Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2007; 13(42): 5618-5628
Published online Nov 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i42.5618
Published online Nov 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i42.5618
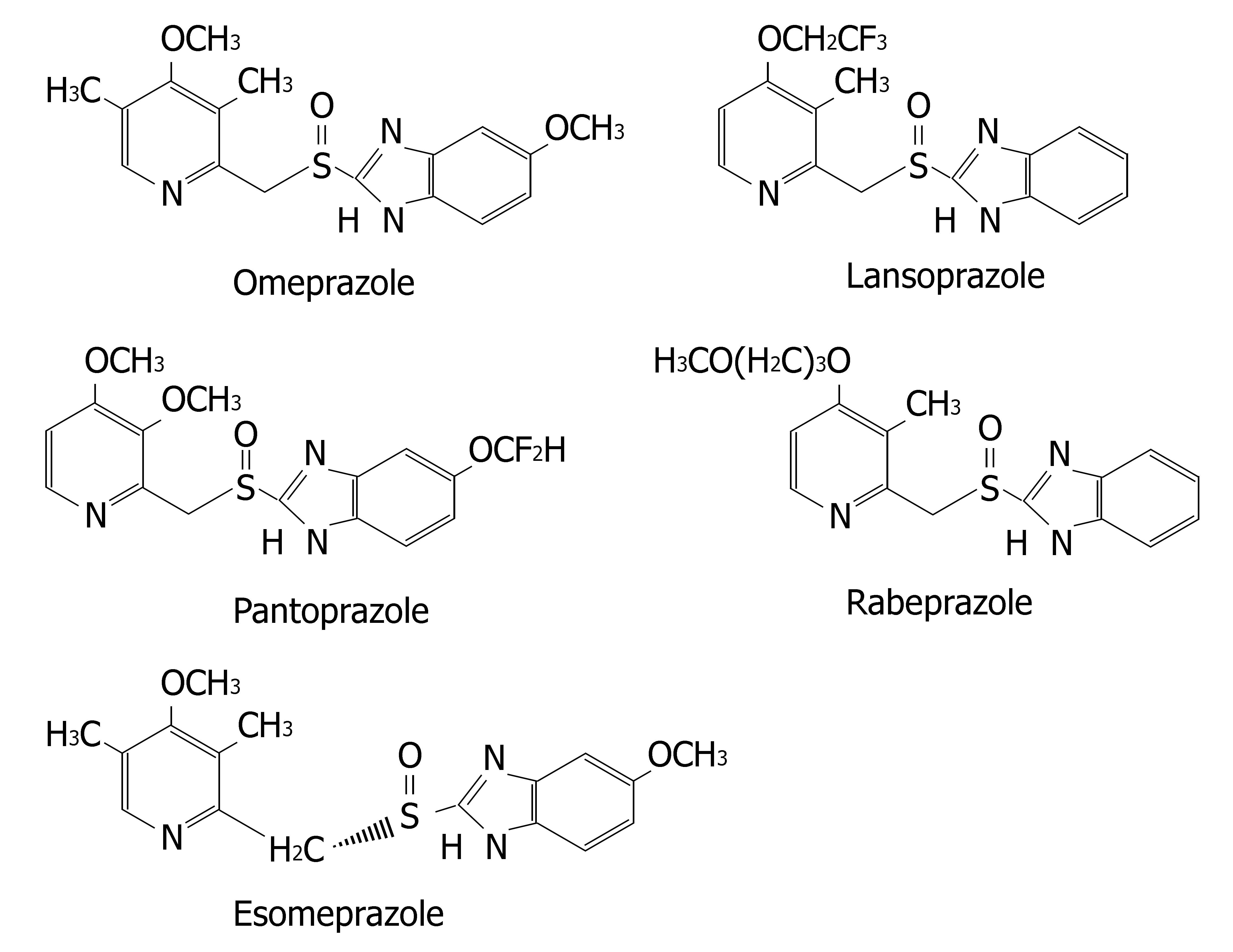
Figure 1 Chemical structures of five PPIs.
