©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2007; 13(48): 6478-6491
Published online Dec 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i48.6478
Published online Dec 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i48.6478
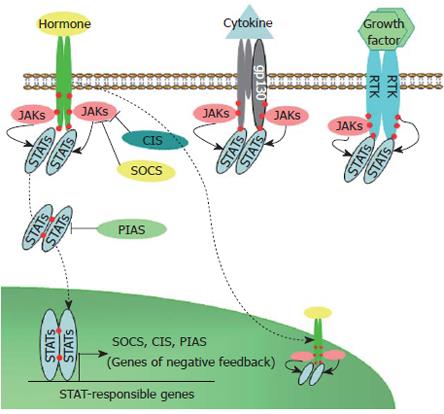
Figure 1 Schematic representation of JAK-STAT signaling induced by hormones, cytokines, and growth factors.
RTK: Receptors tyrosine kinases; JAK: Jannus kinase; STA: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; SOCS: Suppressor of cytokine signaling; CIS: Cytokine induced suppressor; PIAS: Protein inhibitors of activated STATs. Solid arrows - phosphorylation; Dashed arrows - nuclear translocation; Blunt arrows - inhibition; Red circles - phosphorylated tyrosines.
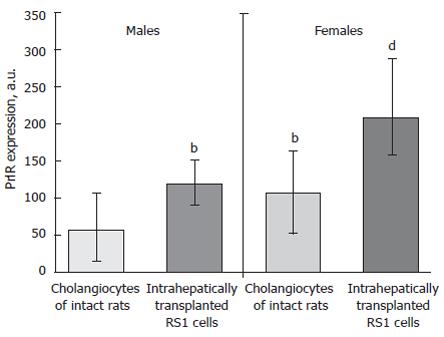
Figure 2 Increasing of prolactin receptor expression in rat liver transplanted RS-1 cholangiocarcinoma cell line.
a.u, arbitrary units of intensity of PrlR expression. Medians, upper and lower quartiles. bP < 0.001, vs intact males, dP < 0.001, vs intact females.
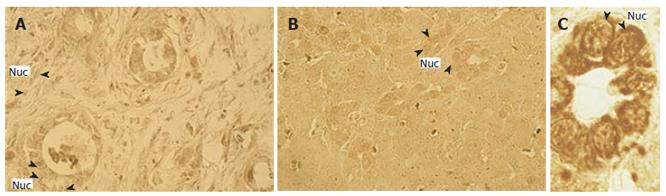
Figure 3 Immunohistochemistry for prolactin receptor (PrlR) expression in human cholangiocarcinoma sample (A) and in female (B) and male (C) rat liver tissue 14 d after common bile duct ligation.
Intensive nuclear (Nuc), PrlR-posititive immunoreactivity is shown. Orig. mag, A, B: x 40; C: x 100.
- Citation: Smirnova OV, Ostroukhova TY, Bogorad RL. JAK-STAT pathway in carcinogenesis: Is it relevant to cholangiocarcinoma progression. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(48): 6478-6491
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i48/6478.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i48.6478