©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2011; 17(13): 1746-1752
Published online Apr 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i13.1746
Published online Apr 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i13.1746
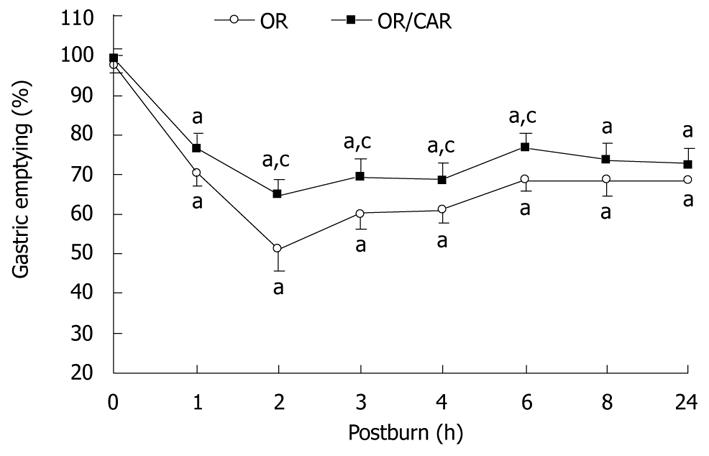
Figure 1 Carbachol promoted gastric emptying rate in oral fluid resuscitation/Carbachol group compared with those of oral fluid resuscitation group at 2, 3, 4 and 6 h after burn injury.
aP < 0.05 vs 0 h, cP < 0.05 vs oral fluid resuscitation (OR) group (one-way ANOVA). Error bars represent mean ± SD. CAR: Carbachol.
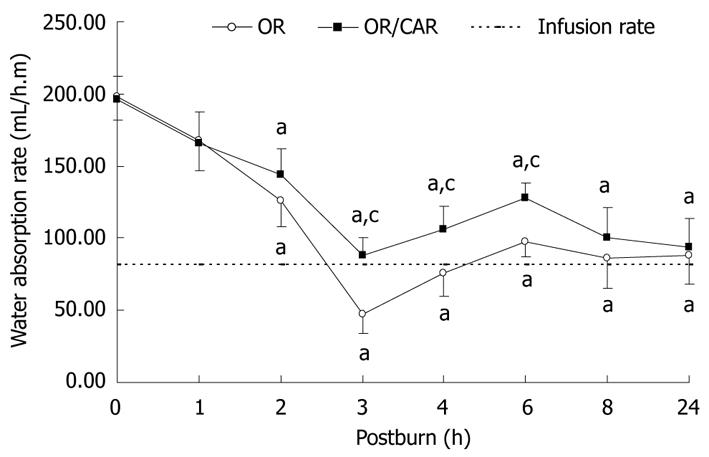
Figure 2 Carbachol significantly improved rate of water absorption of intestine in oral fluid resuscitation/Carbachol group compared with those of oral fluid resuscitation group at 3, 4 and 6 h after burn injury.
aP < 0.05 vs 0 h, cP < 0.05 vs oral fluid resuscitation (OR) group (one-way ANOVA). Error bars represent mean ± SD. CAR: Carbachol.
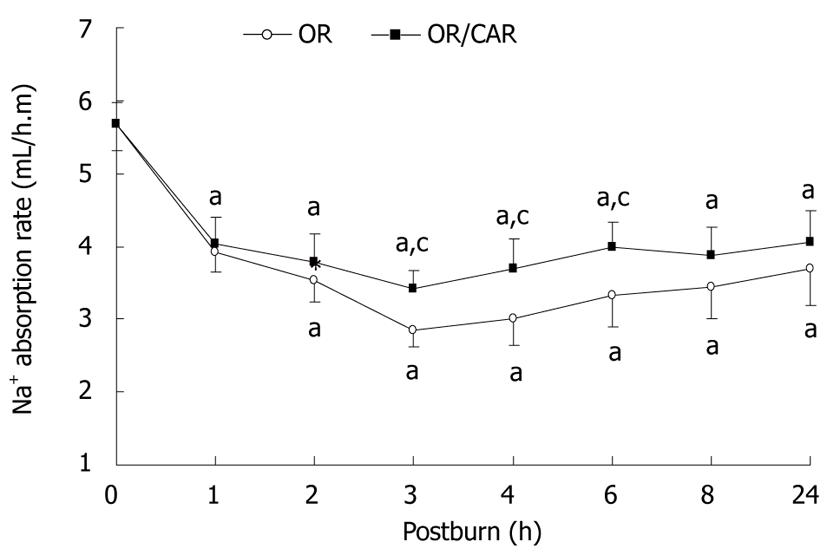
Figure 3 Carbachol significantly improved rate of Na+ absorption of intestine in oral fluid resuscitation/Carbachol group compared with those of oral fluid resuscitation group at 3, 4 and 6 h after burn injury.
aP < 0.05 vs 0 h, cP < 0.05 vs oral fluid resuscitation (OR) group (one-way ANOVA). Error bars represent mean ± SD. CAR: Carbachol.
- Citation: Hu S, Che JW, Tian YJ, Sheng ZY. Carbachol promotes gastrointestinal function during oral resuscitation of burn shock. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(13): 1746-1752
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i13/1746.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i13.1746