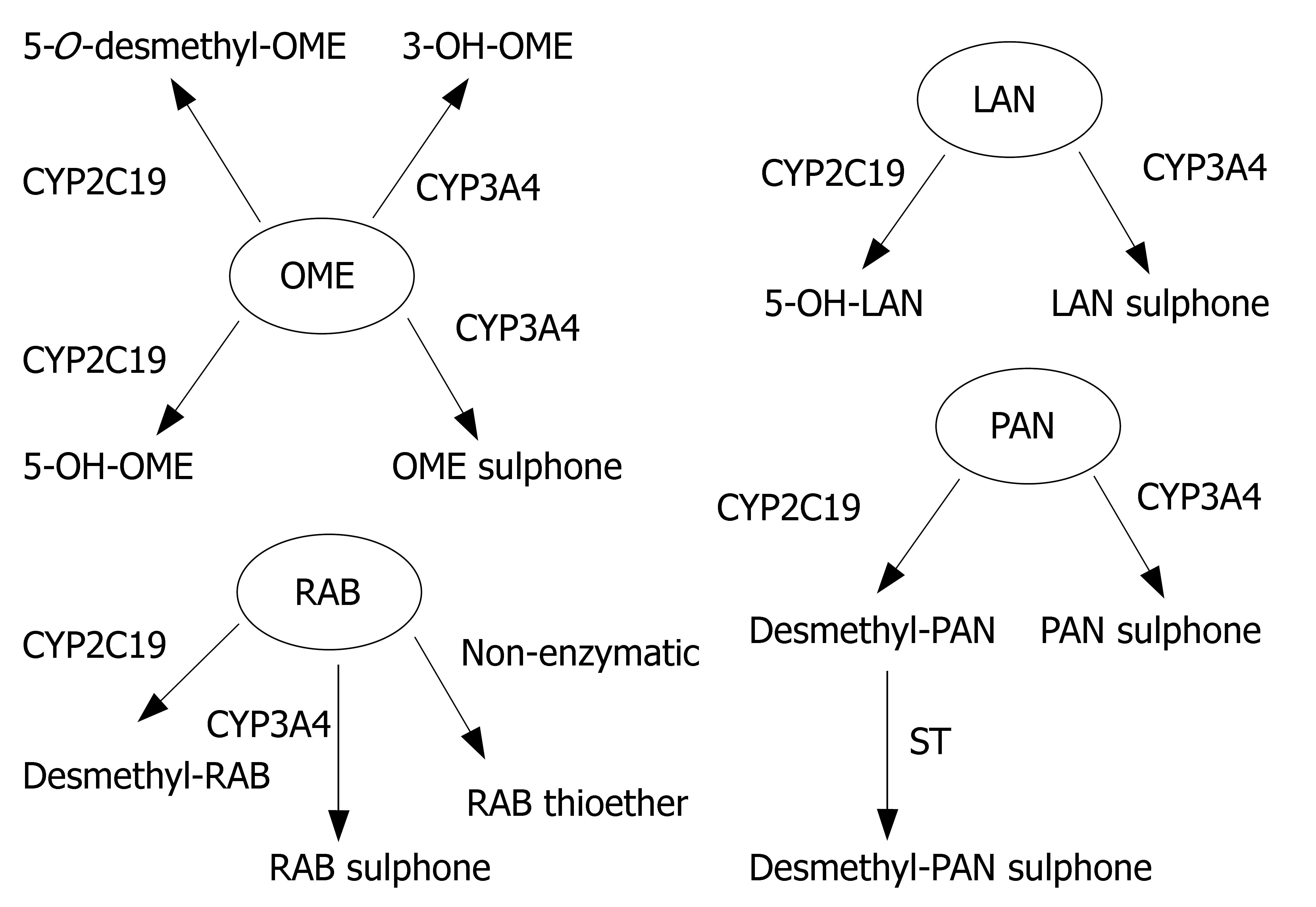
Figure 2 Metabolic differences between four PPIs (OME: omeprazole; LAN: lansoprazole; RAB: rabeprazole; PAN: Pantoprazole).
