Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2012; 18(23): 2995-3003
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2995
Published online Jun 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2995
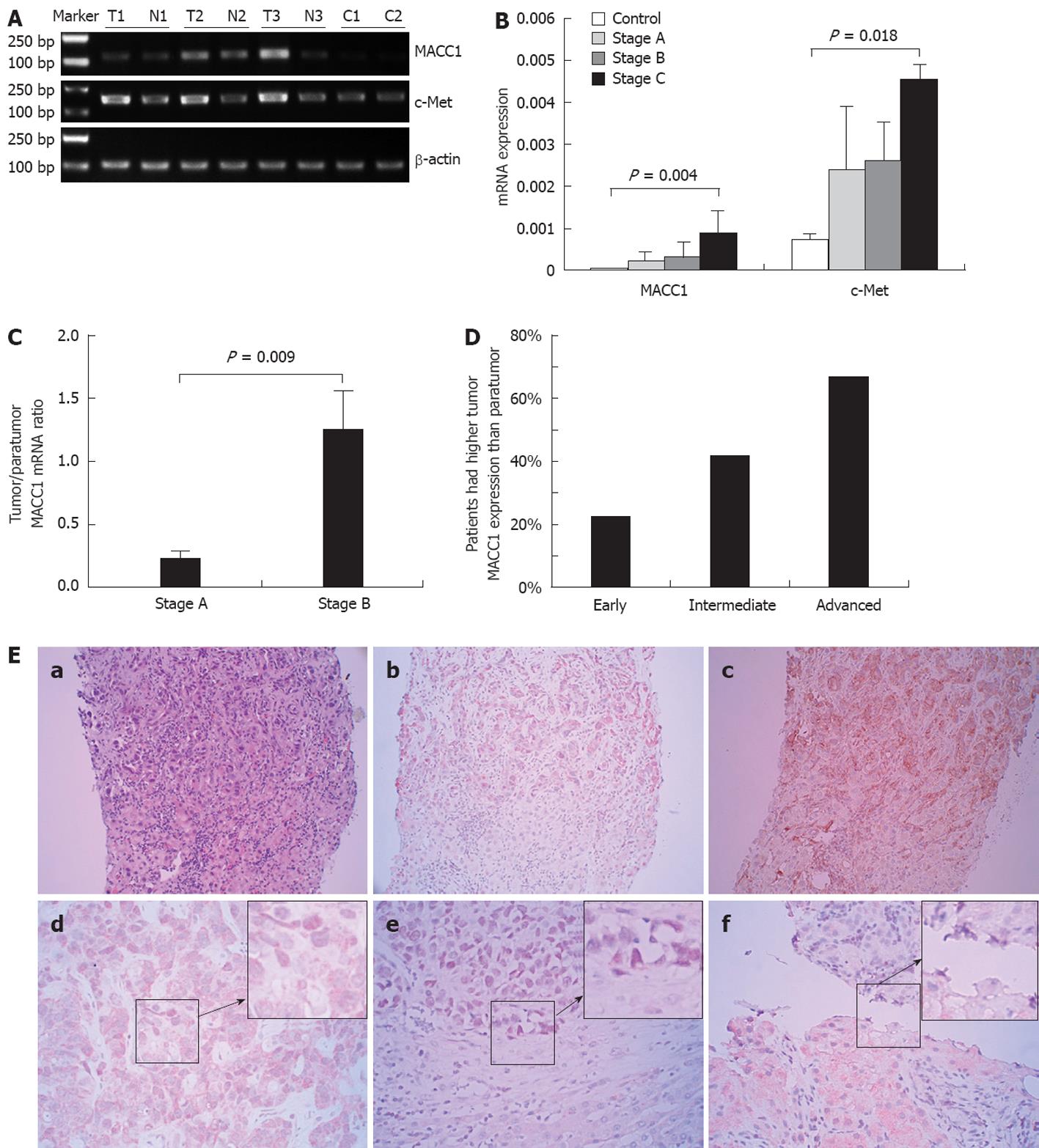
Figure 1 Analysis of metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 and c-Met expression in liver tissues.
A: Representative metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 (MACC1) and c-Met mRNA in intratumoral [T: T1 as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) stage A, T2, T3 as HCC stage B] and matching paratumor tissues (N: N1, N2 and N3) and normal liver tissues (C) by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR); B: Comparison of MACC1 and c-Met expression levels in 10 normal liver tissue, and HCC with stage A (n = 138), stage B (n = 96), stage C (n = 120) by real-time quantitative-PCR; C: The ratio for MACC1 mRNA levels in HCC stage A and stage B tumor tissues relative to matching paratumor tissues; D: Comparison of the intratumoral and peritumoral MACC1 expression in HCC stage A and stage B, as determined by immunohistochemistry; E: Immunohistochemical staining of MACC1 expression in HCC. a-c: MACC1 and c-Met expression in tumor and matching paratumor tissues in one same HCC patient (× 200). a: HE showed the tumor and paratumor cells; b: MACC1 expression was higher in tumor cytoplasm than in paratumor cells; c: c-Met was expressed on the tumor cell membrane, but no staining on nontumor liver cell membrane; d-f: Representative expression of MACC1 in HCC tumor tissues (× 400). d: MACC1 positive staining occurred mainly in the cytoplasm; e: Nuclear staining of MACC1 in cancer cells; f: Relatively weak staining of MACC1 in an early stage HCC cancer cells, as compared to paratumor cells.
