©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2009; 15(21): 2579-2586
Published online Jun 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2579
Published online Jun 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2579
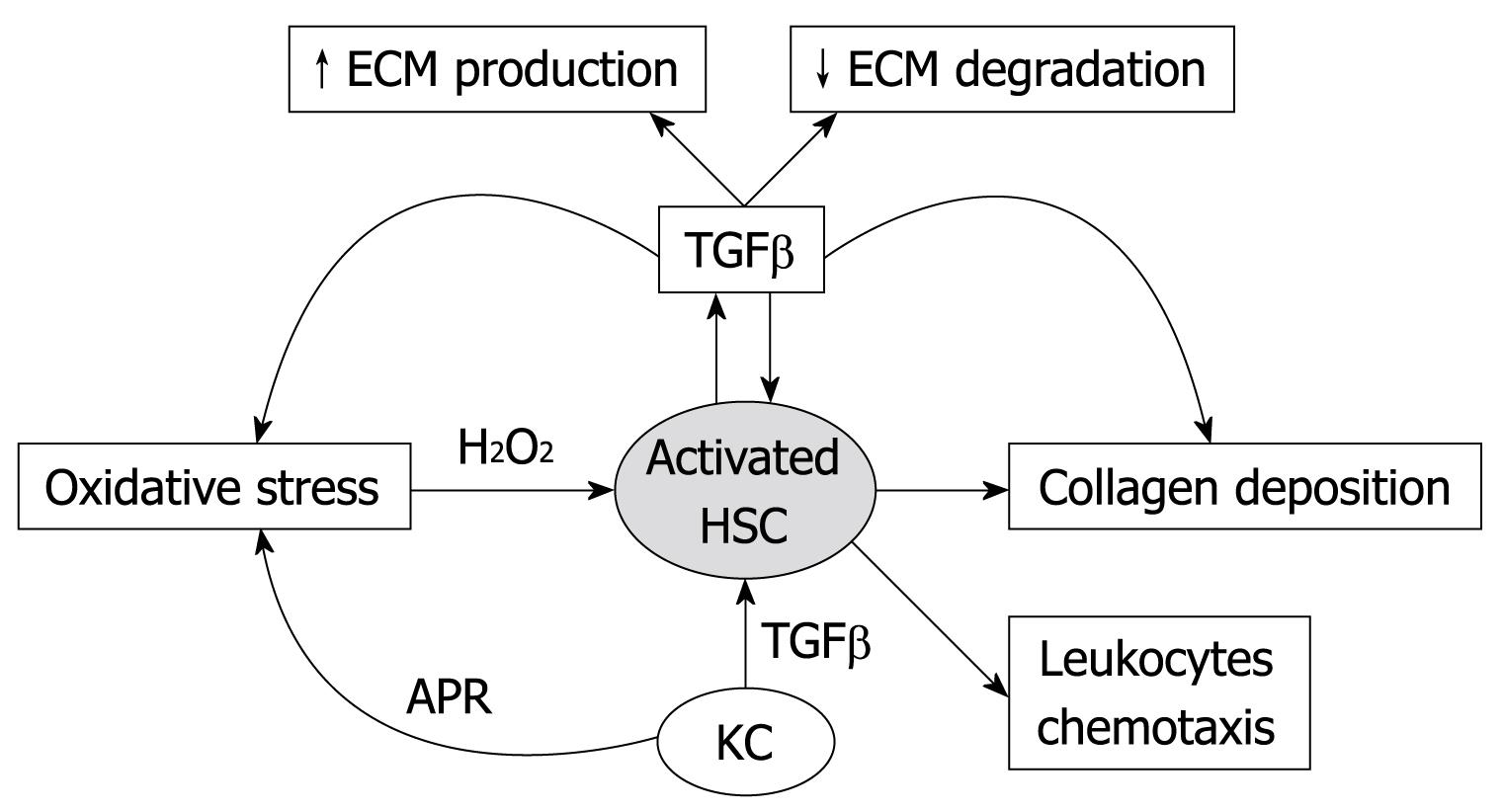
Figure 1 Diagram of activated hepatic stellate cell actions and interactions in liver fibrosis process.
HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; KC: Kupffer cell; APR: Acute phase response; ECM: Extracellular matrix; TGFβ: Transforming growth factor-β.