Arrow thickness represents relative contribution to metabolism.
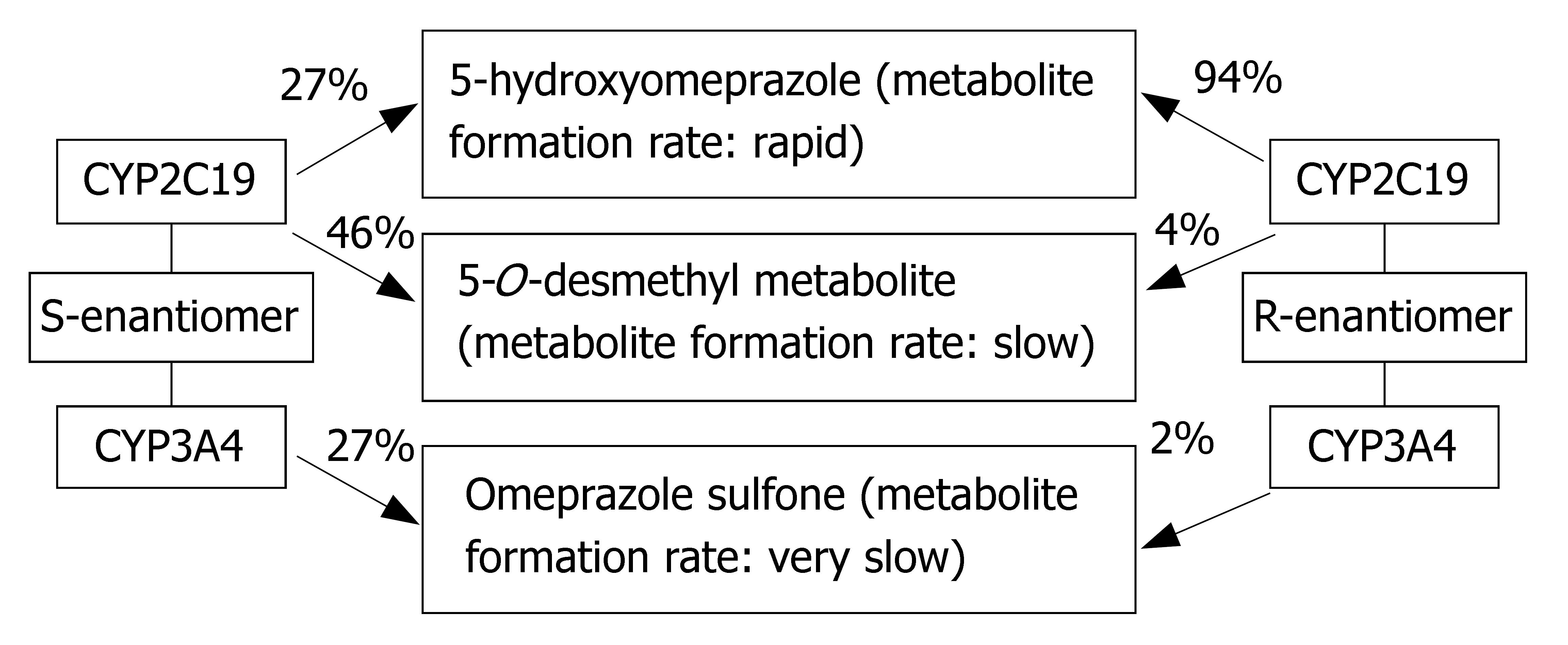
Figure 3 Stereoselective metabolism of omprazole in human.
