©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2008; 14(41): 6339-6346
Published online Nov 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6339
Published online Nov 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6339
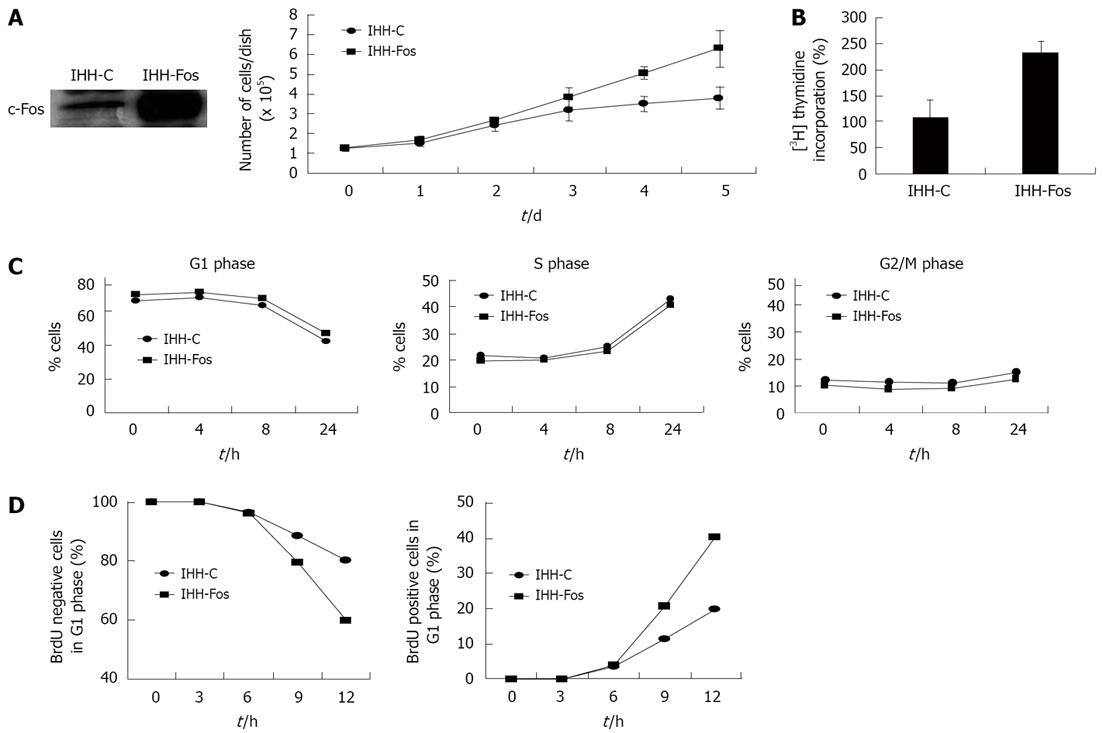
Figure 1 Overexpression of c-Fos accelerates the cell cycle.
A: IHH-C and IHH-Fos were grown in 1% FCS, cultured for 5 d and counted daily. Cell growth was determined by counting the number of attached cells every day. Results are the mean ± SE of three independent experiments; B: [3H] thymidine incorporation into DNA. Non-synchronized IHH-C or IHH-Fos serum starved for 24 h then serum stimulated for 4 h were incubated with [3H] thymidine for 4 h. DNA was extracted as described in materials and methods, and [3H] thymidine incorporation into DNA was assessed by scintillation counting. Results are expressed as percentage of increase of [3H] thymidine incorporation in serum-stimulated cells over that of quiescent cells for each cell population. Results are the mean ± SE of six independent experiments; C: Flow cytometry analysis for quantification of cell cycle phase distribution and progression through cell cycle. IHH-C or IHH-Fos serum starved for 24 h were incubated with BrdU for 1 h and stained with propidium iodide 0, 4, 8 and 24 h after serum stimulation. The percentage of cells in each phase is plotted against time. Results of a representative experiment are shown (out of 3); D: IHH-C or IHH-Fos serum starved for 24 h were serum stimulated for 12 h, BrdU pulsed for 1 h, chased with fresh medium for 0, 3, 6, 9, 12 h, and then stained with propidium iodide. The percentage of BrdU-negative cells in the G1 phase (G1 exit) (left panel) and of the BrdU-positive cells in the G1 phase (G1 entry) (right panel) of the cell cycle is plotted against time. Results are representative of four independent experiments.
