©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2009; 15(48): 6134-6136
Published online Dec 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.6134
Published online Dec 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.6134
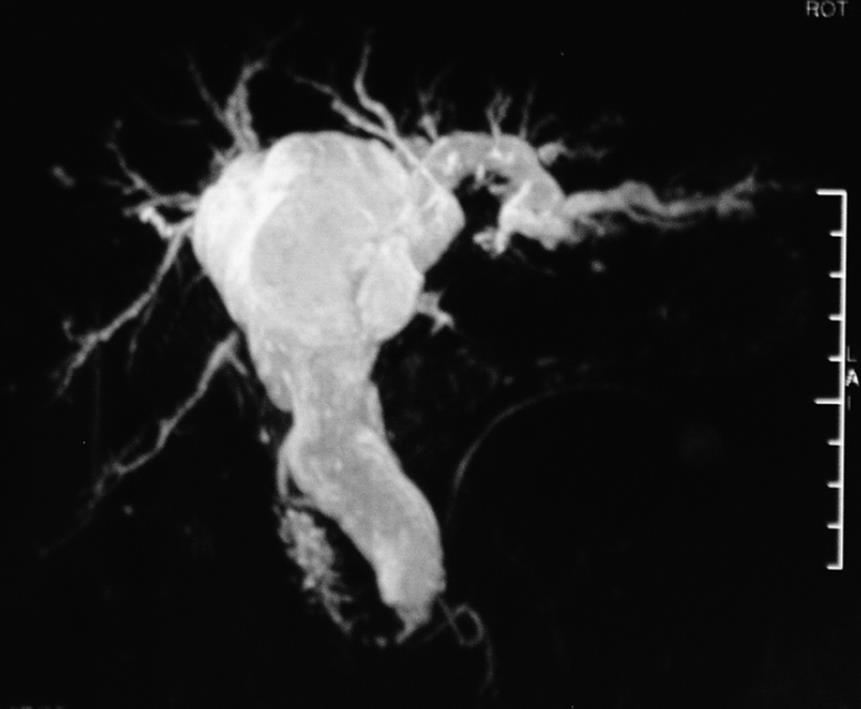
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) showing the dilation of extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts lacking of asymmetry.
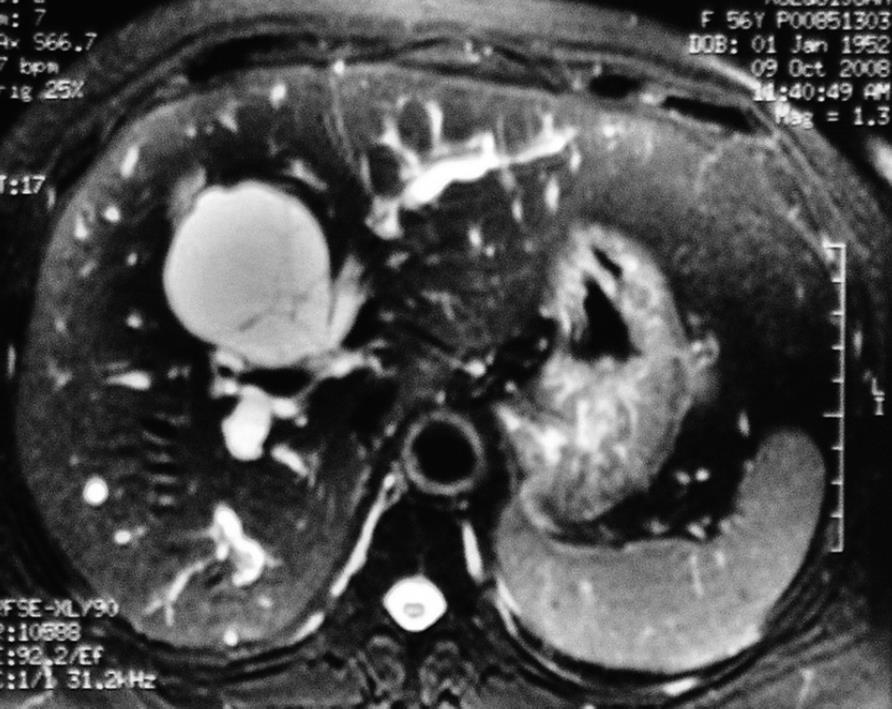
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showing different bile signals between the right and left intrahepatic ducts in a multiloculated lesion with internal septation.
