©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2012; 18(18): 2262-2269
Published online May 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2262
Published online May 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2262
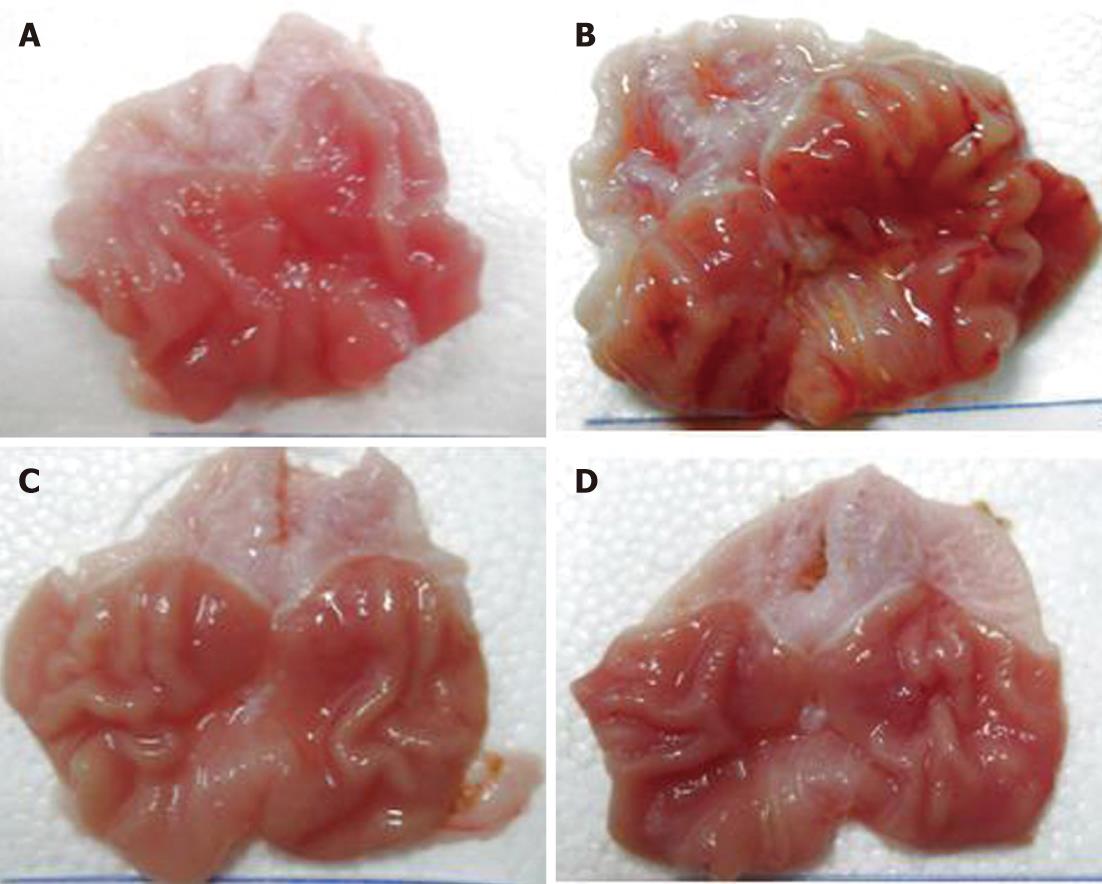
Figure 1 The gross anatomy of gastric mucosa in different groups.
A: Gastric mucosa of normal control group was non-destructive; B Gastric mucosa of model control group showed erosion and ulcer; C: The gastric mucosa damage of low-dose model therapy group was relatively reduced according to model control group; D:The gastric mucosa damage of high-dose model therapy group was significantly reduced according to model control group.
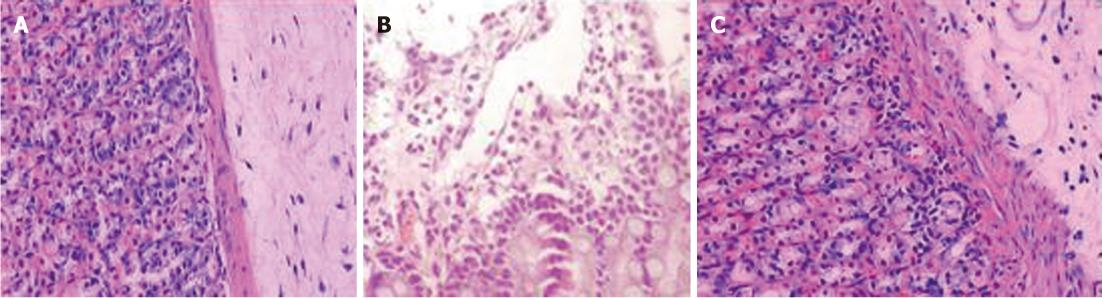
Figure 2 Histological changes of different groups.
