©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2009; 15(19): 2361-2366
Published online May 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2361
Published online May 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2361
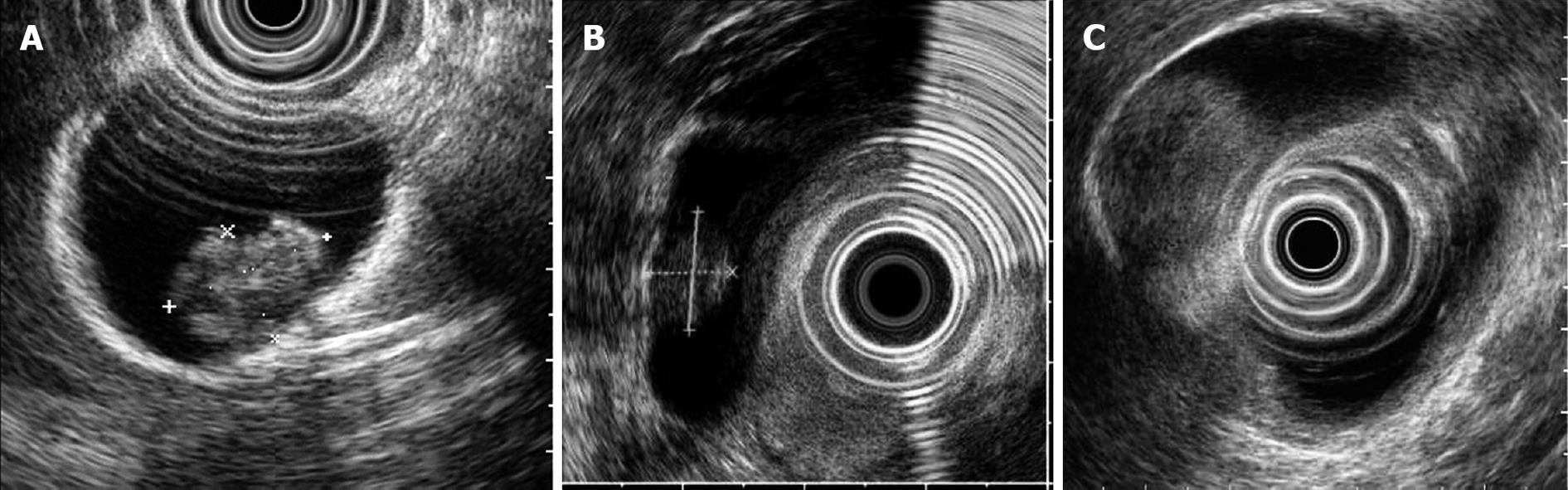
Figure 1 Polypoid lesions of gallbladder.
A: Cholesterol polyp of the gallbladder. EUS shows a 13-mm-diameter, granular-surfaced, pedunculated mass with an internal echo pattern characterized by an aggregation of echogenic spots. Histological examination of the surgical specimen showed a cholesterol polyp; B: Adenoma of the gallbladder. EUS shows a 10-mm-diameter, homogeneously isoechoic, pedunculated mass. The histological diagnosis was tubulovillous adenoma with focal high-grade dysplasia; C: Adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder. EUS shows a 19-mm-diameter, smooth-surfaced, heterogeneously echogenic, pedunculated mass. Histological examination of the surgical specimen showed adenocarcinoma.
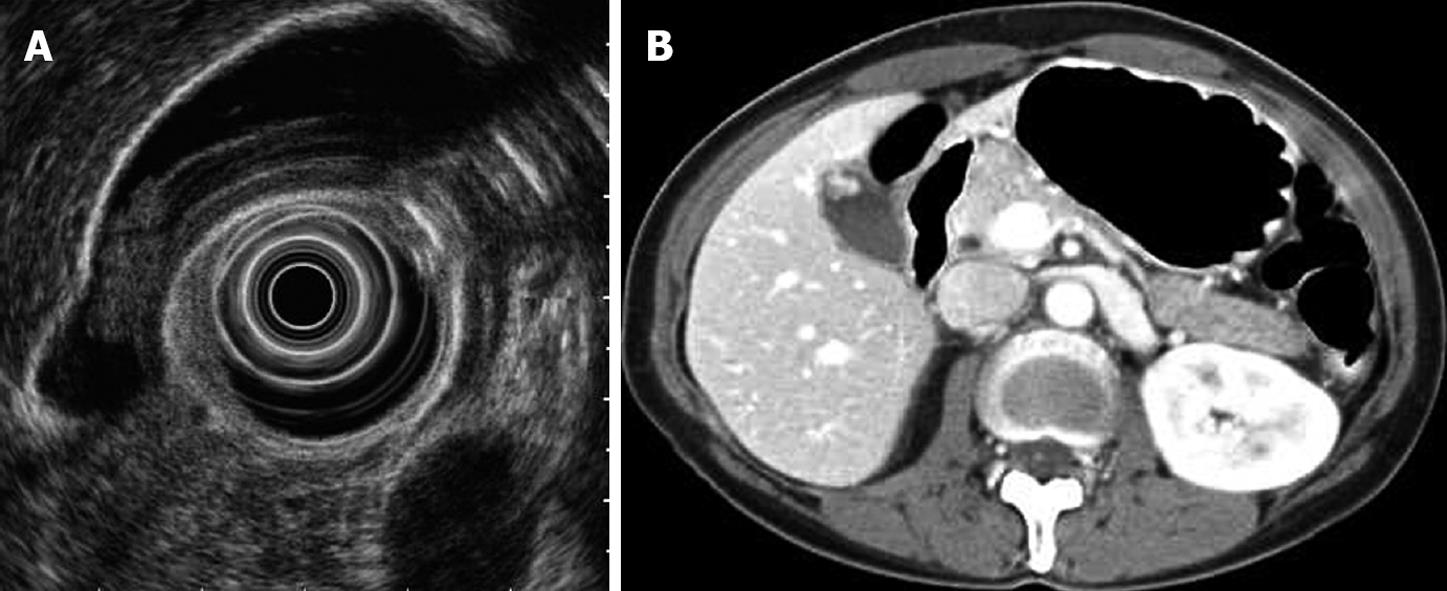
Figure 2 Misjudged case diagnosed as adenoma or carcinoma before surgery.
A: EUS shows a 17.5-mm-diameter, homogeneously isoechoic, pedunculated mass; B: Abdominal CT shows an enhanced polypoid mass of the gallbladder in arterial phase. Histological examination of the surgical specimen showed a cholesterol polyp.
- Citation: Cheon YK, Cho WY, Lee TH, Cho YD, Moon JH, Lee JS, Shim CS. Endoscopic ultrasonography does not differentiate neoplastic from non-neoplastic small gallbladder polyps. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(19): 2361-2366
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i19/2361.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.2361