©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2009; 15(41): 5200-5205
Published online Nov 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5200
Published online Nov 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5200
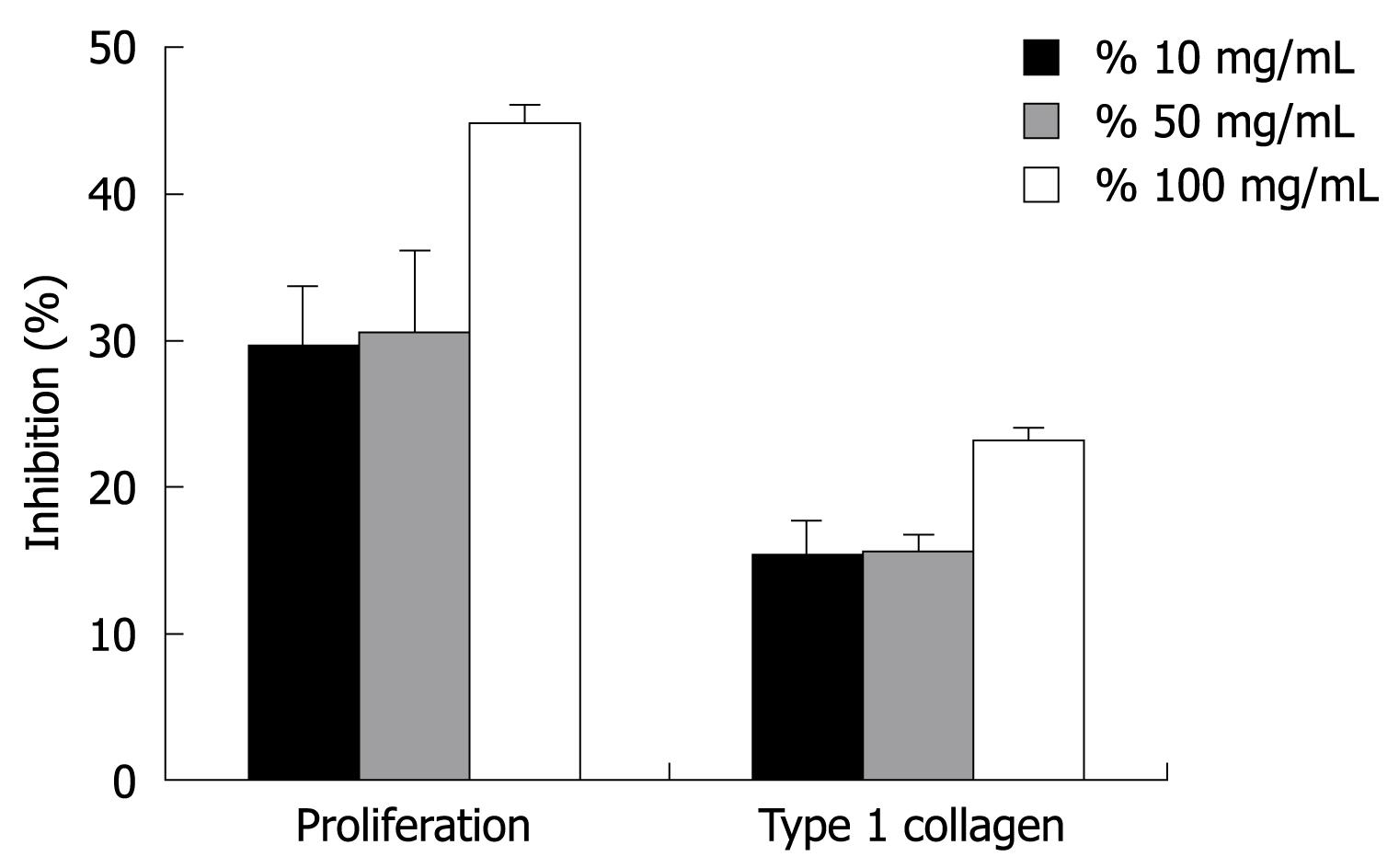
Figure 1 Inhibitory effects of green tea on HSC-T6 cell proliferation and type 1 collagen expression.
Green tea suppressed HSC-T6 cell proliferation and type 1 collagen expression in a dose-dependent manner. Data are expressed as mean ± SD.
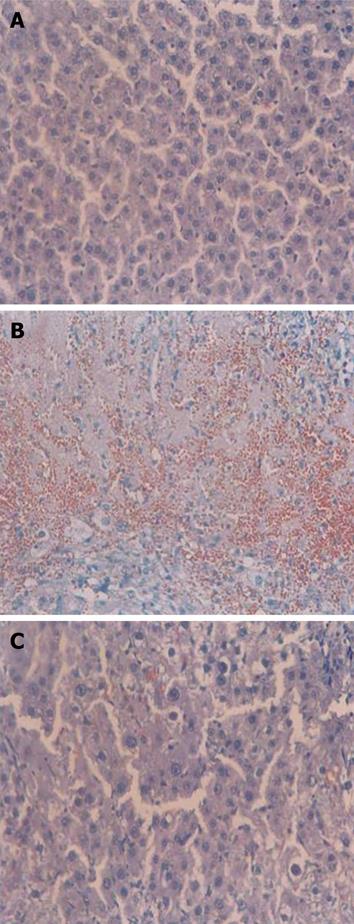
Figure 2 Effects of green tea extract on liver tissue morphology in DMN-induced fibrosis model.
