©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2009; 15(15): 1901-1903
Published online Apr 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1901
Published online Apr 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1901
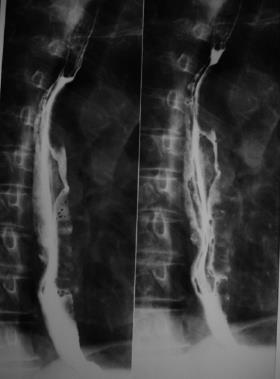
Figure 1 Double-contrast barium swallow, showing enlargement of the mucosal folds and mild dilation of the esophageal lumen below the level of the aortic arch.
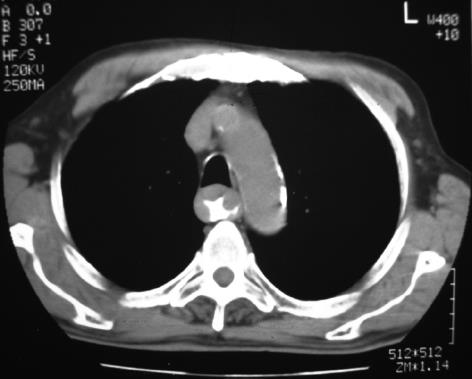
Figure 2 CT of the chest shows marked thickening of the wall of the esophagus from the aortic arch to the gastrointestinal junction.
There was no enlargement of the mediastinal or hilar lymph nodes.
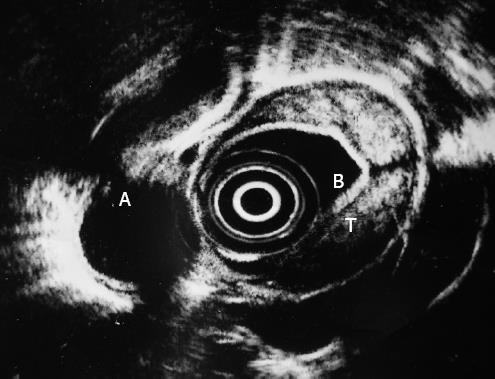
Figure 3 Endoscopic ultrasonography shows a transmural thickening of the esophageal wall and a heterogeneous, mainly hyperechoic, submucosal lesion.
A: Thoracic aorta, B: Water-filled balloon, T: Tumor.
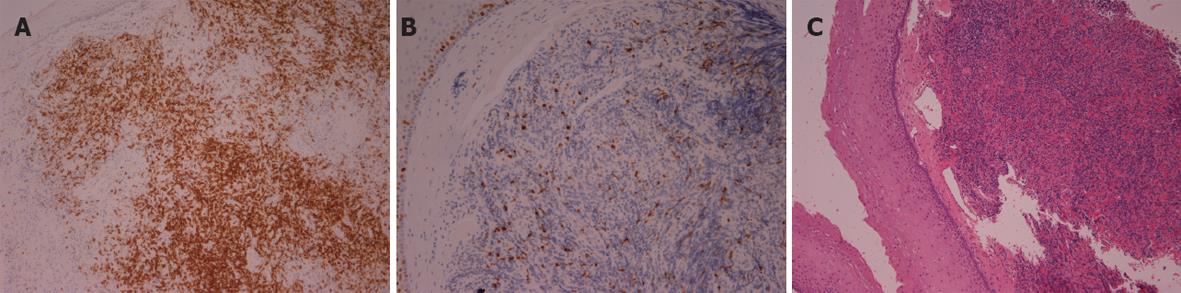
Figure 4 Histologic examination shows the presence of a B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (A) infiltration of the esophageal mucosa by lymphoplasmatoid cells; (B) expression of CD20 antigen by lymphoid cells; (C) Ki-67 antigen (index of proliferation) in lymphoma cells.
- Citation: Kalogeropoulos IV, Chalazonitis AN, Tsolaki S, Laspas F, Ptohis N, Neofytou I, Rontogianni D. A case of primary isolated non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the esophagus in an immunocompetent patient. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(15): 1901-1903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i15/1901.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.1901