A: Normal control group: gastric mucosa was smooth, with clear boundaries, and no significant inflammatory cell infiltration and edema (HE staining × 200); B: Model control group: the gastric mucosa surface was uneven with erosion, ulcer bleeding, edema and telangiectasia, the submucosal gastric glands was incompleted (HE staining × 200); C: Geranylgeranylacetone treated group: the gastric surface mucus layer was basic intact, with scattered mucosal damage, local congestion and edema, fewer inflammatory cell infiltration (HE staining × 200).
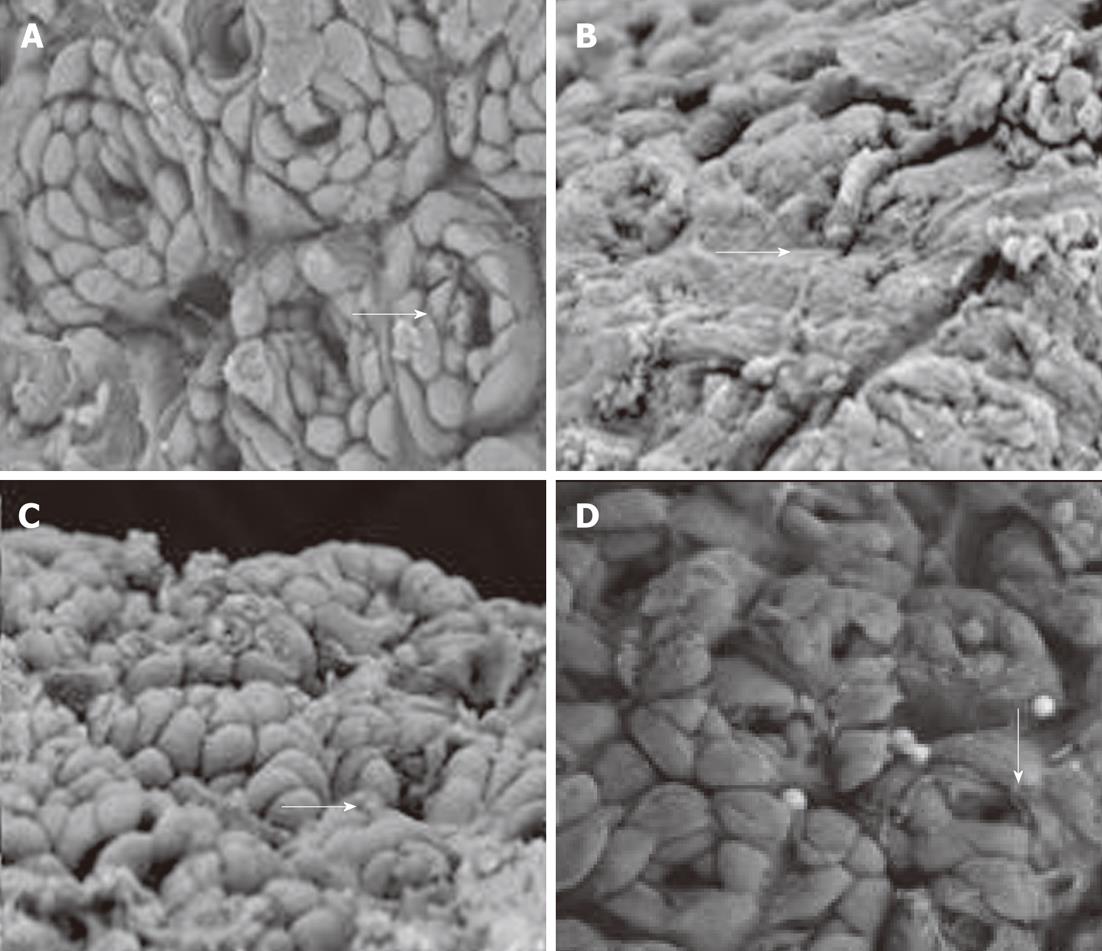
Figure 3 Ultrastructural changes under scanning electron microscopy.
