©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2011; 17(37): 4247-4250
Published online Oct 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i37.4247
Published online Oct 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i37.4247
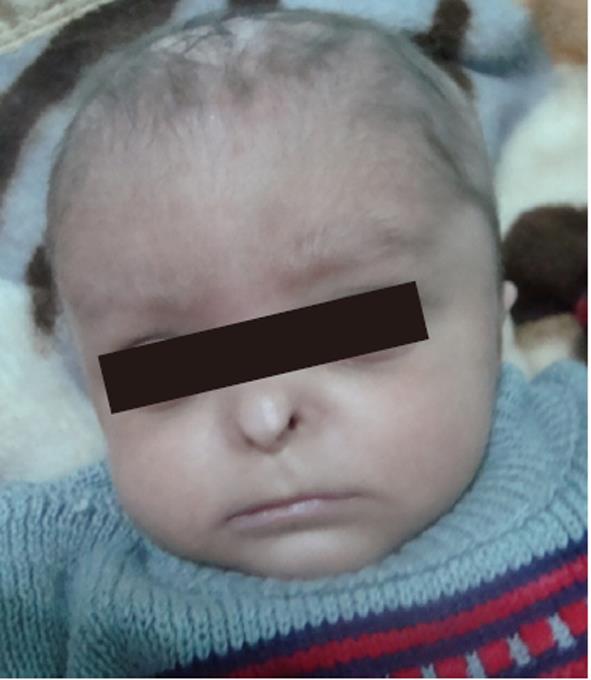
Figure 1 Typical facial appearance of this patient with Johanson-Blizzard syndrome, showing aplasia of alae nasi, scalp defect, and sparse hair.
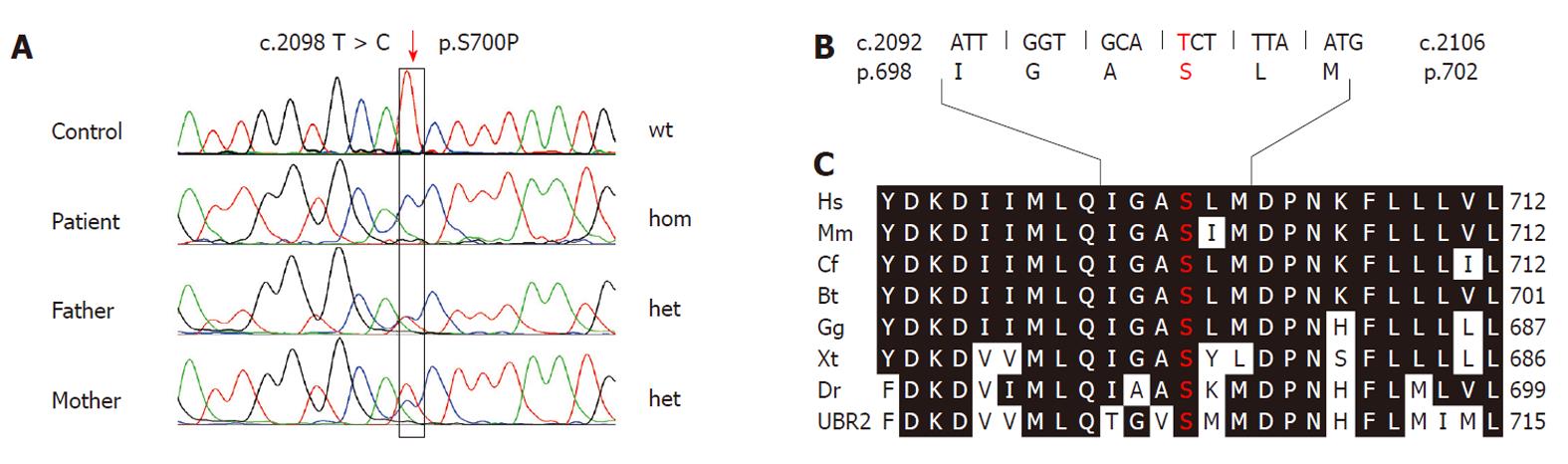
Figure 2 Demonstration and characterization of the familial mutation.
A: Comparison of electropherograms around the T > C transition at position c.2098; B: Nucleotide and amino acid sequence; C: Multiple protein alignement (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2) of vertebrate UBR1. Black shading indicates identical residues. wt: Wild-type; Hom: Homozygous; Het: heterozygous; Hs: Homo sapiens; Mm: Mus musculus; Cf: Canis familiaris; Bt: Bos taurus; Gg: Gallus gallus; Xt: Xenopus tropicalis; Dr: Danio rerio; UBR2: Human UBR2 protein.
- Citation: Almashraki N, Abdulnabee MZ, Sukalo M, Alrajoudi A, Sharafadeen I, Zenker M. Johanson-Blizzard syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(37): 4247-4250
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i37/4247.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i37.4247