©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2009; 15(17): 2116-2124
Published online May 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2116
Published online May 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2116
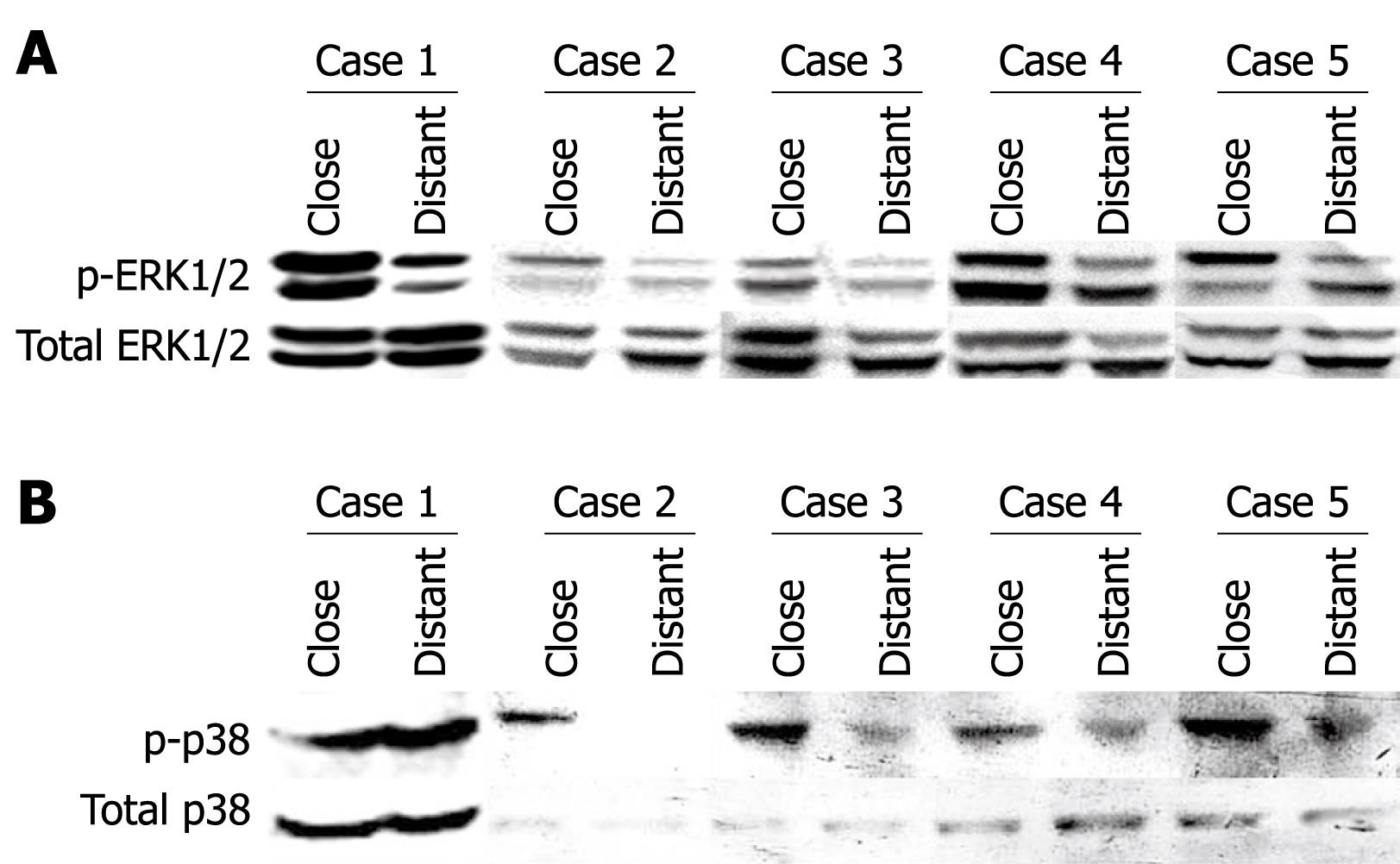
Figure 1 ERK1/2 (A) and p38 (B) activation in liver samples from five AE patients.
Western immunoblot analyses were performed on lysates with antibodies that recognize phosphorylated and total ERK1/2 respectively (A), and phosphorylated- and total p38, respectively (B). Close: Liver samples close to the parasitic lesions in AE patients; Distant: Liver samples distant from the parasitic lesions in AE patients.