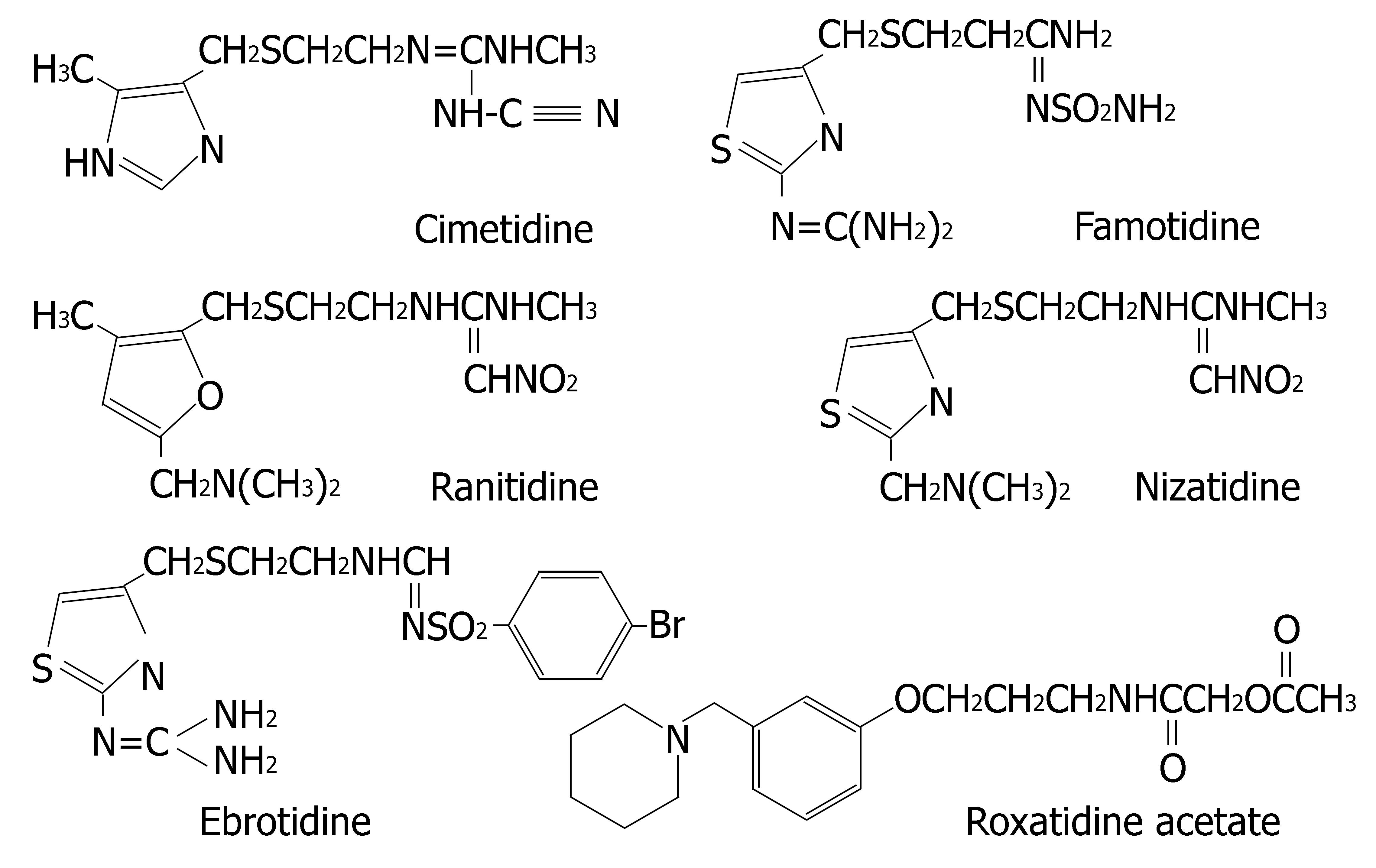
Figure 4 Chemical structures of six H2-receptor antagonists.
