©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2011; 17(9): 1160-1166
Published online Mar 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i9.1160
Published online Mar 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i9.1160
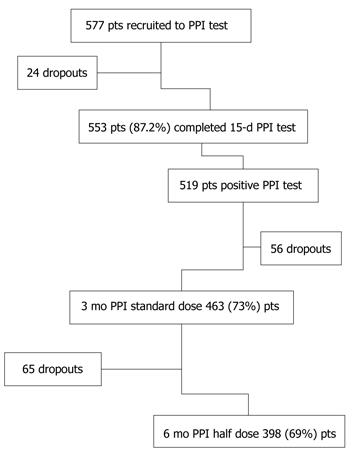
Figure 1 Study design (the percentages refer to recruited patients).
PPI: Proton pump inhibitor. Pts: Patients.
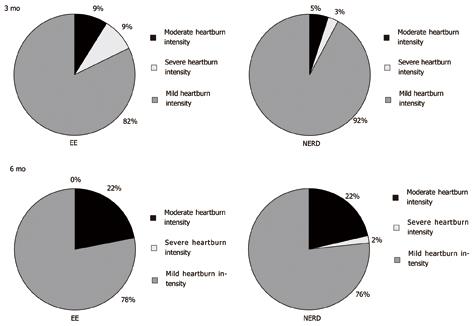
Figure 2 Distribution of heartburn intensity at 3 mo (top panels) and 6 mo (bottom panels) therapy in erosive esophagitis (left panels) and non erosive reflux disease patiens (right panels).
EE: Erosive esophagitis; NERD: Non erosive reflux disease.
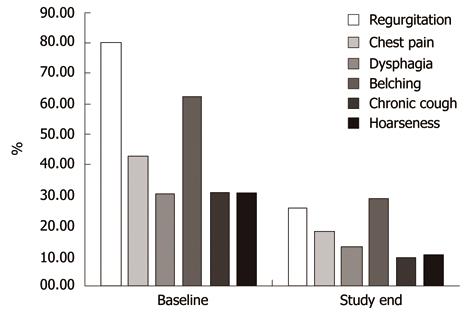
Figure 3 Additional symptoms assessed at baseline and at study end by QUestionario Italiano Diagnostico questionnaire (data are presented for the 398 patients completing the study).
Baseline vs study end, for all symptoms, P < 0.001.
- Citation: Pace F, Riegler G, Leone A, Dominici P, Grossi E, Group TES. Gastroesophageal reflux disease management according to contemporary international guidelines: A translational study. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(9): 1160-1166
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i9/1160.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i9.1160