©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2012; 18(2): 99-104
Published online Jan 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i2.99
Published online Jan 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i2.99
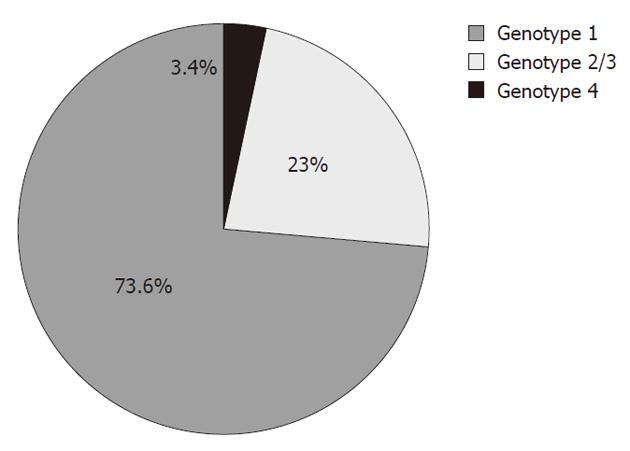
Figure 1 Distribution of genotypes in the five representative prospective trials using polyethylene glycol-interferon α-2b and polyethylene glycol-interferon α-2a in combination with ribavirin, published between 2005 and 2011.
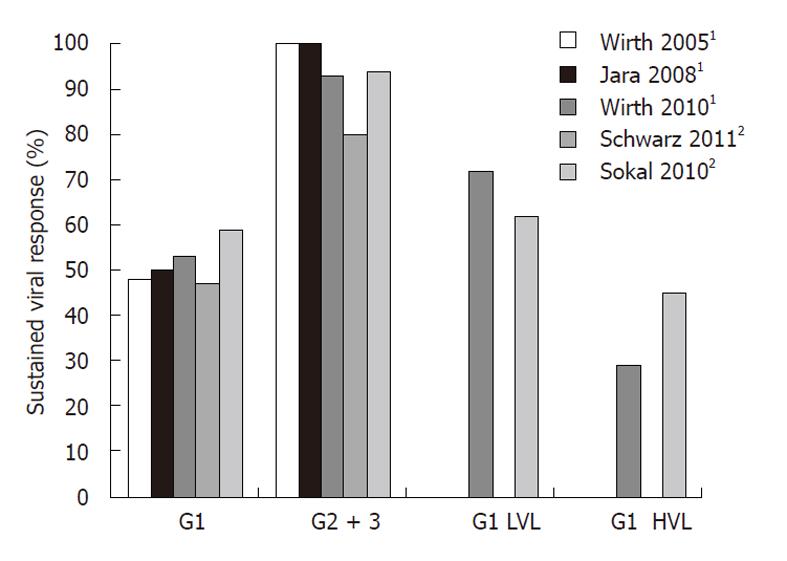
Figure 2 Sustained viral response in five large prospective trials with polyethylene glycol-interferon α-2b1/α-2a2 and ribavirin stratified for genotype and viral load[27,28,30-32].
G: Genotype; HVL: High viral load, > 600 000 U/mL, (Wirth et al[32]), > 500 000 U/mL (Sokal et al[30]); LVL: Low viral load, < 600 000 U/mL (Wirth et al[32]), < 500 000 U/mL (Sokal et al[30]).
- Citation: Wirth S. Current treatment options and response rates in children with chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(2): 99-104
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i2/99.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i2.99