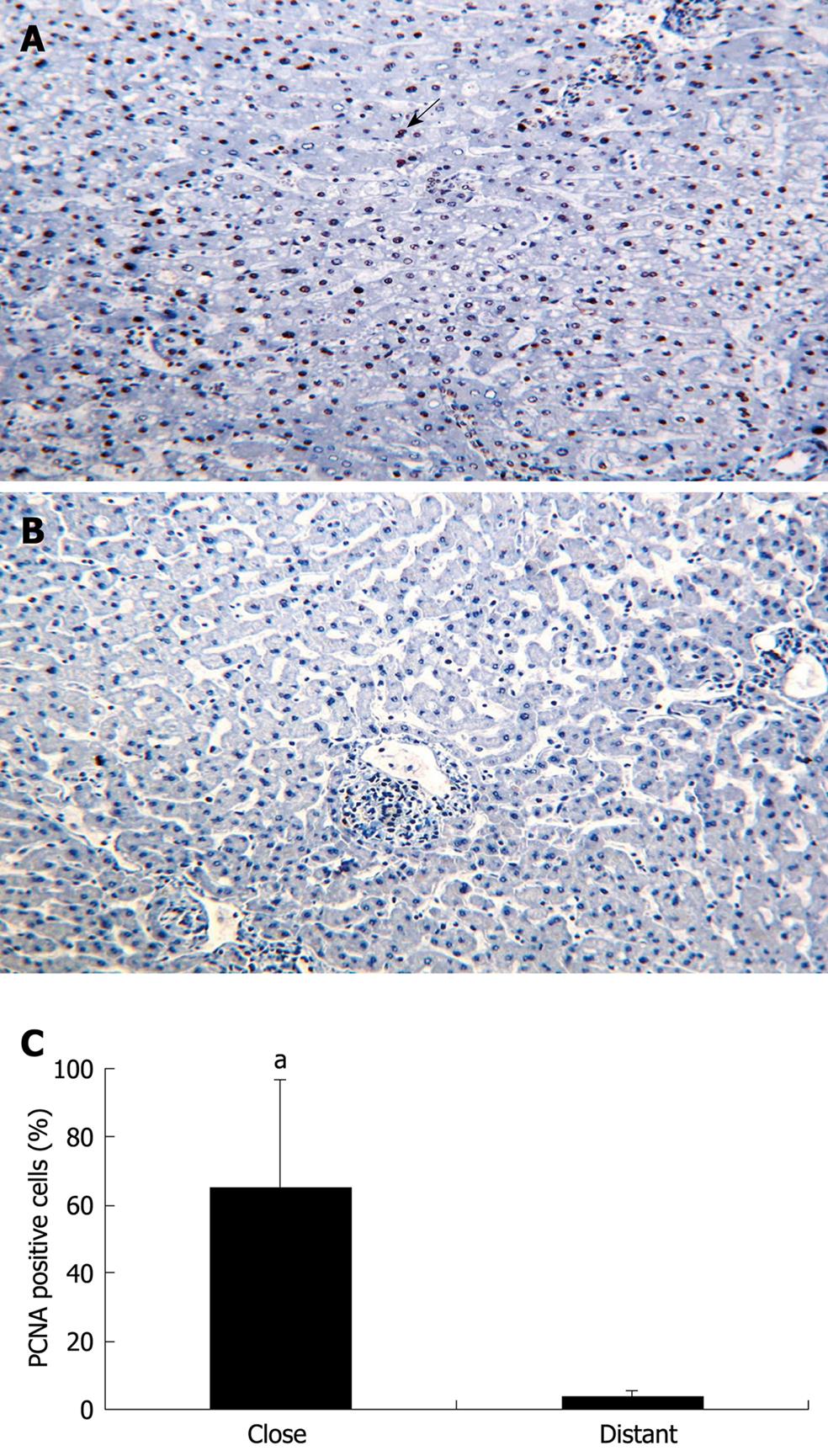
Figure 2 PCNA expression by hepatic cells in the liver from five patients with AE (immunohistochemical analysis).
A: Hepatic cells close to the parasitic lesions were strongly labeled by the anti-PCNA antibody; all cells with a dark-brown/black nucleus are positive cells; some of them indicated by an arrow (initial magnification: × 20); B: Hepatic cells distant from the parasitic lesions did not express PCNA (initial magnification: × 20); C: Quantitative expression of PCNA was significantly higher in the liver cells close to the parasitic lesions than in those distant to them (aP < 0.05).