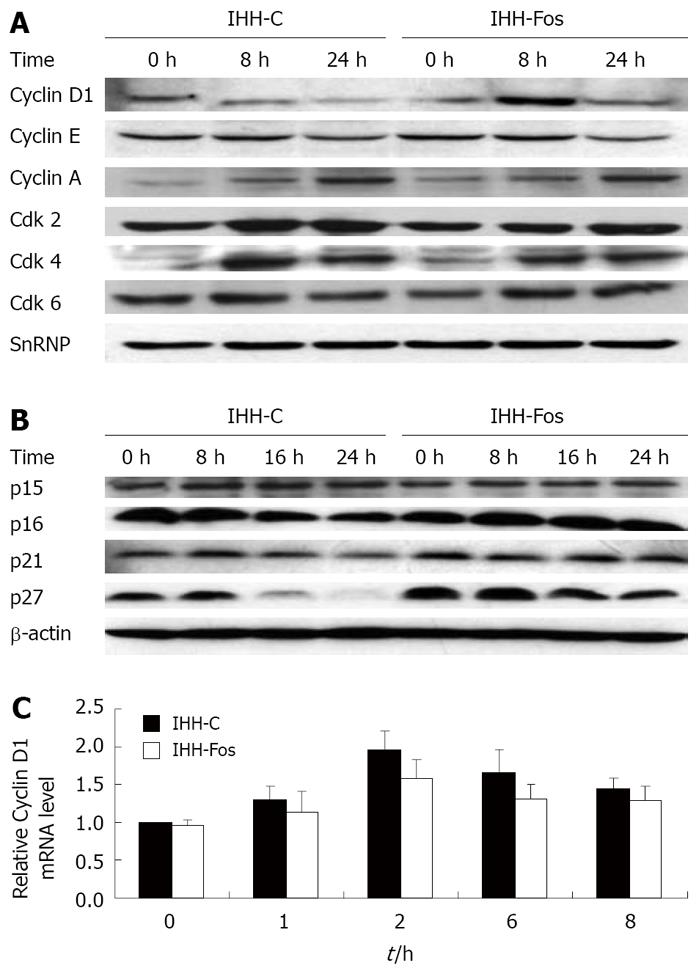
Figure 2 Induction of cell cycle regulatory proteins after serum refeeding.
IHH-C or IHH-Fos were serum starved for 24 h. Nuclear (A) or total (B) extracts prepared before or after serum stimulation for 8 h or 24 h were immunoblotted with antibodies, as indicated. Loading of nuclear or total extracts was normalized using a SnRNP or a β-actin antibody, respectively. Results of a representative experiment are shown (out of 3); C: Quantitative real time PCR of Cyclin D1 mRNA levels in quiescent IHH-C or IHH-Fos serum stimulated for the indicated times. Bars indicate mean ± SE of three independent experiments each performed in triplicate.
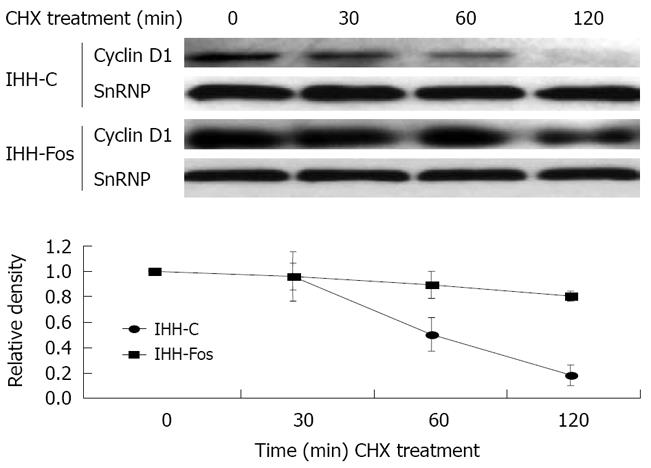
Figure 3 Nuclear Cyclin D1 stability is increased by c-Fos overexpression.
