©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2011; 17(23): 2821-2828
Published online Jun 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2821
Published online Jun 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2821
Figure 1 Diffusion-weighted imaging of hepatic injury at different time point.
A: At the end of the 1st wk after transplantation, the mean apparent diffusion coefficient value of the acute hepatic injury liver in the transplantation control was (0.69 ± 0.05) × 10-3 mm2/s; B: At the end of the 1st wk after transplantation, the mean apparent diffusion coefficient value of the acute hepatic injury liver in the cell transplantation group was (1.07 ± 0.07) × 10-3 mm2/s; C: At the end of the 2nd wk after transplantation, the mean apparent diffusion coefficient value of the acute hepatic injury liver in the transplantation control group was (0.84 ± 0.06) × 10-3 mm2/s; D: At the end of the 2nd wk after transplantation, the mean apparent diffusion coefficient value of the acute hepatic injury liver in the cell transplantation group was (1.41 ± 0.04) × 10-3 mm2/s; E: At the end of the 4th wk after transplantation, the mean apparent diffusion coefficient value of the acute hepatic injury liver in the transplantation control group was (0.86 ± 0.04) × 10-3 mm2/s; F: At the end of the 4th wk after transplantation, the mean apparent diffusion coefficient value of the acute hepatic injury liver in the cell transplantation group was (1.68 ± 0.04) × 10-3 mm2/s.
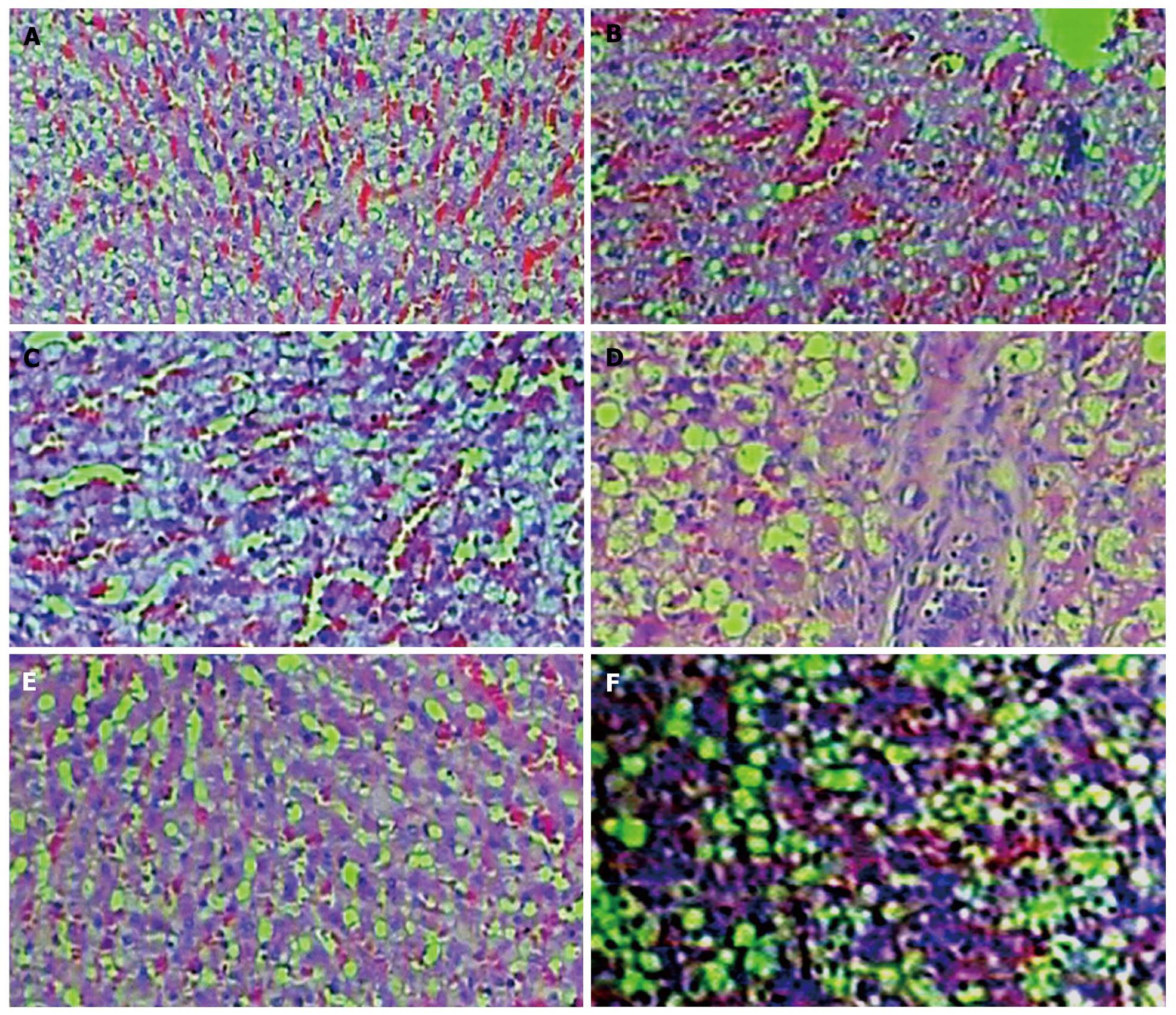
Figure 2 Pathological change of hepatic injury at different time point (Hematoxylin and eosin × 100).
A: At the end of the 1st wk after transplantation, the pathological sections of the cell transplantation group showed extensive hepatic cell degenerations, few binucleate cells, abnormal hepatic cords and local inflammatory cell infiltration; B: At the end of the 1st wk after transplantation, the pathological sections of the transplantation control group showed obvious and extensive edema of hepatic cells, spotty hepatolysis, abnormal hepatic cords, local inflammatory cell infiltration and injured vascular endothelium; C: At the end of the 2nd wk after transplantation, the pathological sections of the cell transplantation group showed extensive edema of hepatic cells, abnormal hepatic cords, imperceptible inflammatory cell infiltration and few scattered binucleate cells. (Hematoxylin and eosin ×100); D: At the end of the 2nd wk after transplantation, the pathological sections of the transplantation control group showed obvious and extensive edema of hepatic cells, an increased number of binucleate cells and obvious inflammatory cell infiltration around the header; E: At the end of the 4th wk after transplantation, the pathological sections of the cell transplantation group showed scattering edema of the hepatic cells, hepatic cords, sinusoid near normal and hyperemia in local sinusoid; F: At the end of the 4th wk after transplantation, the pathological sections of the transplantation control group showed scattering and sheet edema of the hepatic cells, hyperemia in local sinusoids and an increased number of binucleate cells.
- Citation: Shang QL, Xiao EH, Zhou QC, Luo JG, Wu HJ. Pathological and MR-DWI study of the acute hepatic injury model after stem cell transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(23): 2821-2828
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i23/2821.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2821