©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2010; 16(47): 5953-5957
Published online Dec 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i47.5953
Published online Dec 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i47.5953
Figure 1 Schematic overview of the reverse cholesterol transport pathways.
ABCA1: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette transporter A1; ABCG1: ATP-binding cassette transporter G1; ABCG5: ATP-binding cassette transporter G5; ABCG8: ATP-binding cassette transporter G8; SR-BI: Scavenger receptor class B type I; TICE: Transintestinal cholesterol efflux.
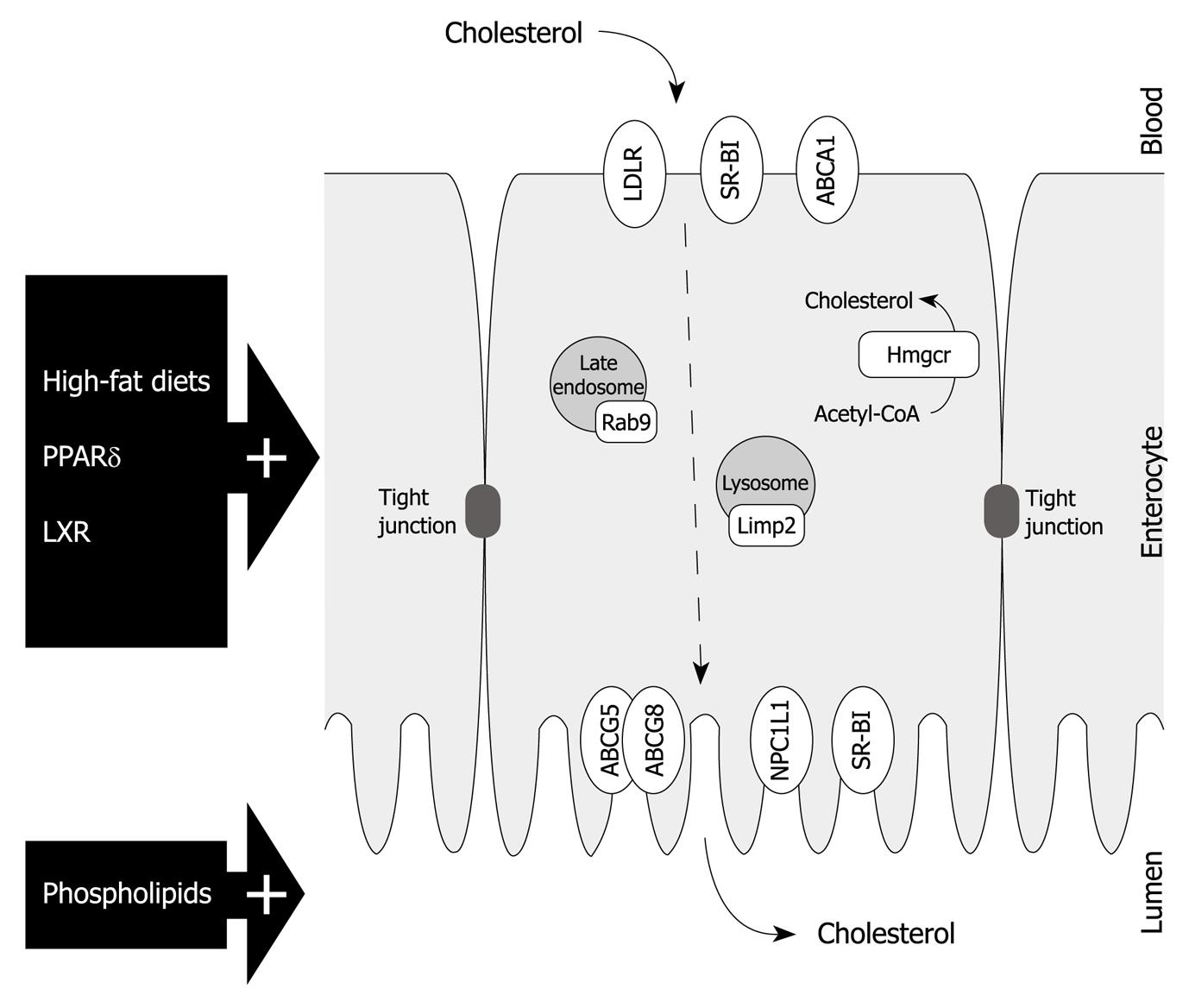
Figure 2 Enterocyte representation with a schematic overview of cholesterol transporters and potential transintestinal cholesterol efflux-related factors as discussed in this paper.
PPARδ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ; LXR: Liver X receptor; LDLR: Low density lipoprotein receptor; SR-BI: Scavenger receptor class B type I; ABCA1: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette transporter A1; ABCG5: ATP-binding cassette transporter G5; ABCG8: ATP-binding cassette transporter G8; Hmgcr: 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase; Limp2: Lysosomal integral membrane protein 2; NPC1L1: Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 protein; TICE: Transintestinal cholesterol efflux.
-
Citation: Vrins CL. From blood to gut: Direct secretion of cholesterol
via transintestinal cholesterol efflux. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(47): 5953-5957 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i47/5953.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i47.5953