©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2009; 15(28): 3472-3479
Published online Jul 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3472
Published online Jul 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3472
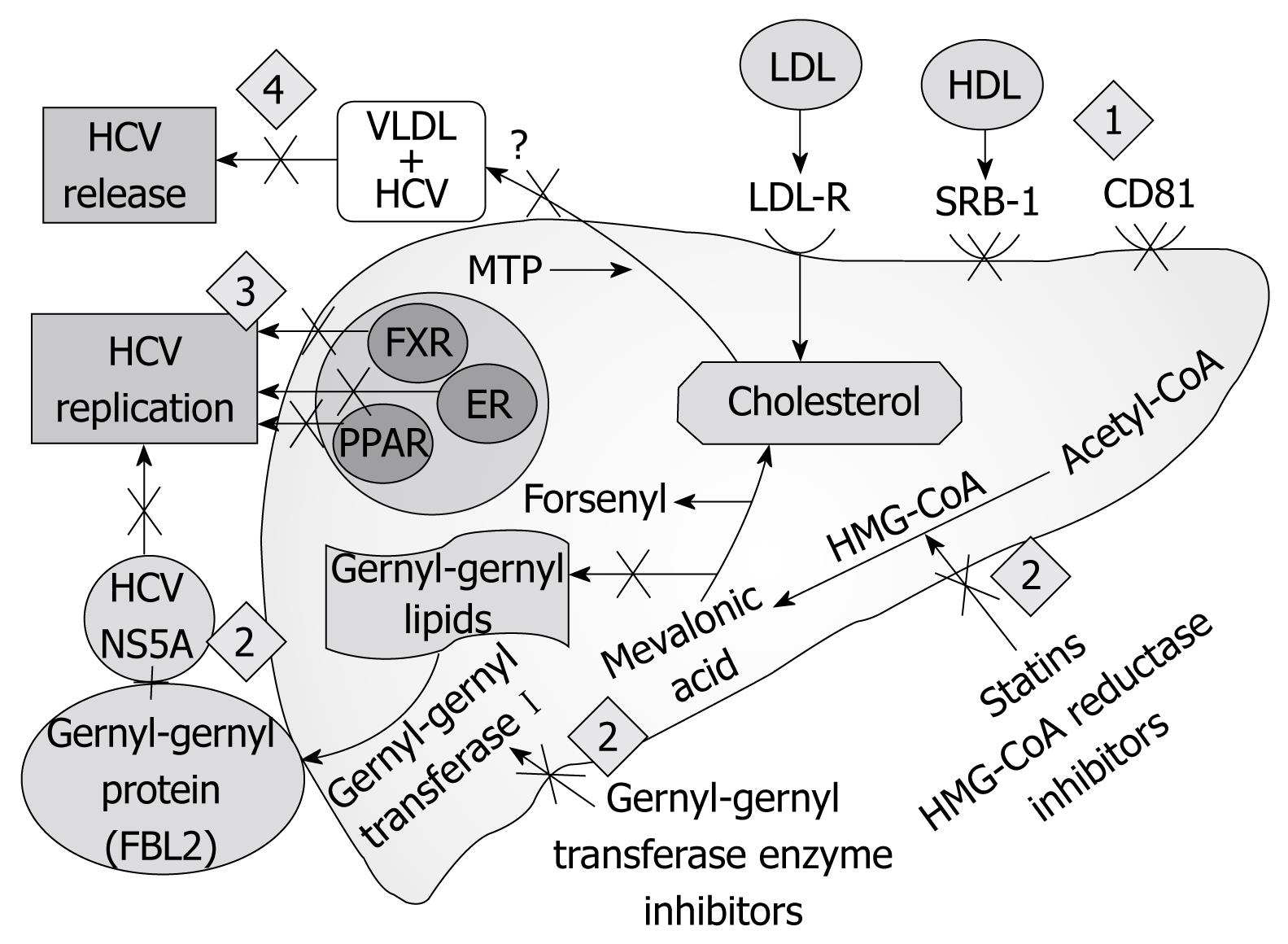
Figure 1 Possible sites targeting host factors as a novel antiviral treatment.
(1) Inhibition of HCV entry by anti-receptor antibodies; (2) Interference with the host metabolic factor involved in HCV replication; (3) Modulation of nuclear receptors involved in HCV replication; (4) Inhibition of HCV release. LDL-R: Low density lipoprotein receptor; HDL: High density lipoprotein; VLDL: Very low density lipoprotein; SRB-1: Scavenger receptor B1; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; ER: Estrogen receptors; MTP: Microsomal triglyceride protein; HMG-CoA: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A.
