©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2012; 18(34): 4729-4735
Published online Sep 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4729
Published online Sep 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4729
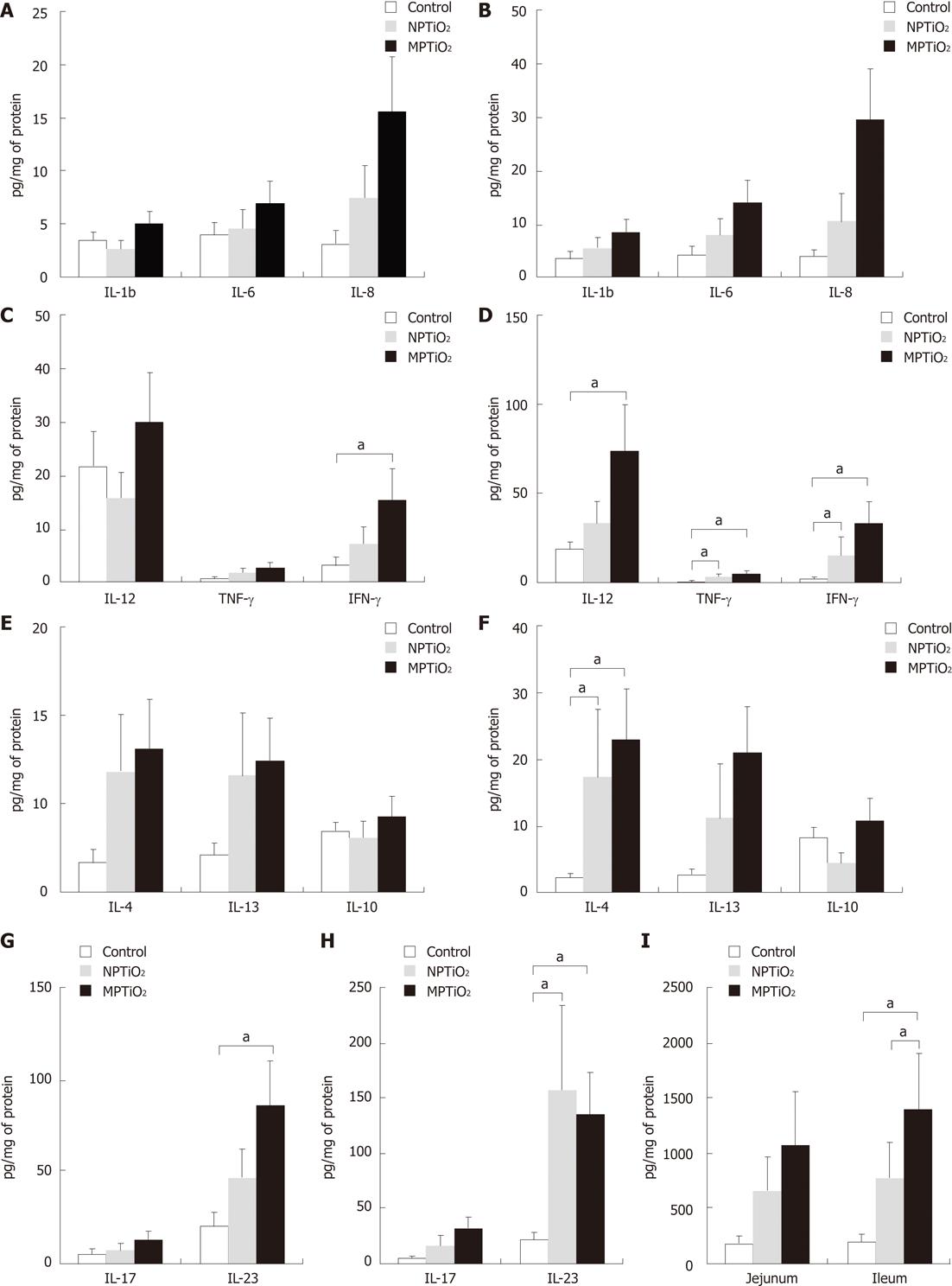
Figure 1 Mean and SE of cytokine concentration in the small intestine of mice according to treatment groups.
A: Pro-inflammatory cytokines in the jejunum; B: Pro-inflammatory cytokines in the ileum; C: T-helper (Th) 1 type cytokines in the jejunum; D: Th1 type cytokines in the ileum; E: Th2 type cytokines in the jejunum; F: Th2 type cytokines in the ileum; G: Th17 type cytokines in the jejunum; H: Th17 type cytokines in the ileum; I: Transforming growth factor (TNF)-β in the jejunum and ileum. aP < 0.05 for pairwise comparison test. NPTiO2: Titanium dioxide nanoparticles; MPTiO2: Titanium dioxide microparticles; IL: Interleukin; IFN: Intracellular interferon.
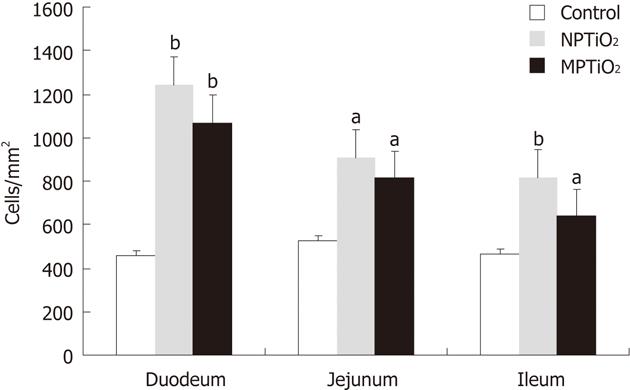
Figure 2 T CD4+ cells quantified by immunohistochemistry in the duodenum, jejunum and ileum of mice, according to treatment group.
Mean and SE of aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group for pairwise comparison test. NPTiO2: Titanium dioxide nanoparticles; MPTiO2: Titanium dioxide microparticles.
- Citation: Nogueira CM, Azevedo WM, Dagli MLZ, Toma SH, Leite AZA, Lordello ML, Nishitokukado I, Ortiz-Agostinho CL, Duarte MIS, Ferreira MA, Sipahi AM. Titanium dioxide induced inflammation in the small intestine. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(34): 4729-4735
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i34/4729.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4729