Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2010; 16(23): 2959-2962
Published online Jun 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2959
Published online Jun 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2959
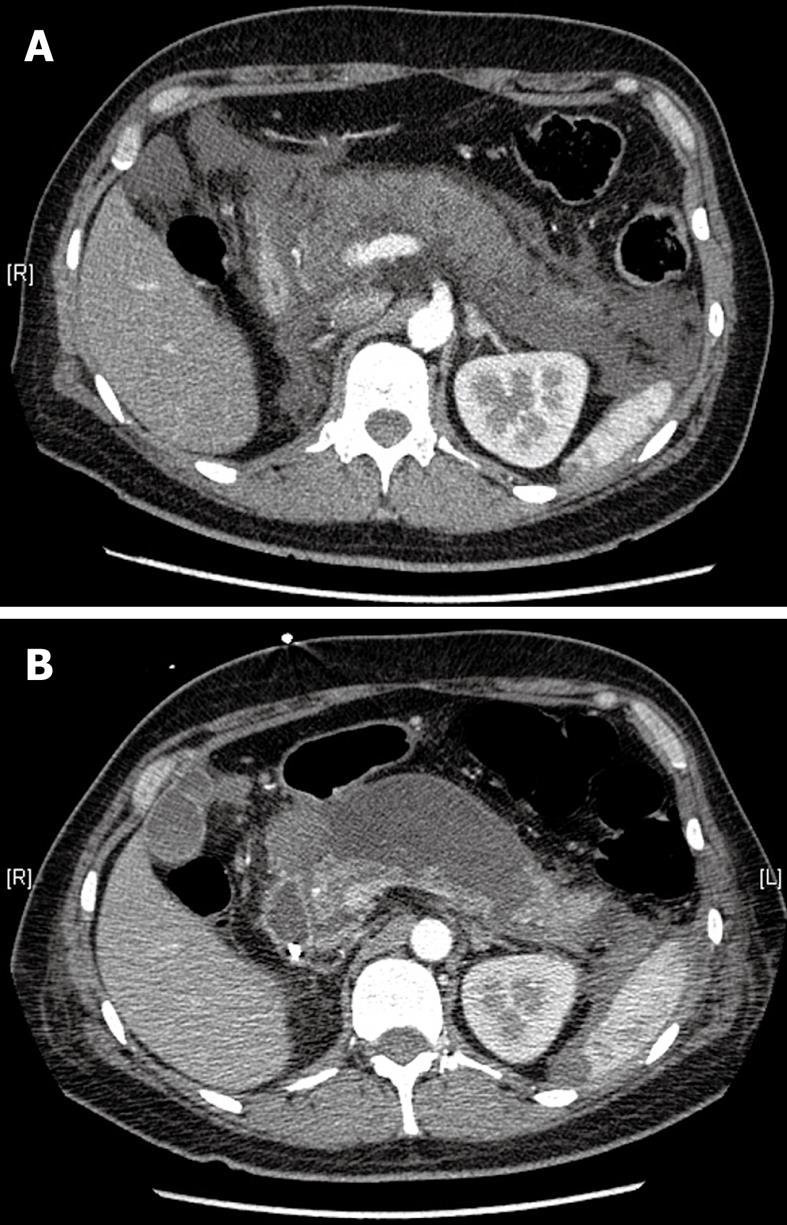
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography scan at the level of the pancreas.
A: On the day of admission showing acute exudative pancreatitis. Note the history of a right nephrectomy; B: On day 20 showing the development of pancreatic pseudocysts and few remnants of normal pancreatic tissue.