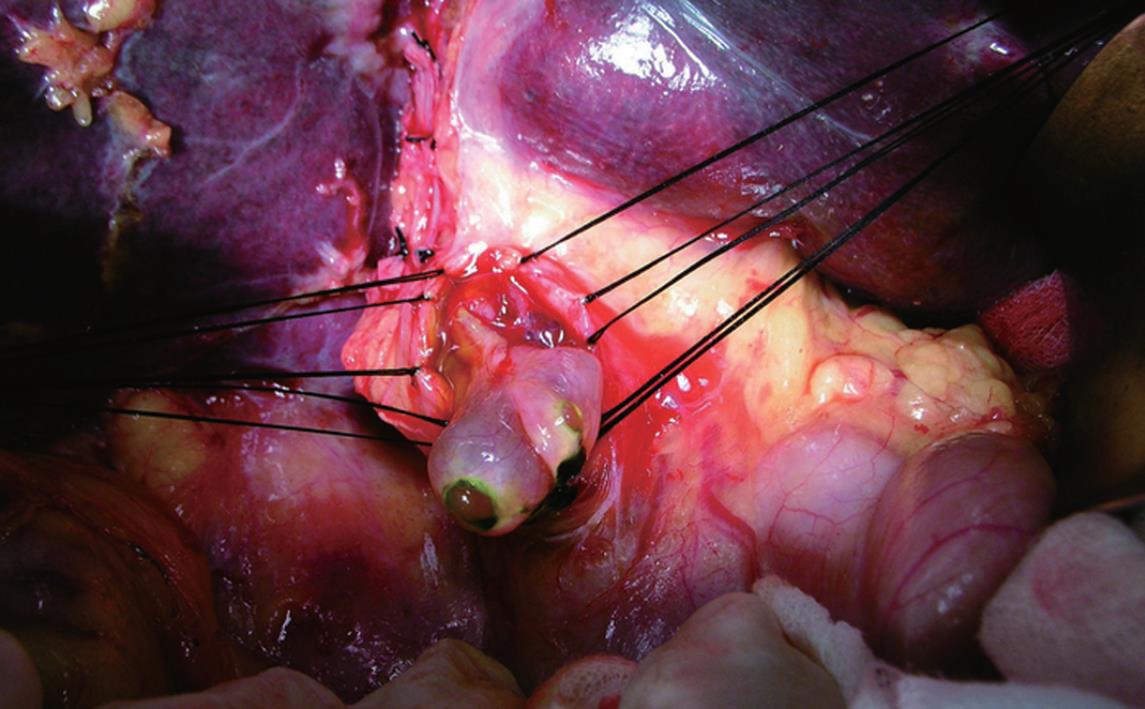
Figure 3 A tumor embolus originating from left intrahepatic duct with smooth surface protrudes the extrahepatic bile duct.