Representative pictures of hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of liver tissue from normal control rat (A), DMN-treated control (B), DMN-treated + green tea extract (100 mg/kg) group (C). Original magnification, × 200.
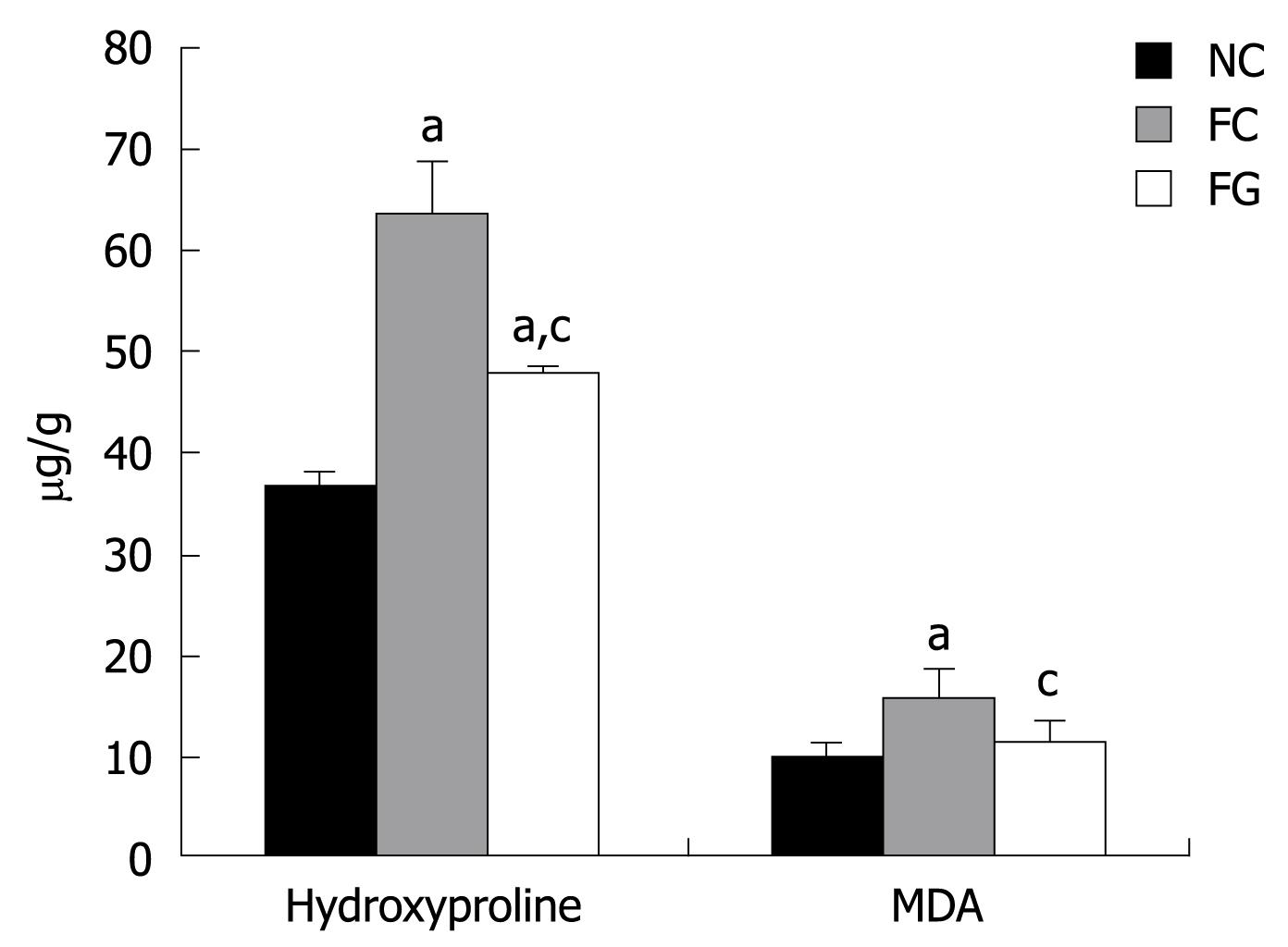
Figure 3 Effects of green tea on hydroxyproline and lipid peroxide (MDA) levels in DMN-treated rat liver.
Data are expressed as mean ± SD. MDA: Malondialdehyde. aP < 0.05 vs normal control (NC), cP < 0.05 vs fibrosis control (FC).
-
Citation: Kim HK, Yang TH, Cho HY. Antifibrotic effects of green tea on
in vitro andin vivo models of liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(41): 5200-5205 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i41/5200.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.5200