IHH-C or IHH-Fos serum starved for 24 h were serum stimulated for 6 h and then treated with CHX (30 μg/mL) for 30 min, 1 h or 2 h. Nuclear extracts were immunoblotted with an antibody against Cyclin D1, and normalized with a SnRNP antibody, as indicated (Upper panels). The Cyclin D1 over SnRNP ratios were quantified by densitometric analysis of the immunoreactive bands (Lower panel). The results are the mean ± SE of three independent experiments.
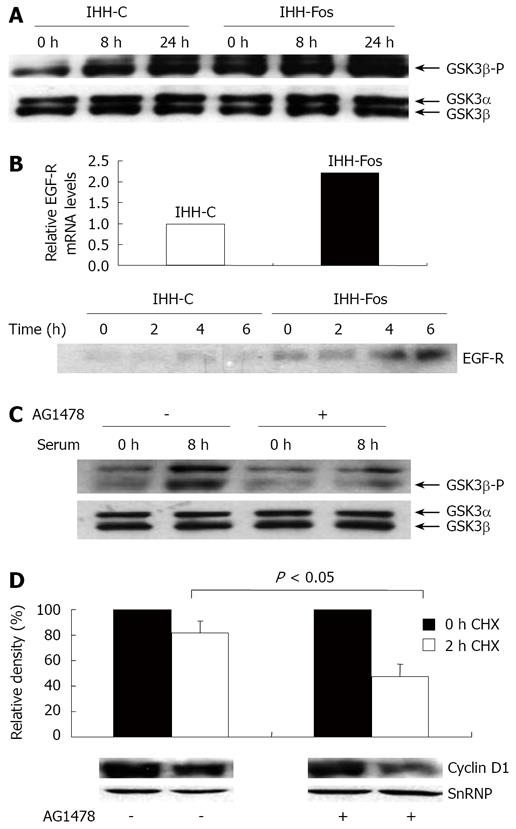
Figure 4 Stimulation of EGF-R signaling by c-Fos overexpression.
A: Total and phosphorylated levels of nuclear GSK-β. IHH-C or IHH-Fos were serum starved for 24 h. Nuclear extracts prepared from unstimulated (0 h), 8 h or 24 h serum stimulated IHH-C or IHH-Fos, were immunoblotted with an antibody against phosphorylated or total GSK3β. B: Upper panel, detection of EGF-R mRNA in IHH-C and IHH-Fos by quantitative real time PCR analysis of mRNA isolated from cells grown in the presence of serum. Lower panel, Western blot analysis of EGF-R in total cell extracts from IHH-C and IHH-Fos cells serum starved for 24 h (0) or stimulated with serum for the indicated times; C: Serum deprived IHH-Fos were pre-treated (+) or not (-) with AG1478 (10 μmol/L) for 1 h. Nuclear proteins were prepared from non stimulated and 8 h serum-stimulated cells. Phosphorylated and total GSK3β levels were detected by Western blot; D: Serum-deprived IHH-Fos were pretreated or not with AG1478 (10 μmol/L) for 1 h, then serum-stimulated for 6 h. Nuclear proteins were extracted before (0 h, filled columns) or after 2 h (empty columns) of CHX treatment (30 µg/mL). Cyclin D1 levels were quantified by Western blotting. The immunoreactive bands were quantified by densitometric analysis after loading normalization of the blot using a SnRNP antibody. The results are expressed as the % of Cyclin D1/SnRNP expression and are the mean ± SE of 3 independent experiments. The lower panel illustrates one representative experiment.
- Citation: Güller M, Toualbi-Abed K, Legrand A, Michel L, Mauviel A, Bernuau D, Daniel F. c-Fos overexpression increases the proliferation of human hepatocytes by stabilizing nuclear Cyclin D1. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(41): 6339-6346
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i41/6339.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6339