A: Normal control group: Epithelial cells were closely joined and ringwise arranged around the gastric gland openings (arrow), the gastric pits were clear with ordered cells (× 2500); B: Model control group: extensive gastric epithelial cell loss, disappearance of gastric pits (arrow), and revealed glandular epithelium (× 2500); C: Low-dose geranylgeranylacetone treated group: the gastric epithelial cells showed basically complete structure and fewer ruptured epithelial cells (arrow, × 2500); D: High-dose geranylgeranylacetone treated group: the gastric epithelial cells showed relatively perfect structure and fewer ruptured epithelial cells (arrow, × 2500).
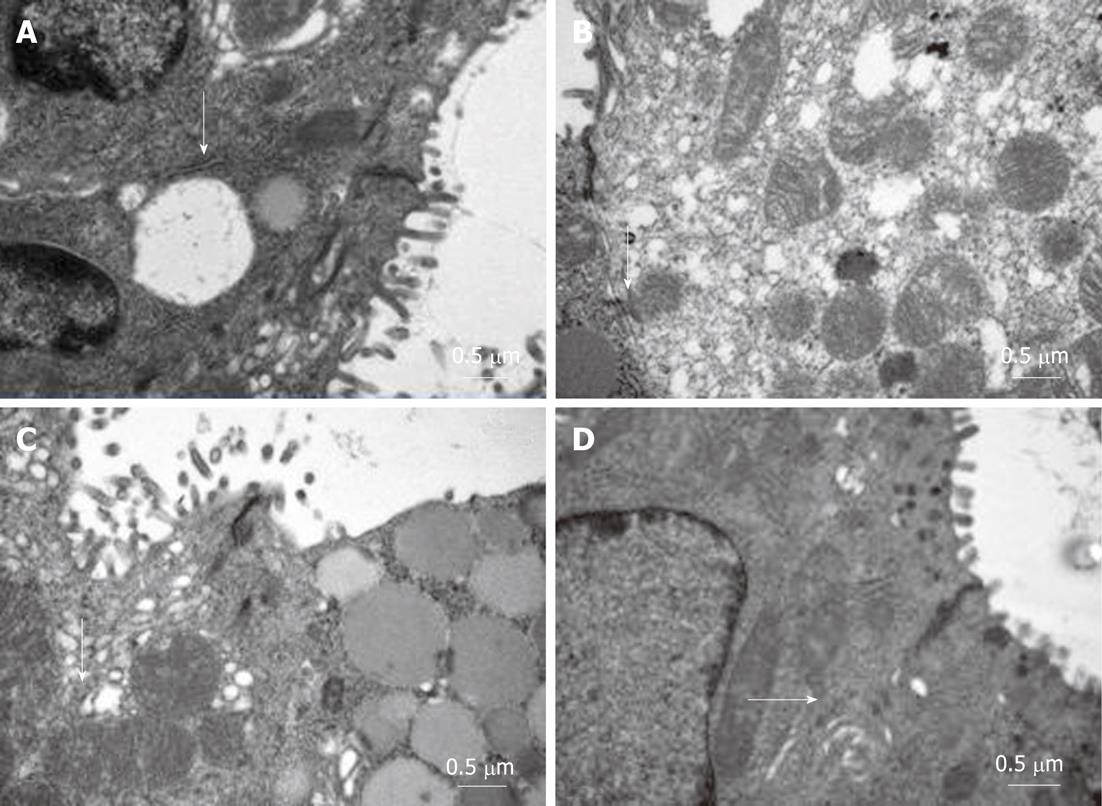
Figure 4 Ultrastructural changes under transmission electron microscope.
A: Normal control group: the microvillis were arranged in neat rows and with no loss, organelles had integrated structure. intercellular junction were distinct (arrow, x 30 000); B: Model control group: widened cell gaps, vague intercellular junction(according to arrow), sparse and deciduous microvillis, and swelling mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum (× 30 000); C: Low-dose geranylgeranylacetone treated group: the cells were arranged in neat rows and the intercellular junction were relative clear (arrow × 30 000), the structure of mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum were mild swelling; D: High-dose geranylgeranylacetone treated group: the cells were arranged in neat rows and the intercellular junction were obvious clear (arrow × 30 000), the structure of mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum were mild swelling.
- Citation: Ning JW, Lin GB, Ji F, Xu J, Sharify N. Preventive effects of geranylgeranylacetone on rat ethanol-induced gastritis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(18): 2262-2269
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i18/2262.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2262