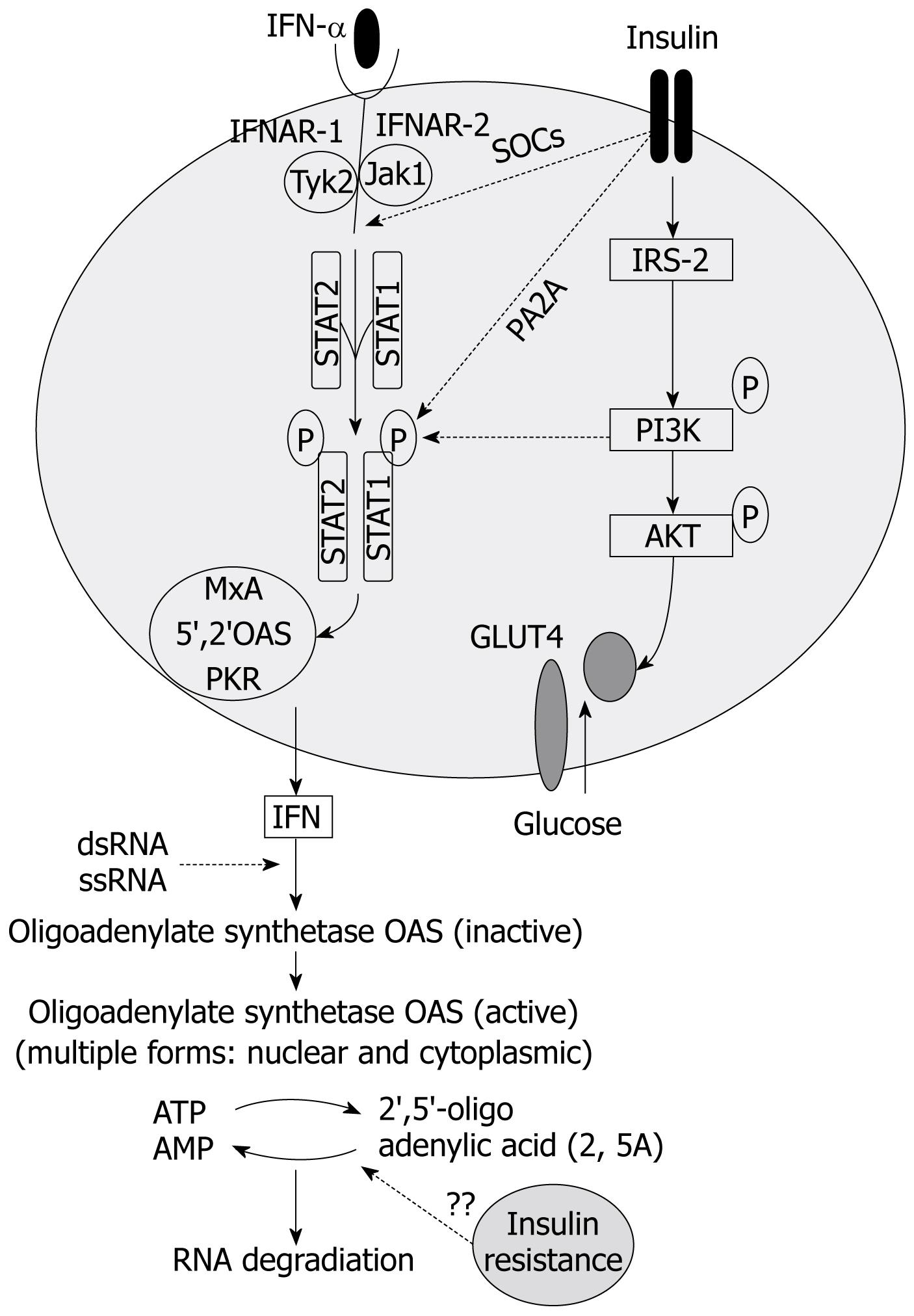
Figure 2 Interaction between insulin and interferon-alfa signaling pathway.
