Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2011; 17(6): 809-816
Published online Feb 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.809
Published online Feb 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.809
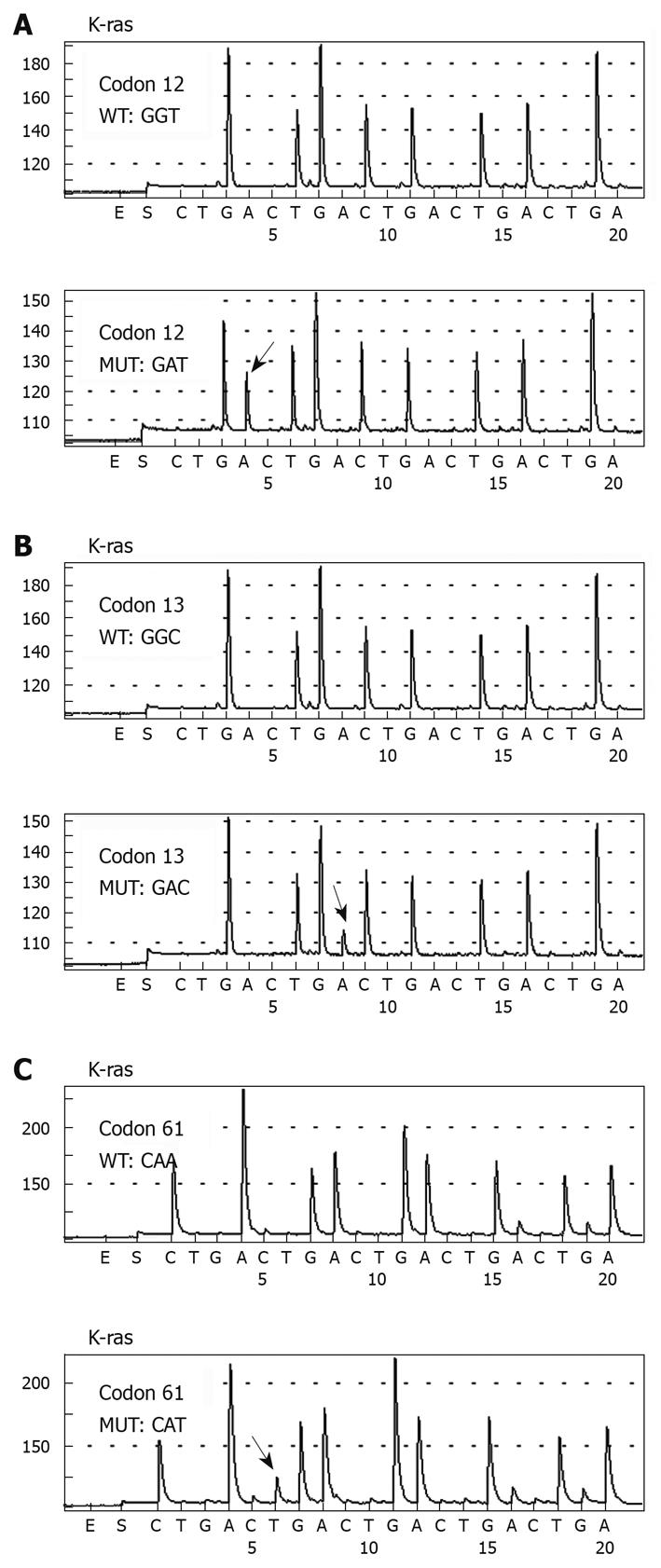
Figure 1 Pyrosequencing analysis of K-ras codons 12, 13, and 61 DNA sequences in colorectal cancer patients.
The highlighted arrow shows the nucleotide change at the mutation site.
Figure 2 Distribution chart of six different K-ras mutations in 118 colorectal cancer patients.
Gly: Glycinel; Gln: Glutamine; Ser: Serine; Asp: Aspartic acid; Val: Valine; Ala: Alanine; His: Histidine.