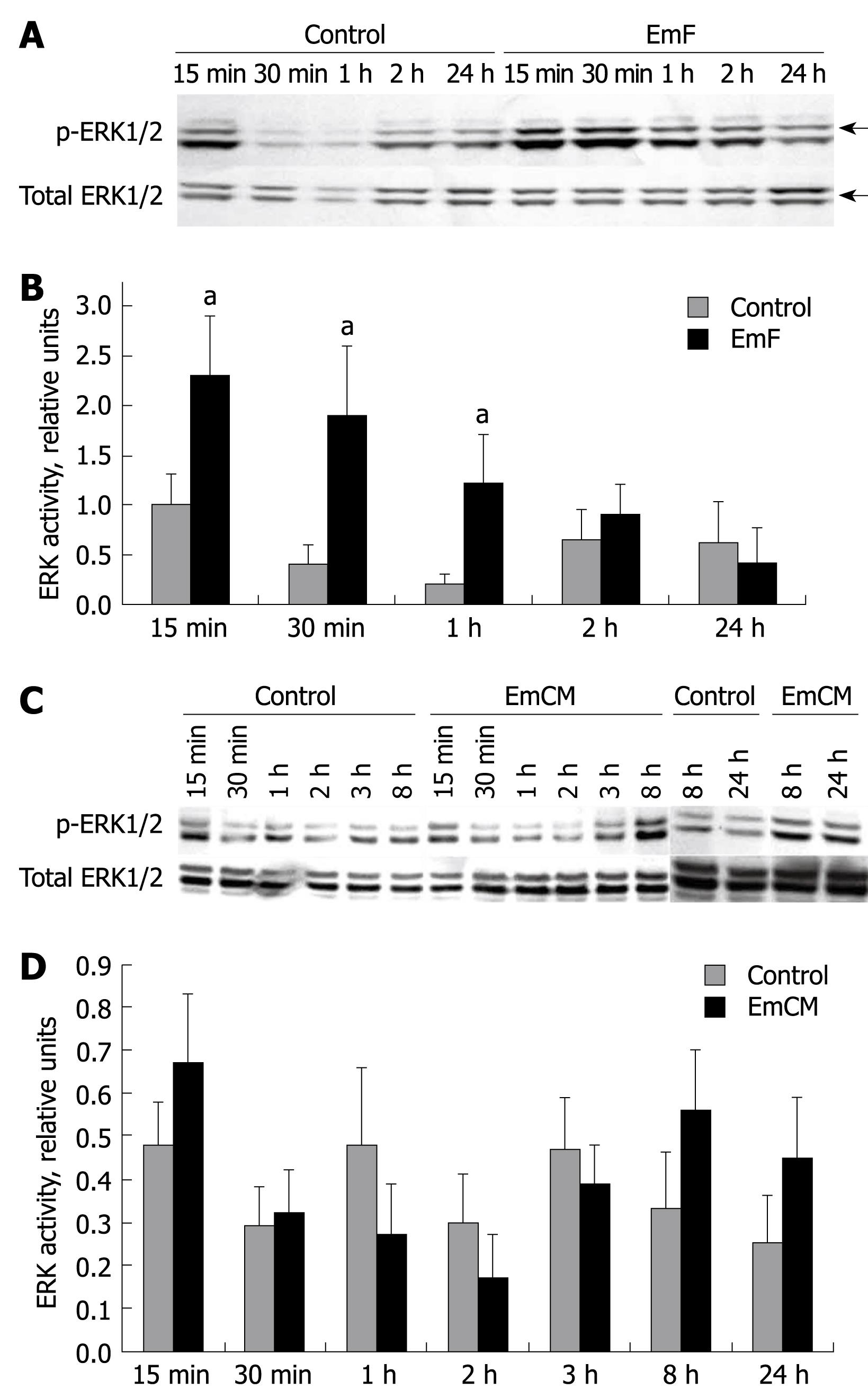
Figure 3 Time course of EmF- or EmCM- induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 kinase.
Primary cultures of rat hepatocytes were stimulated with EmF (A, B) or EmCM (C, D) and harvested at the indicated time points (15 min to 24 h). Western immunoblot analyses were performed on lysates with antibodies that recognize phosphorylated (p-) and total ERK1/2 (A, C), respectively. Relative amount of phosphorylated to total ERK1/2 and ERK1/2 was calculated from semi-quantitative analysis of the Western blotting using densitometry (B, D). aP < 0.05, EmF or EmCM-induced versus control hepatocytes. All experiments were performed three times independently with similar results.