SOCs: Suppressor of cytokine signaling; PA2A: Protein phosphatase 2A; PI3K: Phosphatidil-Inositol 3-kinase; JAK: Janus kinase; STAT: Signal transduction and activator of transcription; TYK2: Tyrosine kinase 2; Dotted lines: Represent inhibition; Continuous lines: Represent activation.
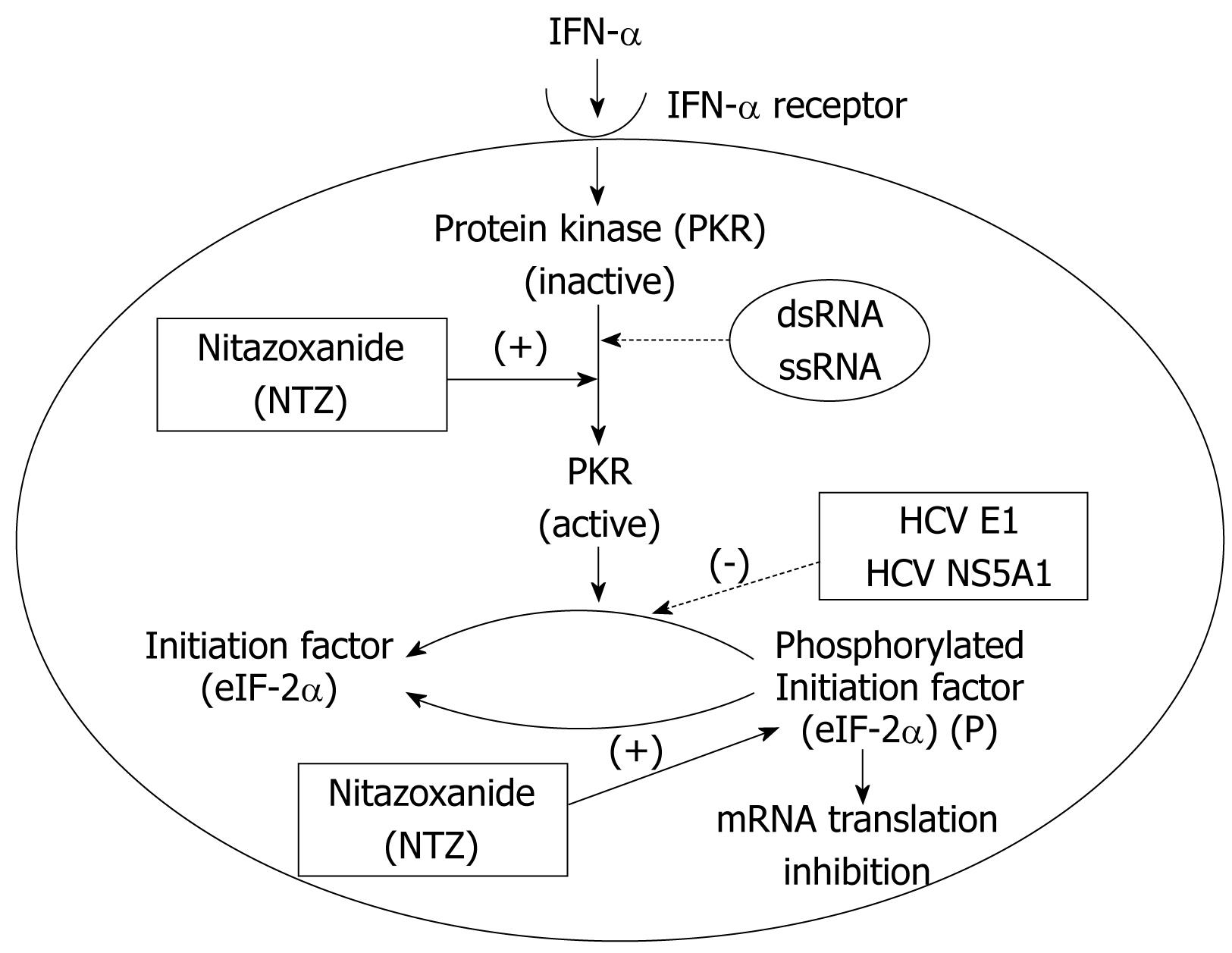
Figure 3 Antiviral mechanism of Nitazoxanide.
Dotted lines: Represent inhibition; Continuous lines: Represent activation.
- Citation: Khattab MA. Targeting host factors: A novel rationale for the management of hepatitis C virus. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(28): 3472-3479
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i28/3472.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.3472