©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2008; 14(18): 2872-2876
Published online May 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2872
Published online May 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2872
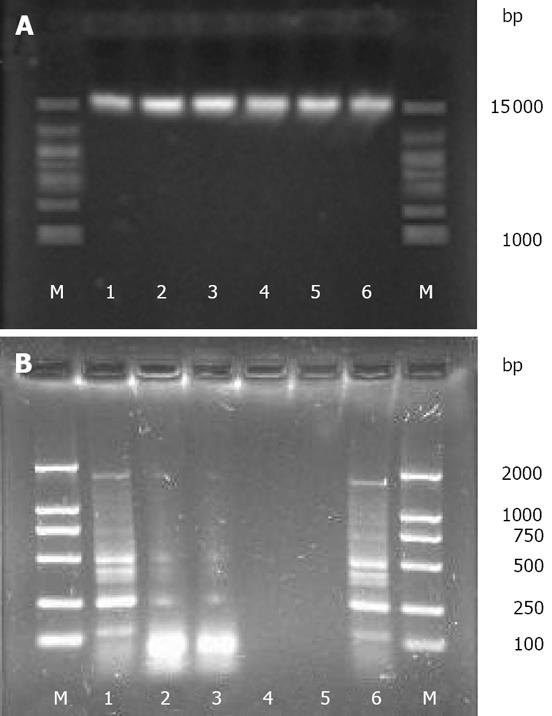
Figure 1 Electrophoresis results with the samples extracted by different methods.
A: The genomic DNA; B: The ERIC-PCR products. M: marker (TIANYI, China, D-15000); 1: C-method; 2: T-method; 3: UW-method; 4: SDS-method; 5: SDSS-method; 6: FDK-method.
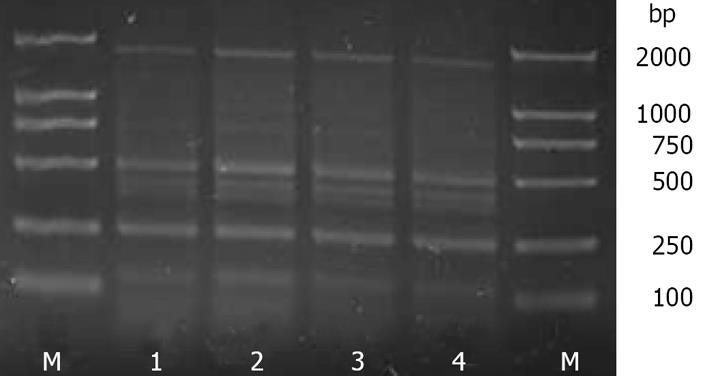
Figure 2 Electrophoresis for ERIC-PCR fingerprint of the samples extracted by C-method and FDK-method.
Lanes: M: marker (TIANYI, China, DL-2000); 1 and 2: C-method; 3 and 4: FDK-method.
- Citation: Yang JL, Wang MS, Cheng AC, Pan KC, Li CF, Deng SX. A simple and rapid method for extracting bacterial DNA from intestinal microflora for ERIC-PCR detection. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(18): 2872-2876
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i18/2872.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.2872