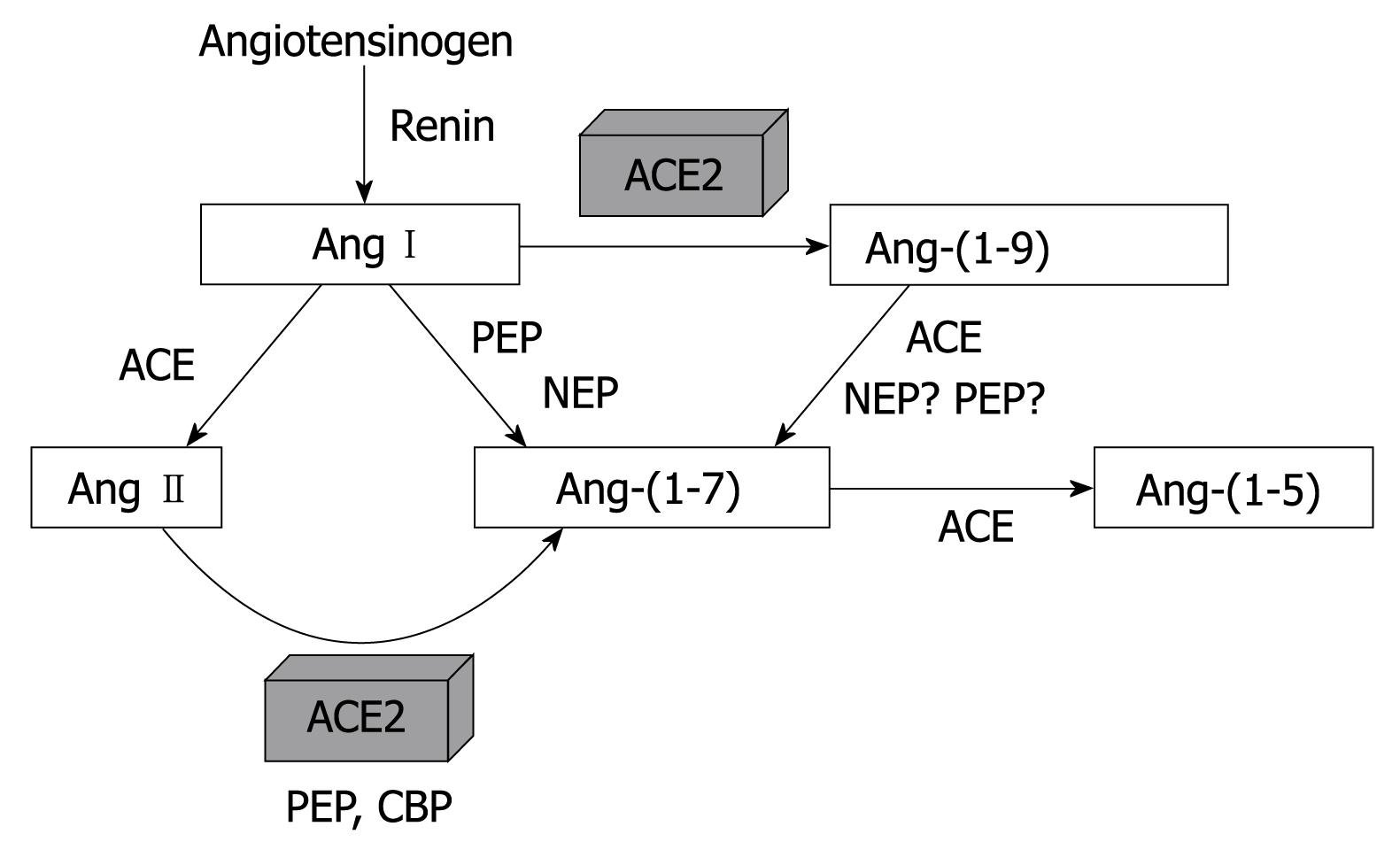
Figure 2 View of the main metabolic pathways of Ang II and Ang-(1-7).
ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2; PEP: Prolyl-endopeptidase; NEP: Neutral endopeptidase; CBP: Carboxypeptidase.
