©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2009; 15(33): 4209-4211
Published online Sep 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4209
Published online Sep 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4209
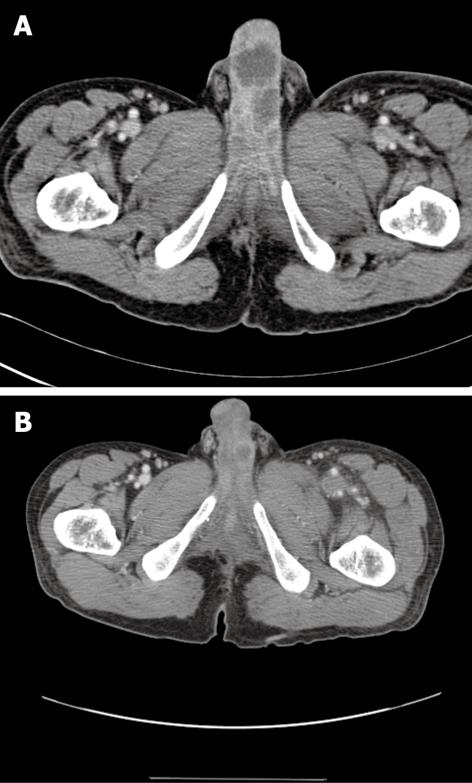
Figure 1 CT image.
A: Multifocal irregular shaped low-density areas along the penis; B: Multifocal irregular shaped low density areas are also seen in an CT image obtained 3 mo earlier.
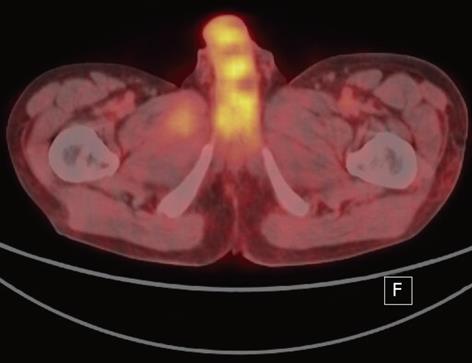
Figure 2 PET image showed low 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the lesions.
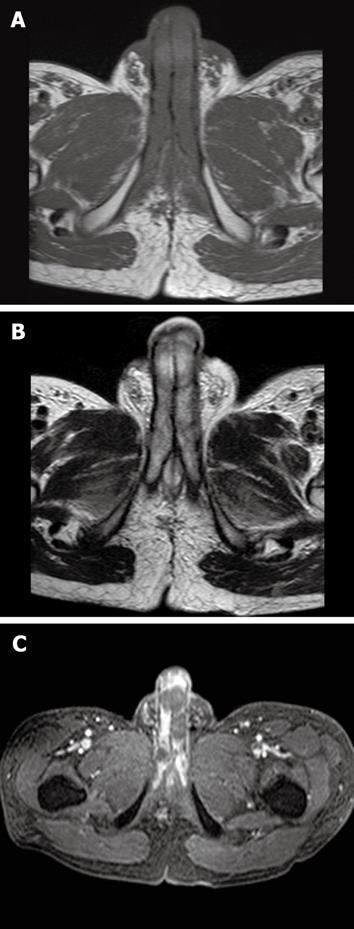
Figure 3 Penile MRI.
A: Low to iso signal intensity as compared with the surrounding corpus cavernosum on an axial T1-weighted image; B: Low to intermediate signal intensity on an axial T2-weighted image; C: The presence of non-enhanced lesions on a gadolinium-enhanced image.
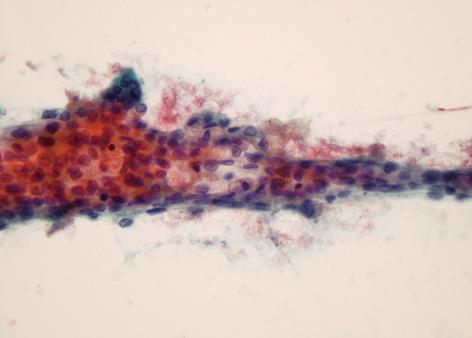
Figure 4 Fine-needle aspiration of penile mass showed nests of acinar-like cells with cytological atypia, consistent with metastatic adenocarcinoma (Papanicolaou stain, × 400).
- Citation: Park JC, Lee WH, Kang MK, Park SY. Priapism secondary to penile metastasis of rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(33): 4209-4211
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i33/4209.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.4209