©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2008; 14(10): 1622-1624
Published online Mar 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1622
Published online Mar 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1622
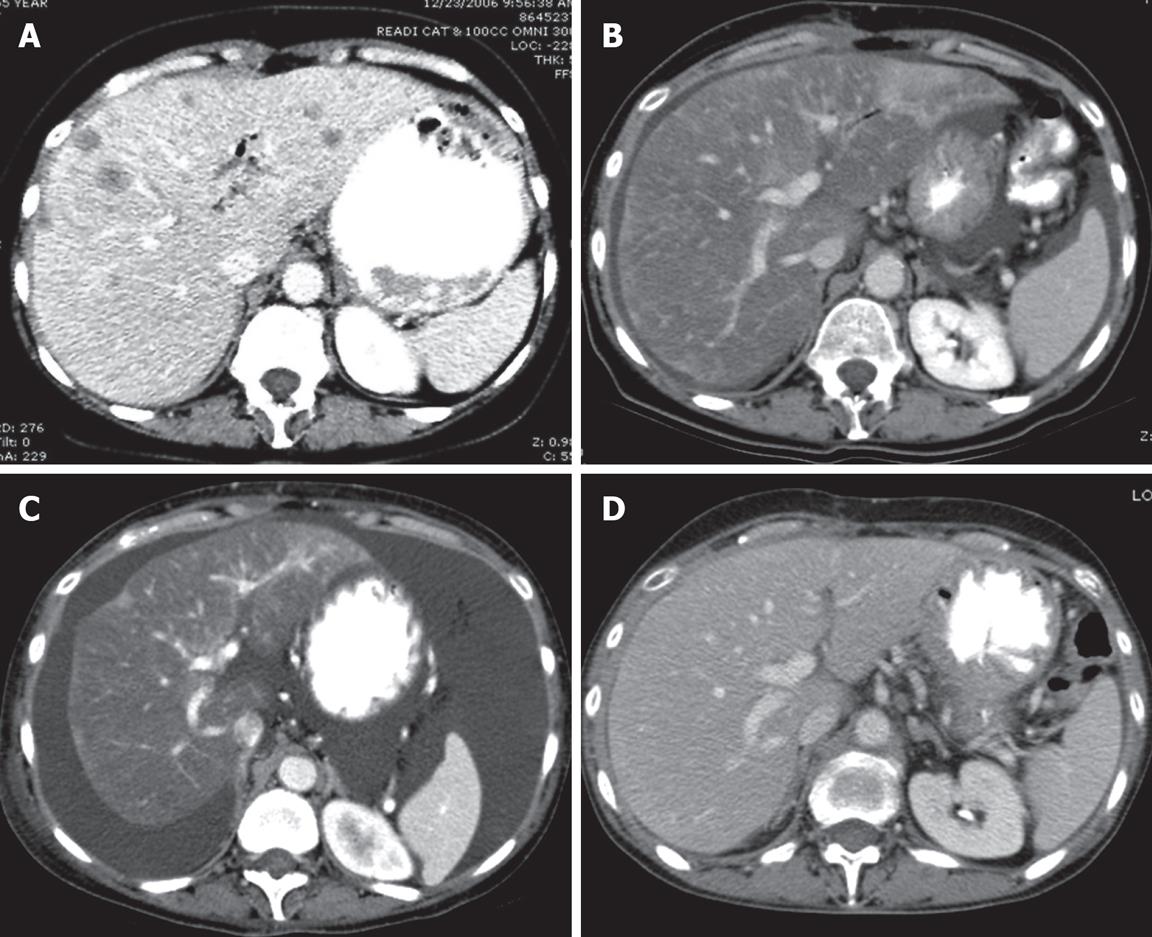
Figure 1 Computed tomography (CT) of the liver.
CT scan is the initial imaging study. A: CT of the liver after contrast enhancement showing numerous liver metastases; B: CT scan 4 mo after initial study showing marked diminution of the metastases and marked fatty infiltration of the liver; C: The liver 2 mo after B showing no evidence of metastasis but findings which simulate cirrhosis with ascites, and irregular contours with retraction. This constellation of CT findings is consistent with a diagnosis of peudocirrhosis; D: CT scan 2 mo after C showing a nearly normal liver and only a trace of ascites present in the pelvis (image not shown).
- Citation: Kang SP, Taddei T, McLennan B, Lacy J. Pseudocirrhosis in a pancreatic cancer patient with liver metastases: A case report of complete resolution of pseudocirrhosis with an early recognition and management. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(10): 1622-1624
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i10/1622.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.1622