©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2012; 18(12): 1379-1384
Published online Mar 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i12.1379
Published online Mar 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i12.1379
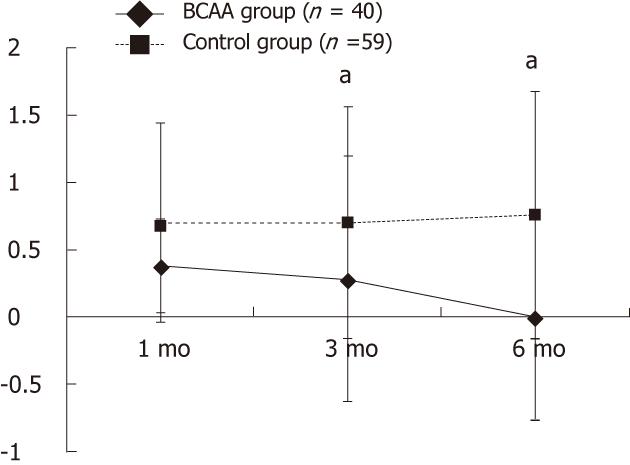
Figure 1 Overall comparison of changes in Child-Pugh score between the branched-chain amino acids group and the control group over time.
There was a significant difference in changes in Child-Pugh score 3 and 6 mo after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. aP < 0.05 vs control group. BCAA: Branched-chain amino acid.
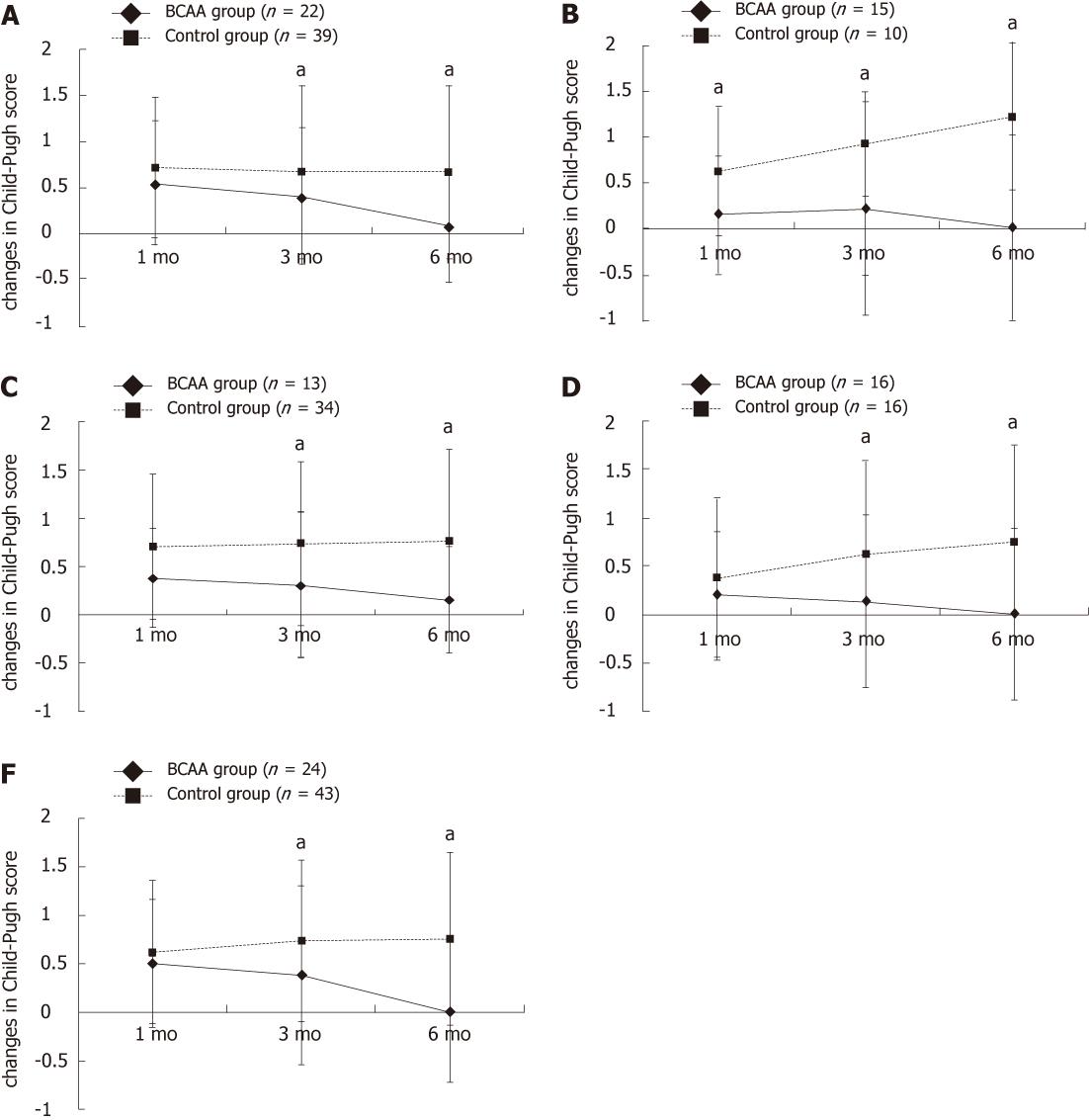
Figure 2 Comparison of changes in Child-Pugh score in Child A and Child B patients: patients with a serum albumin level of 3.
5 g/dL or more, low-dose epirubicin subgroups, high-dose epirubicin subgroups. A: A significant difference was noted in changes in Child-Pugh score 3 and 6 mo after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; B: A significant difference was noted in changes in Child-Pugh score 1, 3 and 6 mo after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; C: A significant difference was observed in changes in Child-Pugh score 3 and 6 mo after TACE; D: A significant difference was noted in changes in Child-Pugh score 3 and 6 mo after TACE; E: A significant difference was noted in changes in Child-Pugh score 3 and 6 mo after TACE. BCAA: Branched-chain amino acids; TACE: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. aP < 0.05 vs control group.
- Citation: Nishikawa H, Osaki Y, Inuzuka T, Takeda H, Nakajima J, Matsuda F, Henmi S, Sakamoto A, Ishikawa T, Saito S, Kita R, Kimura T. Branched-chain amino acid treatment before transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(12): 1379-1384
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i12/1379.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i12.1379