©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2007; 13(5): 699-708
Published online Feb 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i5.699
Published online Feb 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i5.699
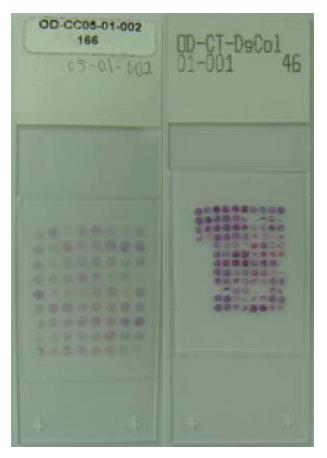
Figure 1 HE staining of 4-μm thick section of the tissue microarray.
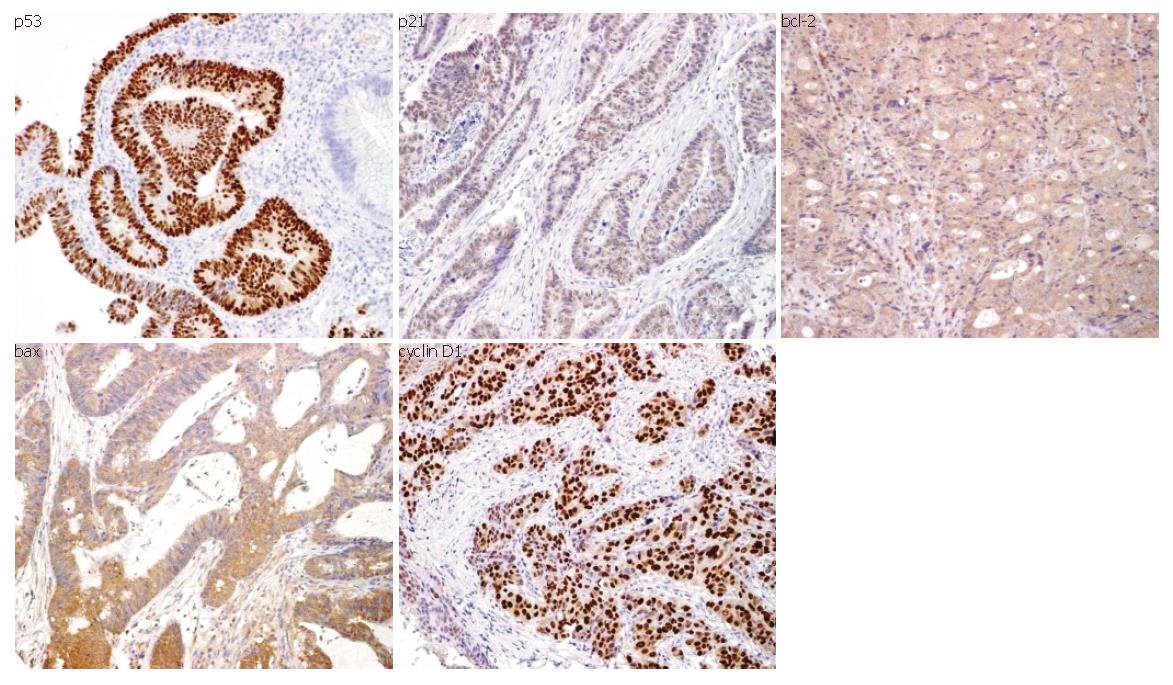
Figure 2 Immunophenotype of the investigated antigens (p53, p21, cyclin D1, bcl-2 and bax) in colon cancer (original magnification x 200).
Positive stainings of p53, p21 and cyclin D1 were located in the cell nuclei, while those of bcl-2 and bax were in the cytoplasm.
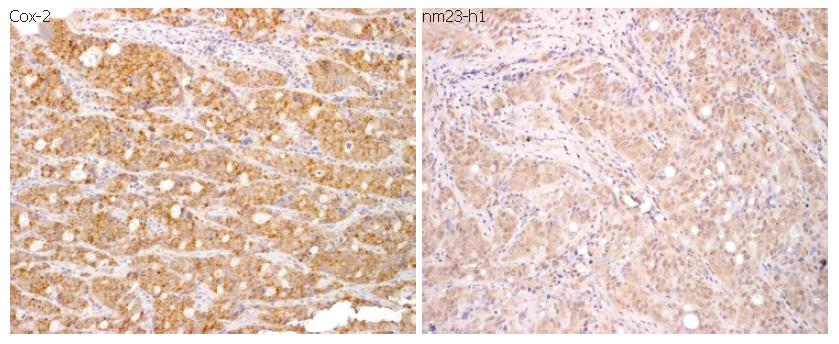
Figure 3 Immunophenotype of the investigated antigens (Cox-2 and nm23-h1) in colon cancer (original magnification x 200).
The protein expressions of Cox-2 and nm23-h1 were detected in the cytoplasm.
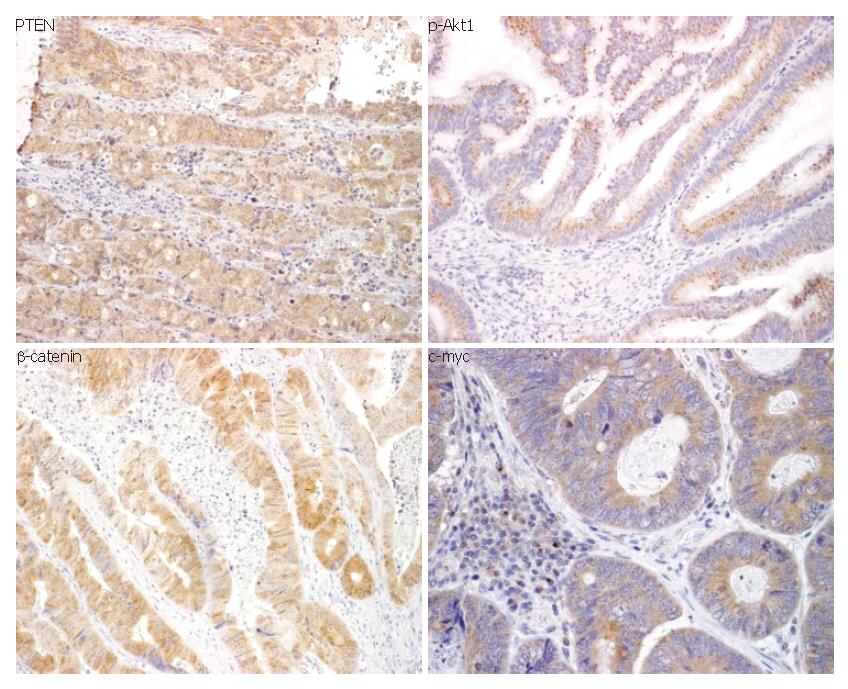
Figure 4 Immunophenotype of the investigated antigens (PTEN, p-Akt1, β-catenin and c-myc) in colon cancer (original magnification x 200).
Expressions of PTEN, p-Akt1, β-catenin and c-myc were detected in the cell cytoplasm.
- Citation: Chen WC, Lin MS, Zhang BF, Fang J, Zhou Q, Hu Y, Gao HJ. Survey of molecular profiling during human colon cancer development and progression by immunohistochemical staining on tissue microarray. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(5): 699-708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i5/699.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i5.699