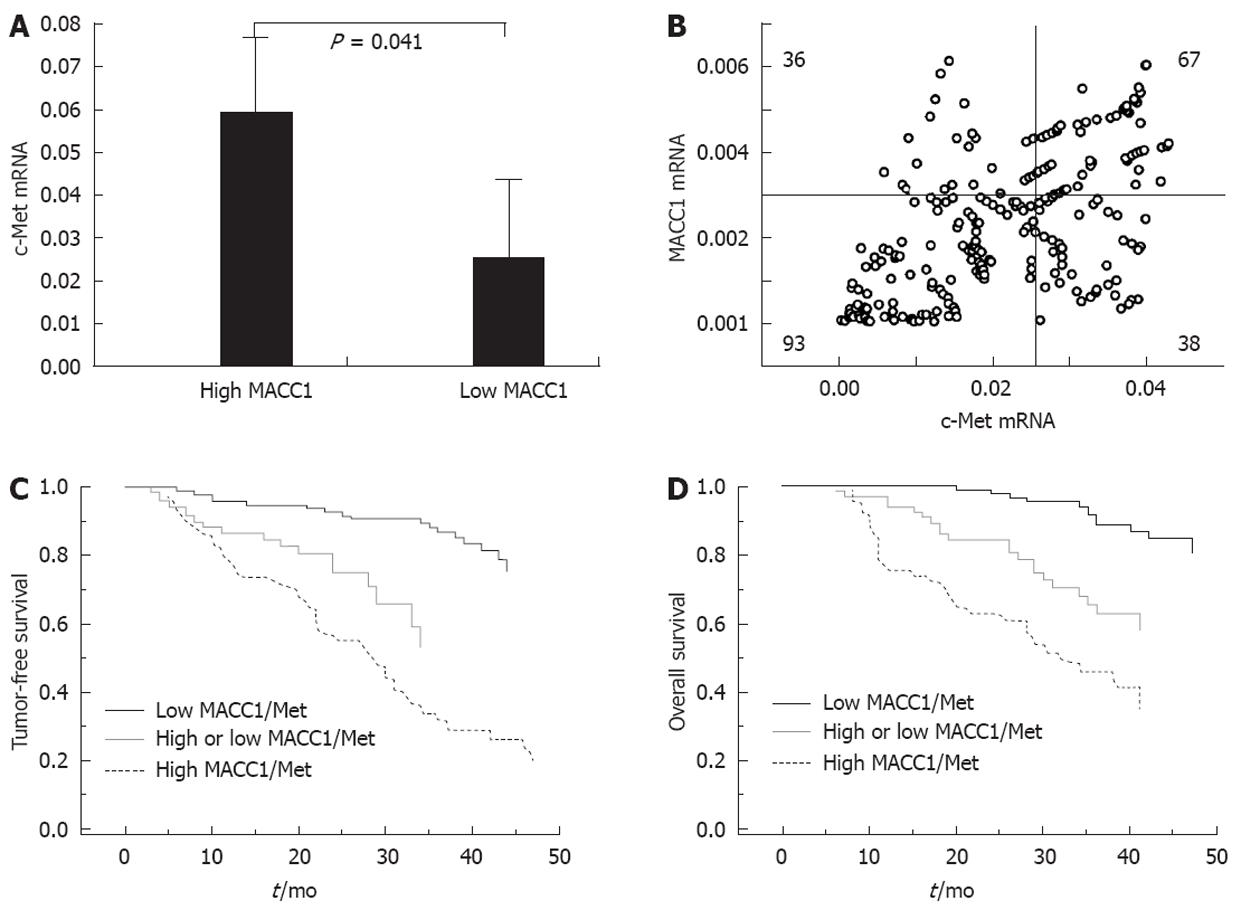
Figure 2 c-Met expression and correlation with metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 in 234 hepatocellular carcinoma patients received resection.
A: Comparison of c-Met expression level in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with high or low intratumoral metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 (MACC1) mRNA expression; B: c-Met level from 234 HCC patients receiving resection specimens were plottered against MACC1 levels from the same patients. Linear regression analysis showed a significant positive correlation between c-Met and MACC1 (r = 0.360, P < 0.001); C: Kaplan-Meier analysis of MACC1 and c-Met co-expression effects on tumor-free survival; D: Kaplan-Meier analysis of MACC1 and c-Met co-expression effects on overall survival.