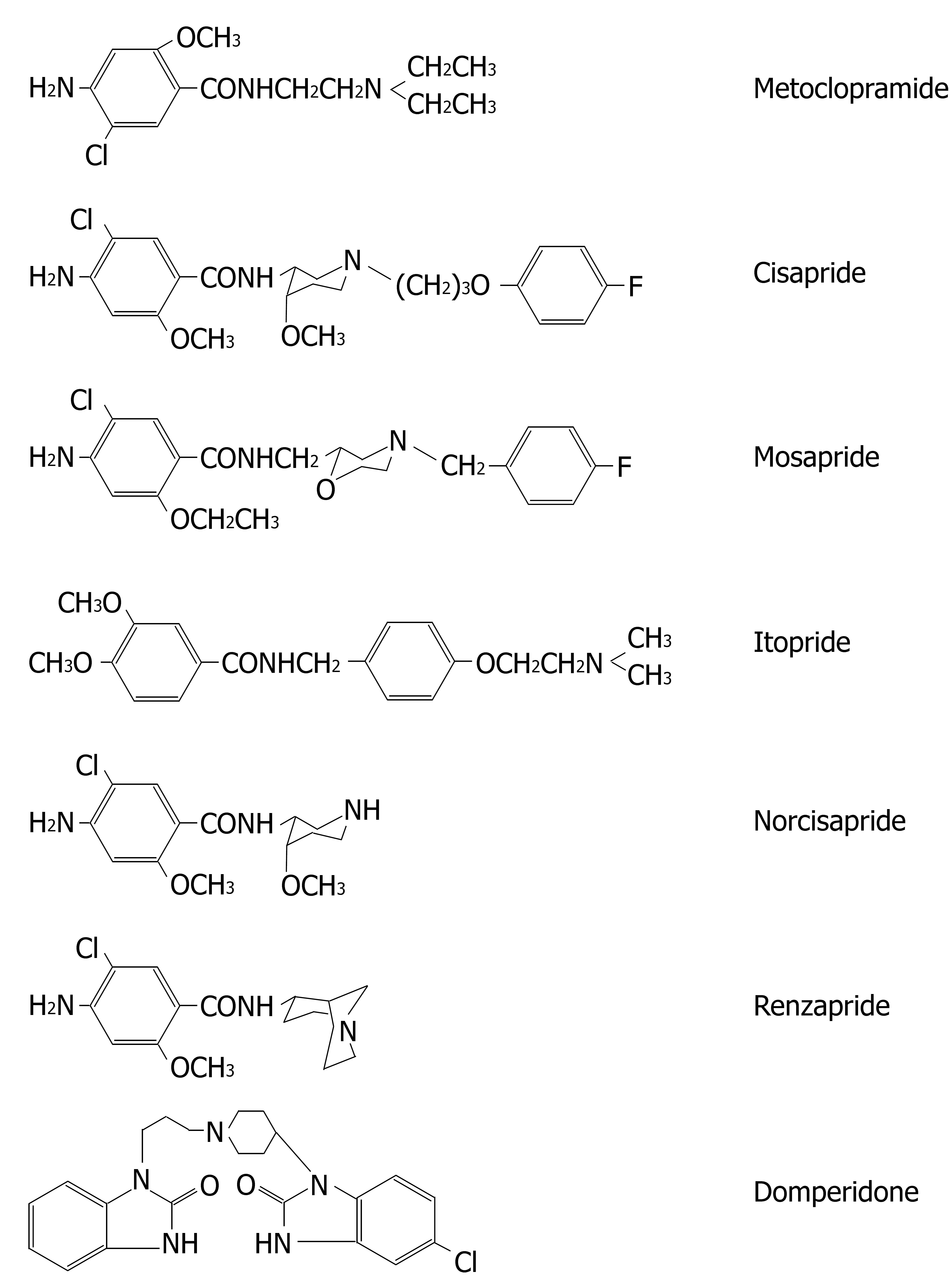
Figure 5 Chemical structures of seven benzamide-type gastroprokinetic agents.