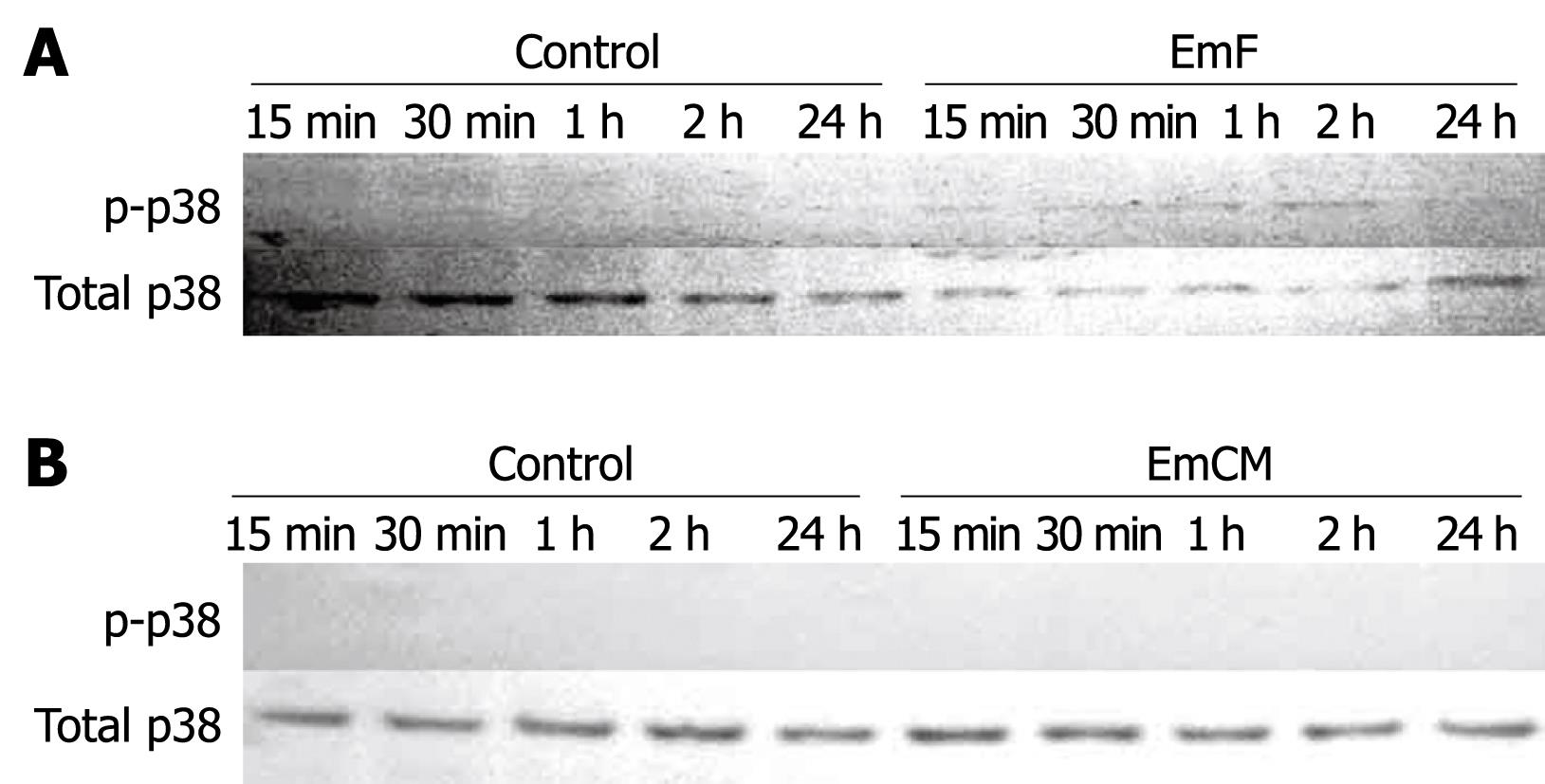
Figure 4 Time course of EmF- or EmCM-induced phosphorylation of p38 kinase.
Primary cultures of rat hepatocytes were stimulated with EmF (A) or EmCM (B) and harvested at the indicated time points (15 min to 24 h). Western immunoblot analyses were performed on lysates with antibodies that recognize phosphorylated (p-) and total p38. All experiments were performed three times independently with similar results.
Figure 5 Time course of EmF- or EmCM-induced phosphorylation of JNK.
Primary cultures of rat hepatocytes were stimulated with EmF (A, B) or EmCM (C, D) and harvested at the indicated time points (15 min to 24 h). Western immunoblot analyses were performed on lysates with antibodies that recognize phosphorylated (p-) and total JNK respectively (A, C). Relative amount of phosphorylated to total JNK was calculated from semi-quantitative analysis of the Western blots using densitometry (B, D). aP < 0.05, EmF or EmCM-induced versus control hepatocytes. All experiments were performed three times independently with similar results.
