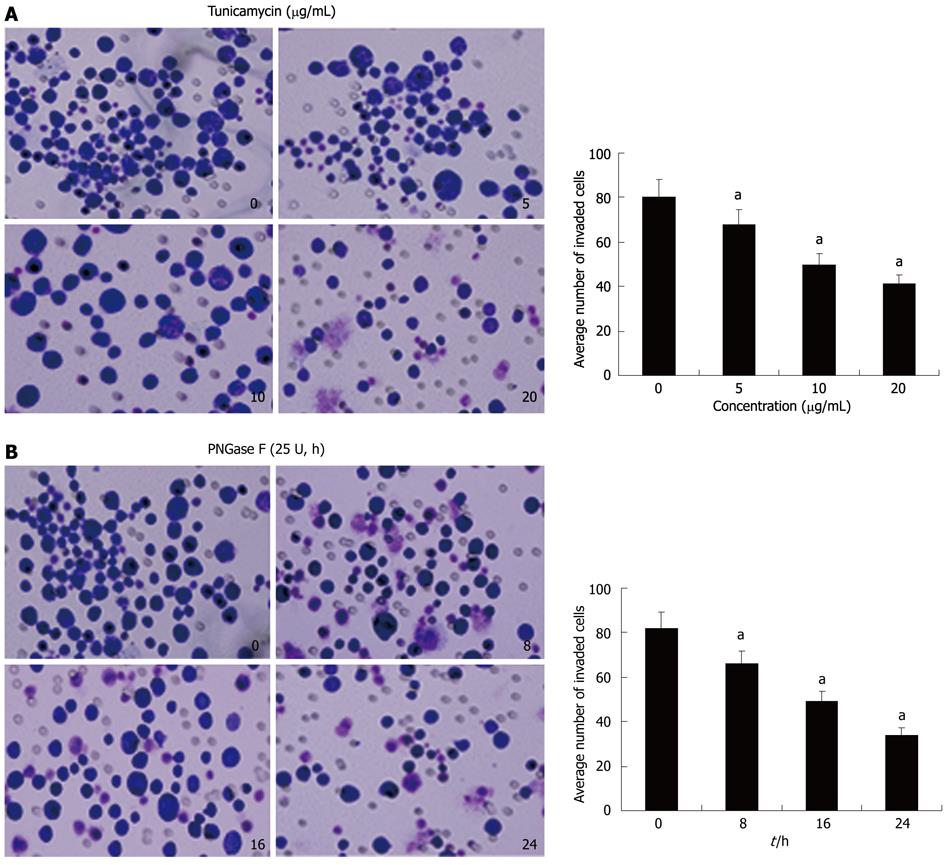
Figure 3 Axl deglycosylation alters the invasive ability of Hca-F cells in vitro.
In vitro ECMatrix gel analysis. Wright-Giemsa staining results of the lower surface filter showed that the cells passed through the filter and attached to the lower side (400 ×). The average number of cells invading the filter was counted. Cells treated with tunicamycin (A) or PNGase F (B) were significantly less invasive (aP < 0.05 vs untreated Hca-F cells) than untreated Hca-F cells. Data was obtained in triplicate.
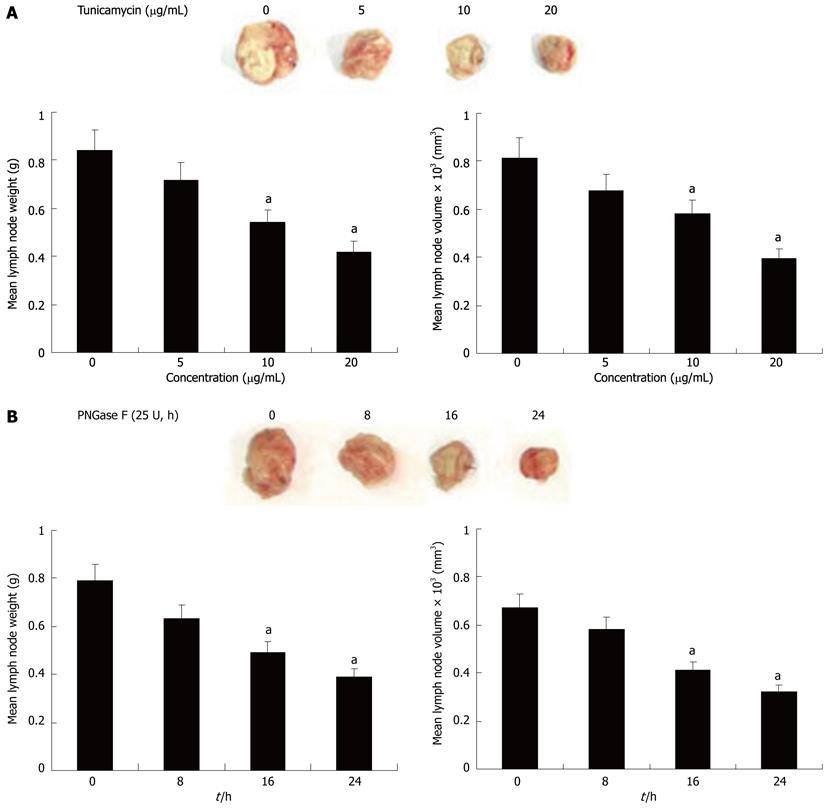
Figure 4 Axl deglycosylation inhibits the ability of Hca-F cells to metastasize to peripheral lymph nodes in vivo.
Untreated and treated Hca-F cells were injected into the footpads of 615-mice. After 3 wk’ inoculation, the mice were sacrificed and axillary lymph nodes isolated, weighed, measured, and photographed. A significant reduction in mean tumor weight (n = 6) of Axl tumor deglycosylation was observed, as compared with untreated Hca-F cells (aP < 0.05 vs untreated Hca-F cells).
- Citation: Li J, Jia L, Ma ZH, Ma QH, Yang XH, Zhao YF. Axl glycosylation mediates tumor cell proliferation, invasion and lymphatic metastasis in murine hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(38): 5369-5376
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i38/5369.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5369