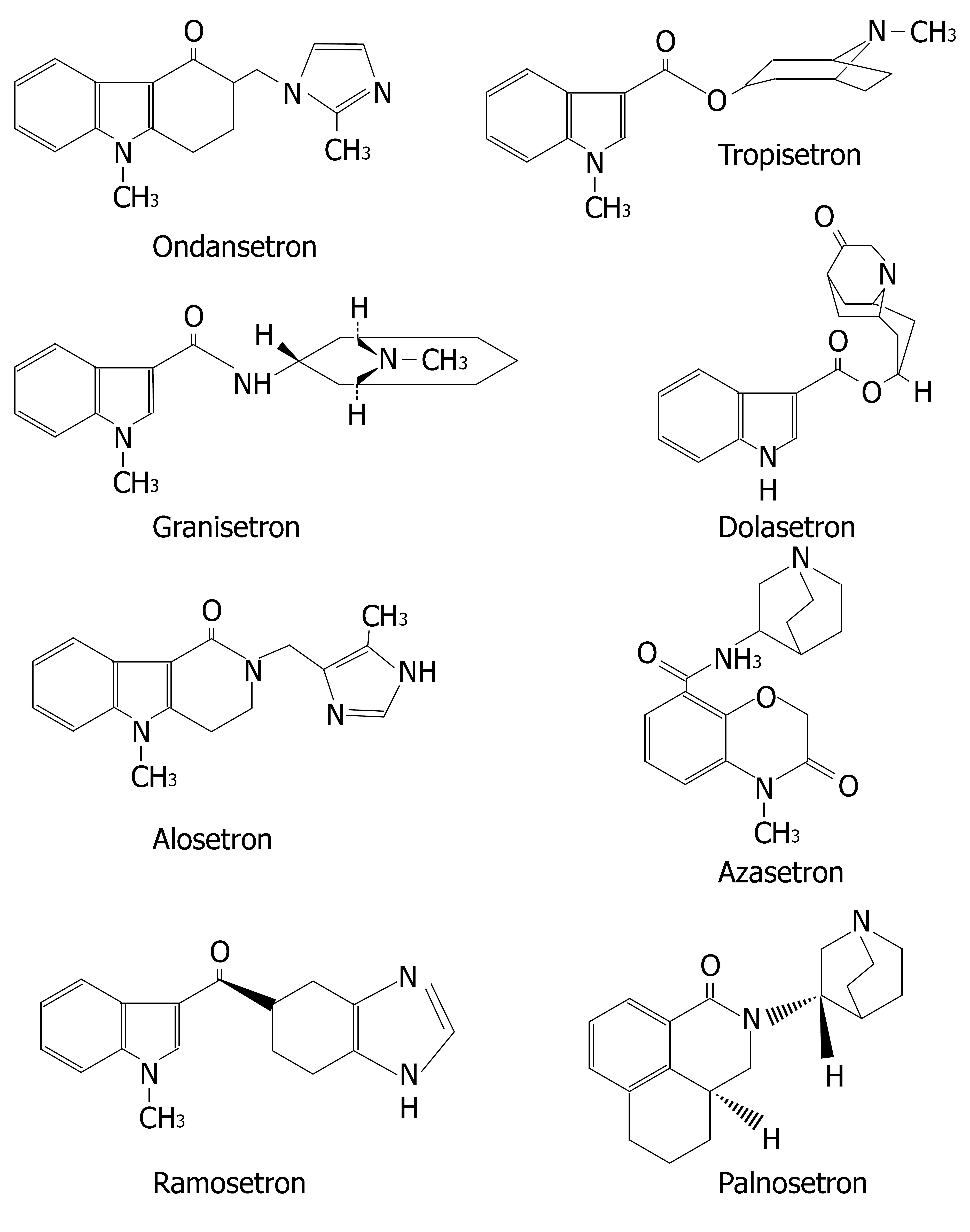
Figure 6 Chemical structures of eight setrons.