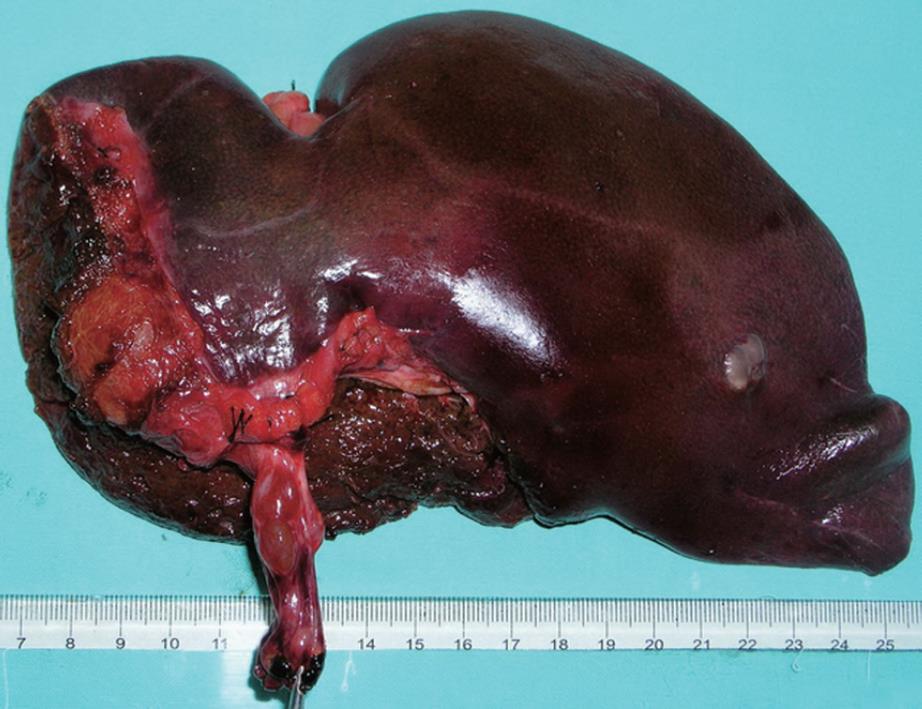
Figure 4 Macroscopy revealing a multilocular cystic lesion containing serous fluid with tumor embolus protruding into the left hepatic duct and the extrahepatic bile duct.
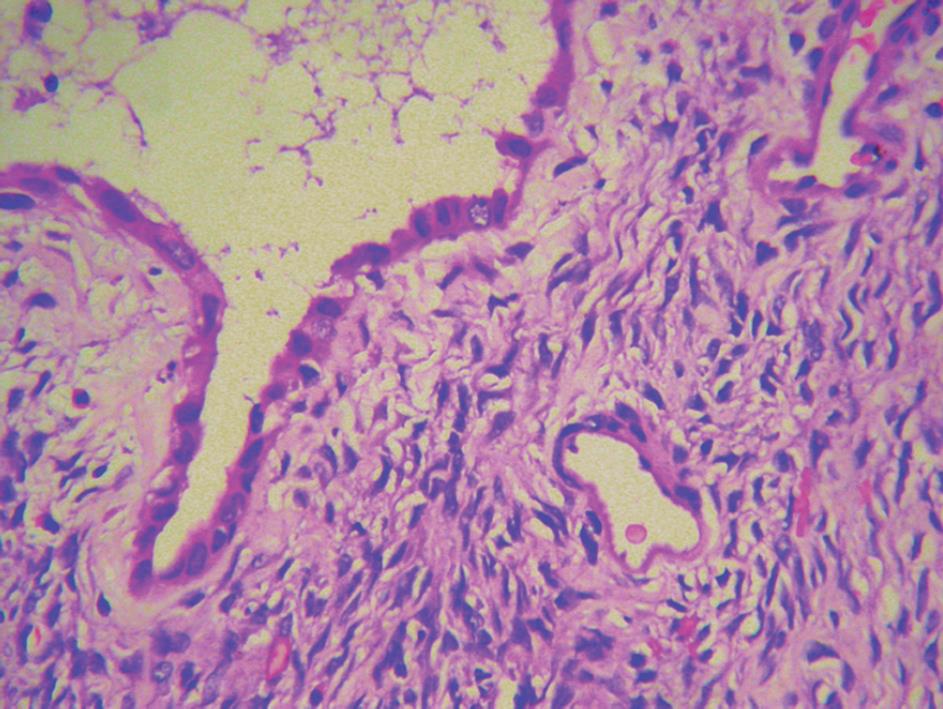
Figure 5 Postoperative pathology showing epithelial lining composed of biliary-type cuboidal cells surrounded by an ovarian-like stroma (400 ×).
- Citation: Yi B, Cheng QB, Jiang XQ, Liu C, Luo XJ, Dong H, Zhang BH, Wu MC. A special growth manner of intrahepatic biliary cystadenoma. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(48): 6134-6136
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i48/6134.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.6134