©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2007; 13(5): 748-753
Published online Feb 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i5.748
Published online Feb 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i5.748
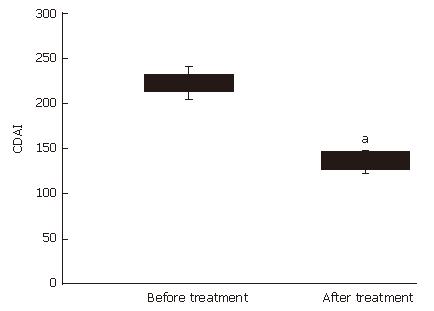
Figure 1 Crohn’s disease activity index (CDAI) was decreased in patients with active Crohn’s disease (n = 10) after 4-wk treatment with mastic caps (aP < 0.
05). Horizontal bars represent the mean value (± SE).
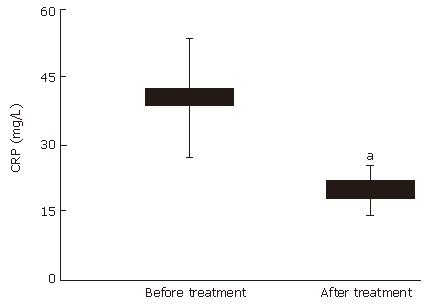
Figure 2 C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations in patients with active Crohn’s disease (n = 10) before and after 4-wk treatment with mastic caps (aP < 0.
05). Horizontal bars represent the mean value (± SE).
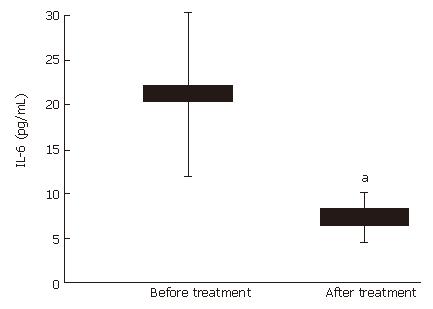
Figure 3 Plasma concentrations of interleukin-6 (IL-6) were suppressed in patients with active Crohn’s disease (n = 10) after 4-wk treatment with mastic caps (aP < 0.
05). Horizontal bars represent the mean value (± SE).
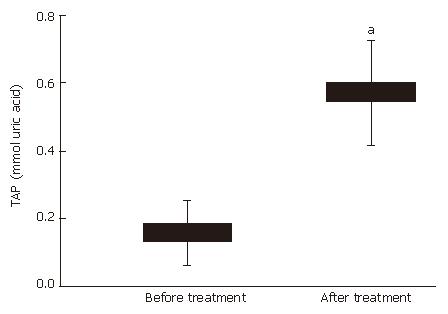
Figure 4 Plasma total antioxidant potential (TAP) was upregulated in patients with active Crohn’s disease (n = 10) after 4-wk treatment with mastic caps (aP < 0.
05), indicating absorption of antioxidants and an improved in vivo antioxidant status. Horizontal bars represent the mean value (± SE).
- Citation: Kaliora AC, Stathopoulou MG, Triantafillidis JK, Dedoussis GV, Andrikopoulos NK. Chios mastic treatment of patients with active Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(5): 748-753
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i5/748.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i5.748