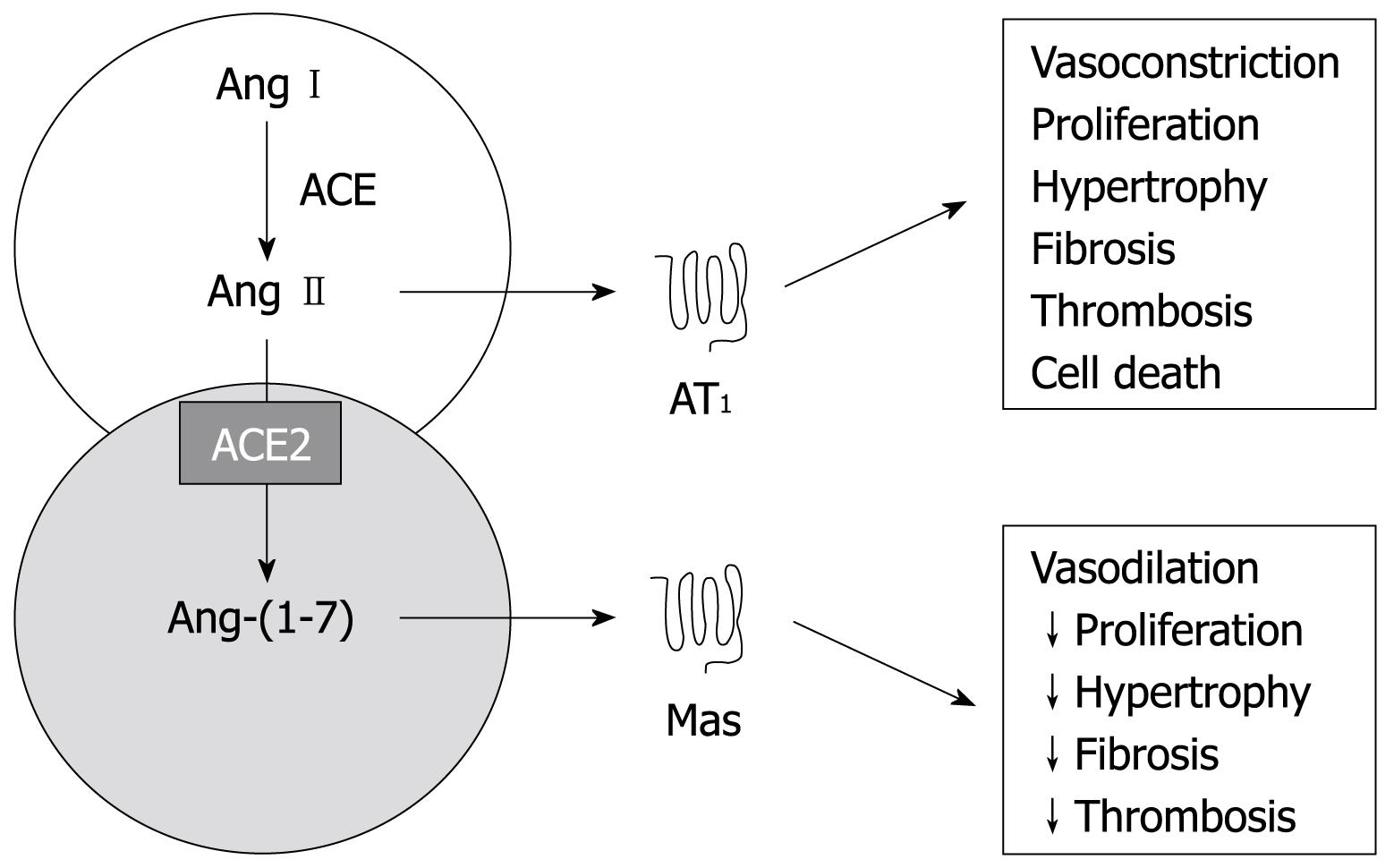
Figure 3 A schematic diagram of both RAS arms.
The counter-regulatory arm of the RAS, ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas axis, produces effects that oppose those of the ACE-Ang II-AT1 receptor axis. Ang: Angiotensin; Mas: G-protein coupled receptor of Ang-(1-7); AT1: Type 1 receptor of Ang II.
- Citation: Pereira RM, Santos RASD, Dias FLDC, Teixeira MM, Silva ACSE. Renin-angiotensin system in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(21): 2579-2586
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i21/2579.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.2579