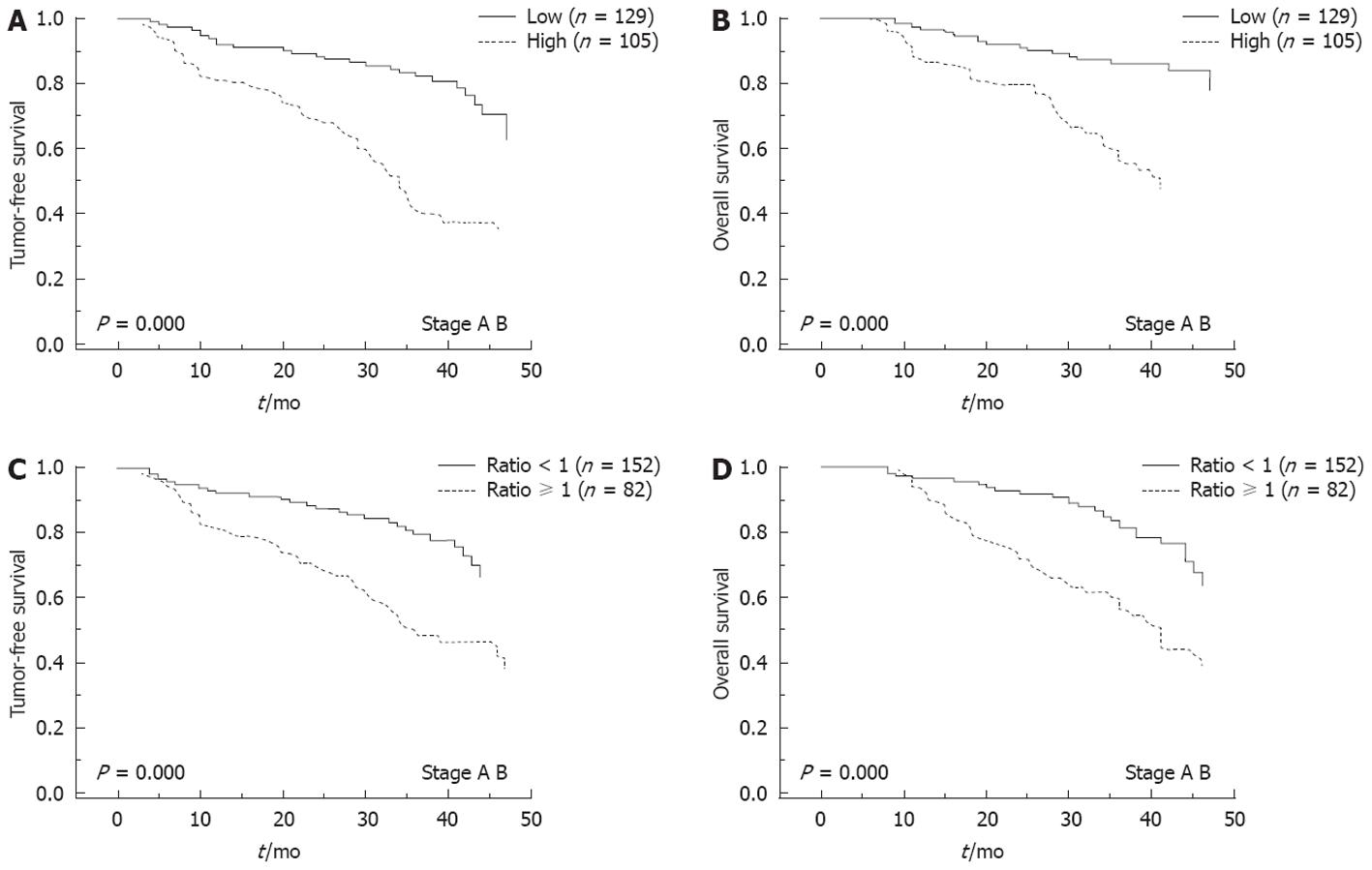
Figure 3 Metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 expression level associated with outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving resection.
A, B: Kaplan-Meier estimates of metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 (MACC1) expression effects on tumor-free survival (TFS) (A) and overall survival (OS) (B); C, D: Kaplan-Meier estimates of ratio of T:N MACC1 expression effects on TFS (C) and OS (D).
- Citation: Qu JH, Chang XJ, Lu YY, Bai WL, Chen Y, Zhou L, Zeng Z, Wang CP, An LJ, Hao LY, Xu GL, Gao XD, Lou M, Lv JY, Yang YP. Overexpression of metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 predicts a poor outcome of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(23): 2995-3003
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i23/2995.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i23.2995