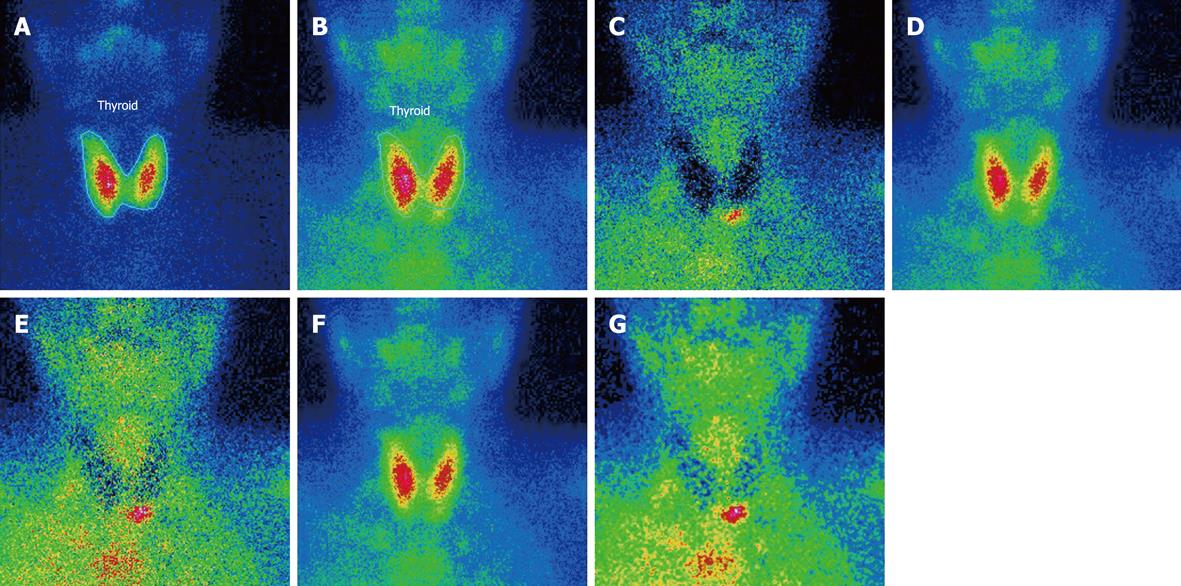
Figure 2 99mTc-Sestamibi scintigraphy showing a lower left side parathyroid adenoma.
A: Thyroid SKM: SK ELUAAT, -Tc-99mANT; B: Parathyroid SKM: SK MIBI, -Tc-99mH1; C: Normalized subtracted f = 1; D: Registered parathyroid; E: Normalized subtracted f = 1.25; F: Normalized parathyroid f = 1.25; G: Smoothed subtracted f = 1.25.
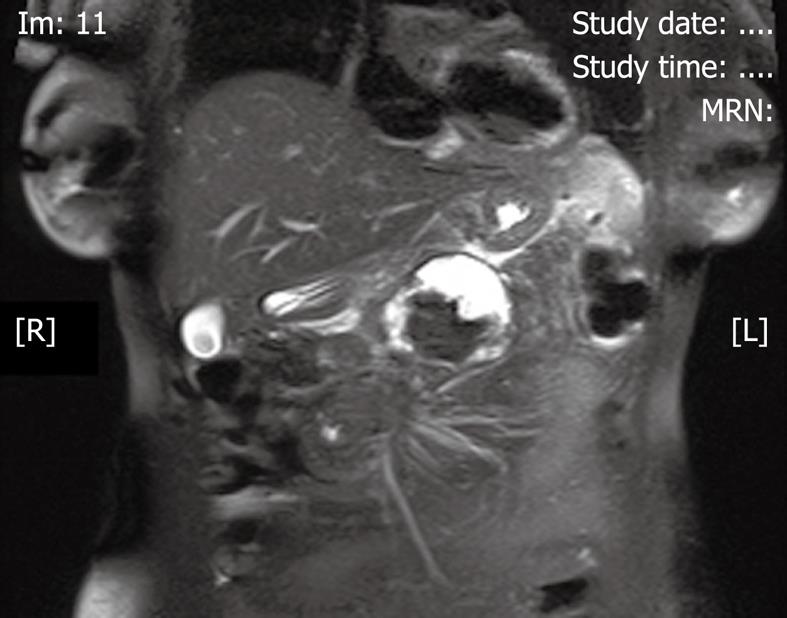
Figure 3 Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging at the level of the pancreas showing debris in the pancreatic pseudocyst.
- Citation: Lenz JI, Jacobs JM, Op de Beeck B, Huyghe IA, Pelckmans PA, Moreels TG. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis as first manifestation of primary hyperparathyroidism. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(23): 2959-2962
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i23/2959.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2959