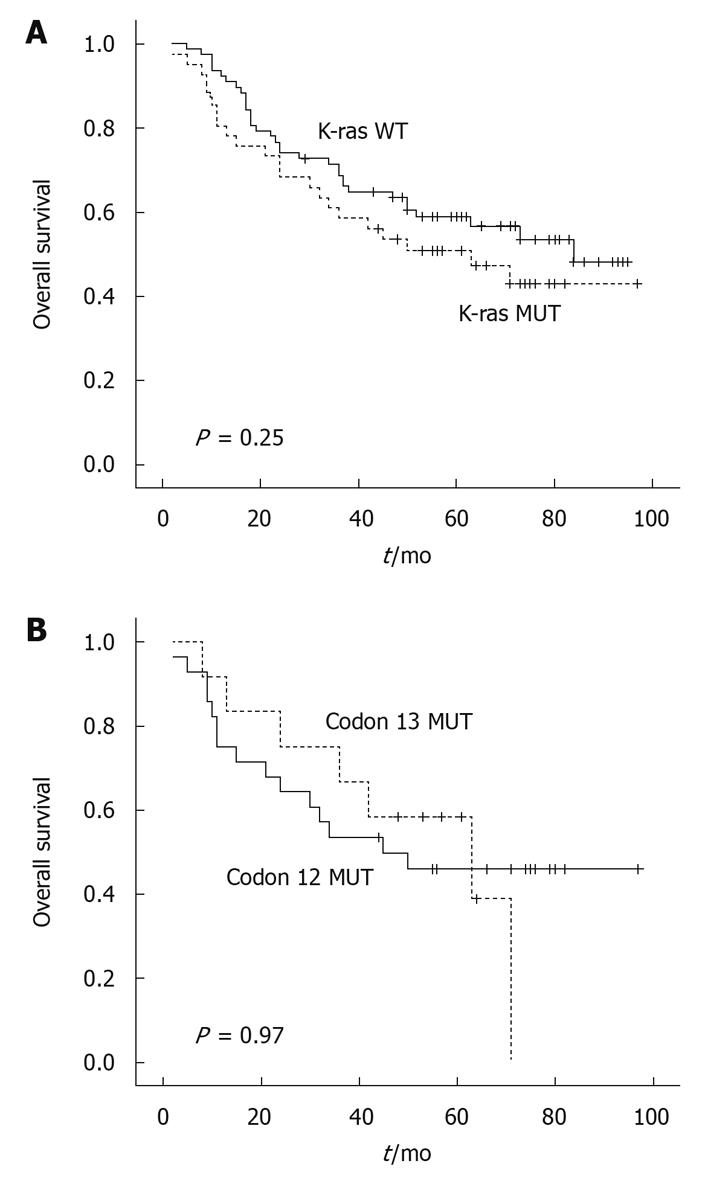
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier survival curve in colorectal cancer patients with regard to K-ras gene codon mutations.
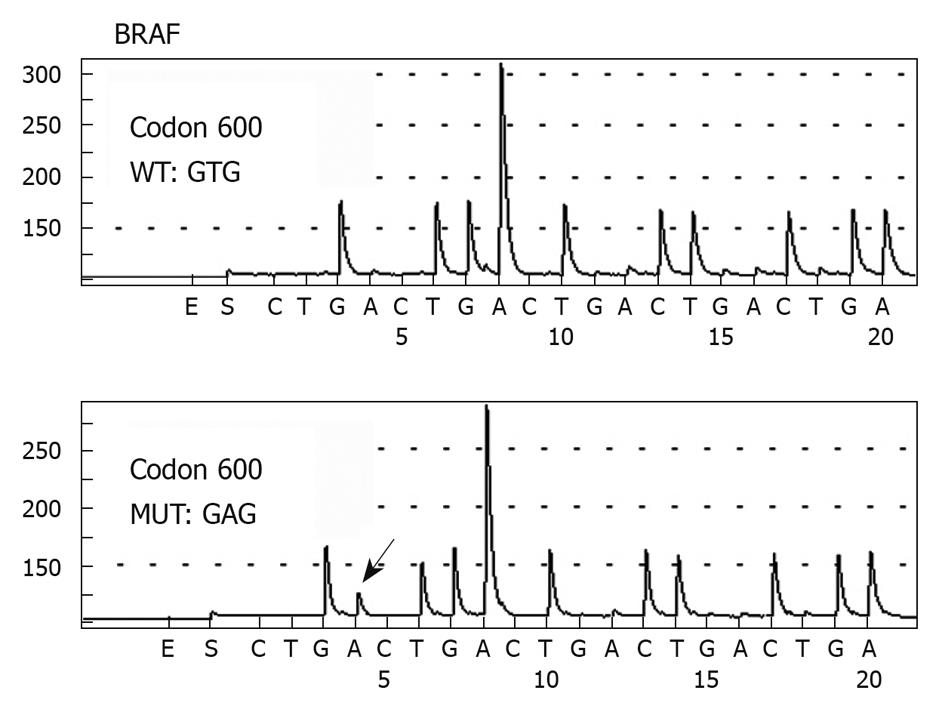
Figure 4 Pyrosequencing analysis of BRAF gene codon 600 DNA sequences in colorectal cancer patients.
The highlighted arrow shows the nucleotide change at the mutation site.
- Citation: Shen H, Yuan Y, Hu HG, Zhong X, Ye XX, Li MD, Fang WJ, Zheng S. Clinical significance of K-ras and BRAF mutations in Chinese colorectal cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(6): 809-816
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i6/809.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.809