©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2008; 14(7): 1091-1096
Published online Feb 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1091
Published online Feb 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1091
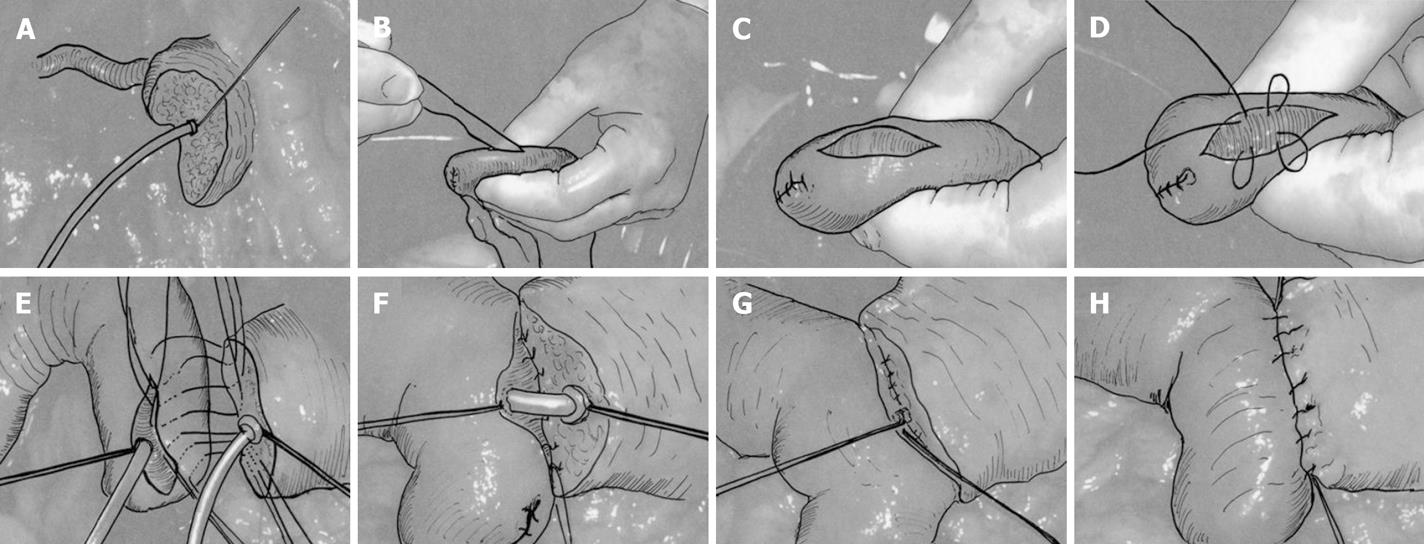
Figure 1 New Duct-to-mucosa contact method.
A: The stent tube was ligated with the pancreatic duct by an irradiated polyglactin 910 suture; B, C, D: The seromuscular layer of the jejunal wall was cut. The submucosa was exposed and a purse-string suture using an irradiated polyglactin 910 suture was performed at the center, where another tip of the stent tube was introduced and ligated by this suture material; E, F, G: After the posterior side of the pancreatic parenchyma was anastomosed to the seromuscular layer of the jejunal wall, two stay sutures of the stent tube were ligated to approximate the pancreatic ductal cut end and the jejunal mucosa; H: The pancreaticojejunostomy was completed by adding an anterior suture to the pancreatic parenchyma and the jejunal wall.
- Citation: Hakamada K, Narumi S, Toyoki Y, Nara M, Ishido K, Miura T, Kubo N, Sasaki M. An easier method for performing a pancreaticojejunostomy for the soft pancreas using a fast-absorbable suture. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(7): 1091-1096
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i7/1091.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.1091