©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2009; 15(15): 1869-1875
Published online Apr 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1869
Published online Apr 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1869
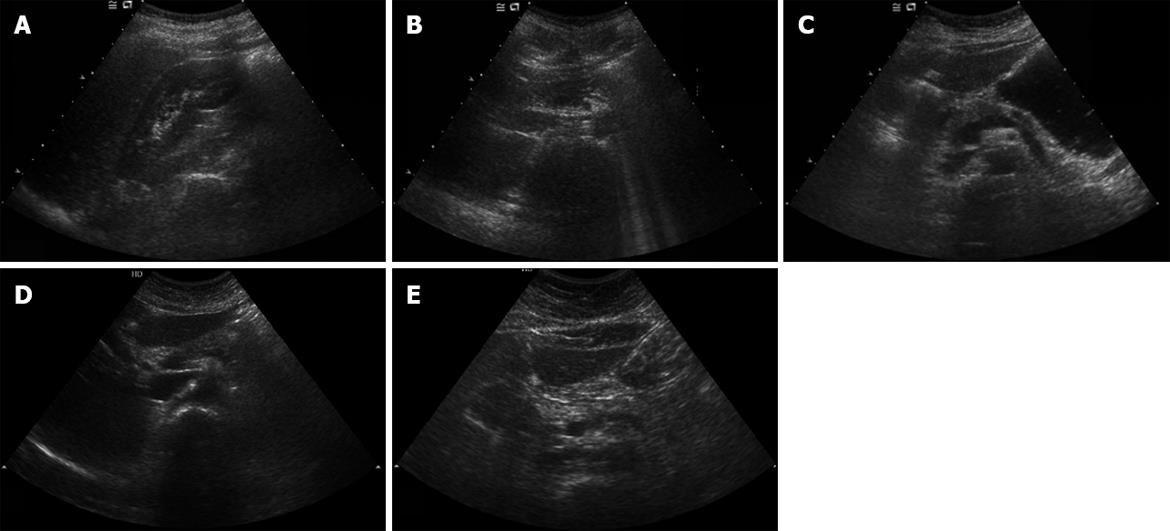
Figure 1 Four echogenicity grades of fatty pancreas.
A and B: Non-fatty pancreas, pancreatic echogenicity is equal to renal cortical echogenicity; C: Mild fatty pancreas, pancreatic echogenicity is definitely lower than retroperitoneal fat; D: Moderate fatty pancreas, pancreatic echogenicity is slightly lower than retroperitoneal fat; E: Severe fatty pancreas, pancreatic echogenicity is equal to retroperitoneal fat.
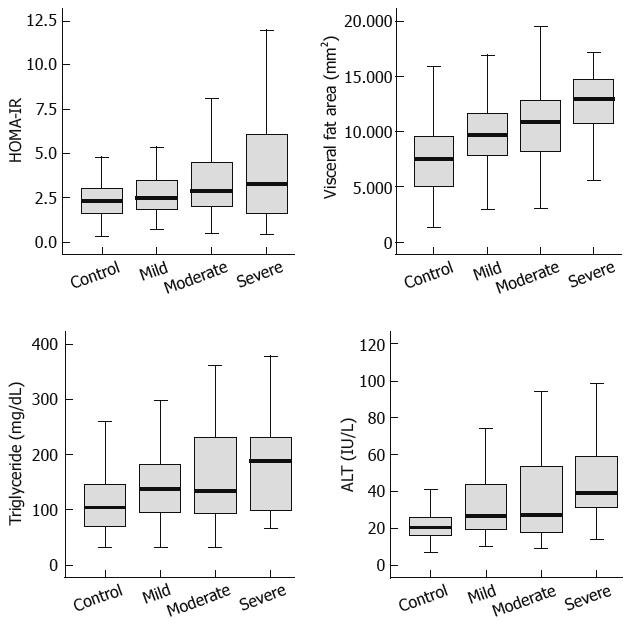
Figure 2 Values of HOMA-IR, visceral fat, triglyceride and ALT in four echogenicity grades of fatty pancreas.
P < 0.05, by ANOVA based on Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
- Citation: Lee JS, Kim SH, Jun DW, Han JH, Jang EC, Park JY, Son BK, Kim SH, Jo YJ, Park YS, Kim YS. Clinical implications of fatty pancreas: Correlations between fatty pancreas and metabolic syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(15): 1869-1875
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i15/1869.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.1869