©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2012; 18(20): 2540-2544
Published online May 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i20.2540
Published online May 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i20.2540
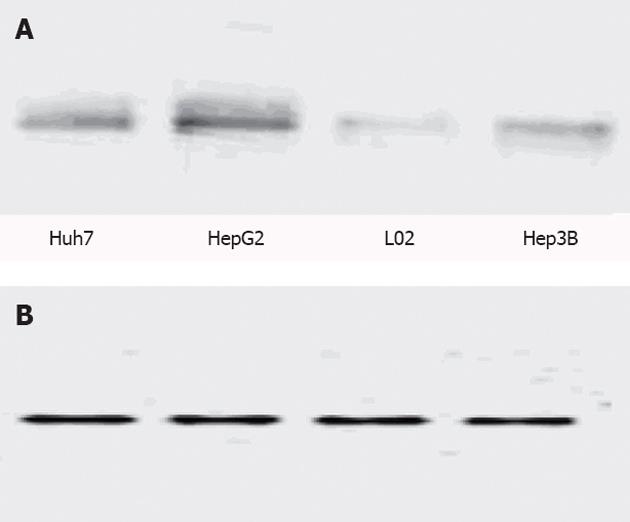
Figure 1 Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E protein and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase protein bands in a normal human liver cell line and three hepatoma carcinoma cell lines.
A: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E protein bands; B: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase protein bands.
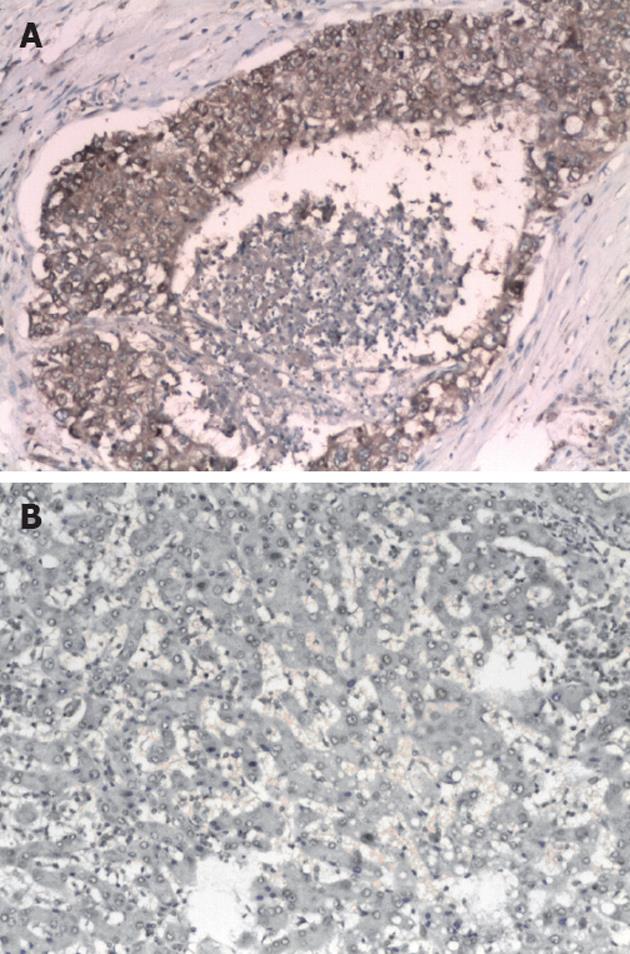
Figure 2 Photo of hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and adjacent tissue by electron microscopy.
A: Hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and adjacent interstitial tissue; B: Adjacent tissue. (Hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×100).
- Citation: Wang XL, Cai HP, Ge JH, Su XF. Detection of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E and its clinical significance in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(20): 2540-2544
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i20/2540.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i20.2540