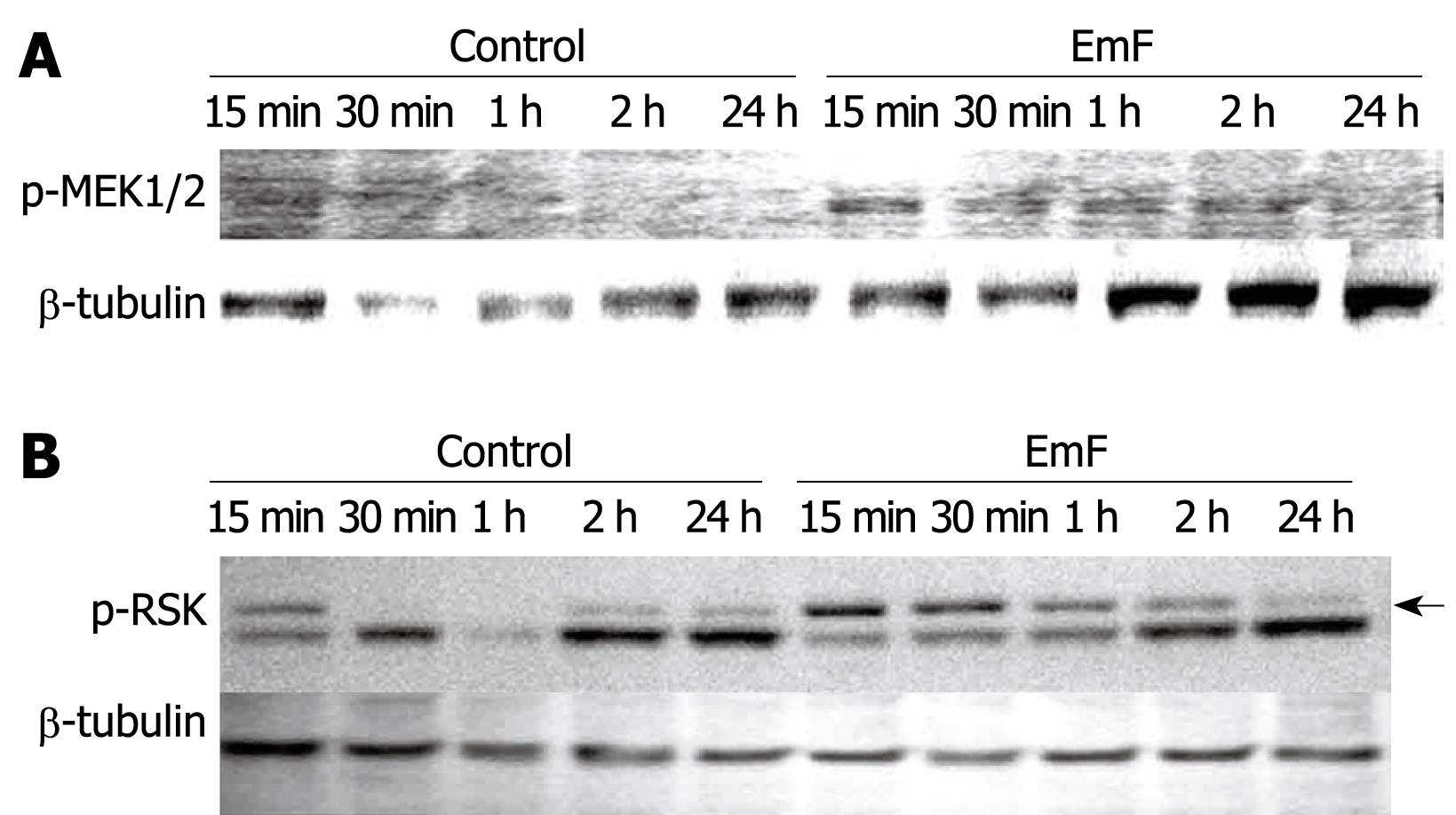
Figure 6 Time course of EmF-induced phosphorylation of MEK1/2 (A) and RSK (B).
Primary cultures of rat hepatocytes were stimulated with EmF and harvested at the indicated time points (15 min to 24 h). Western immunoblot analyses were performed on lysates with antibodies that recognize phosphorylated (p-) MEK1/2 and p-RSK. Protein loading control was performed using β-tubulin. MEK: MAPK/ERK kinase.
-
Citation: Lin RY, Wang JH, Lu XM, Zhou XT, Mantion G, Wen H, Vuitton DA, Richert L. Components of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade are activated in hepatic cells by
Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(17): 2116-2124 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i17/2116.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.2116