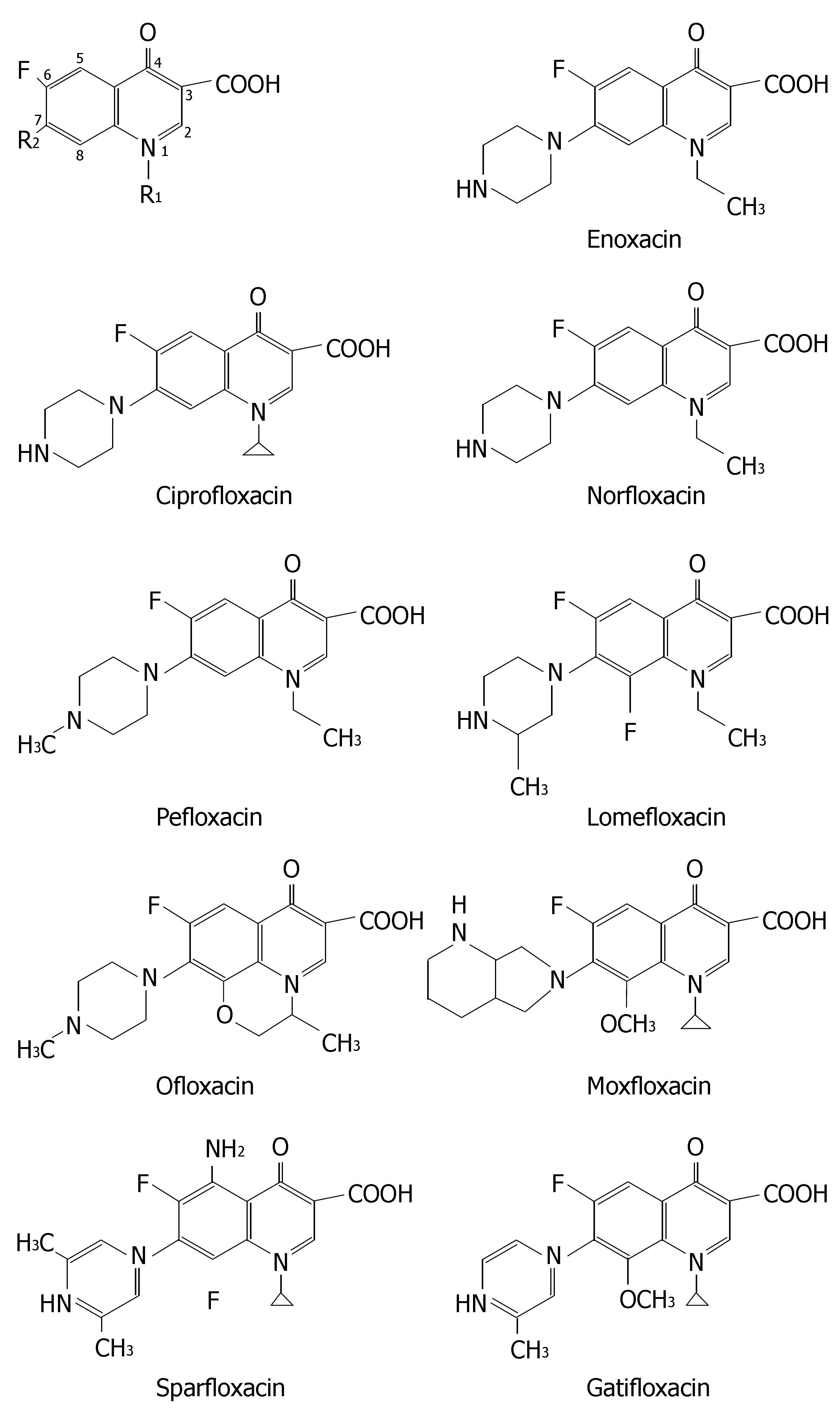
Figure 7 Chemical structures of nine fluoroquinolones.
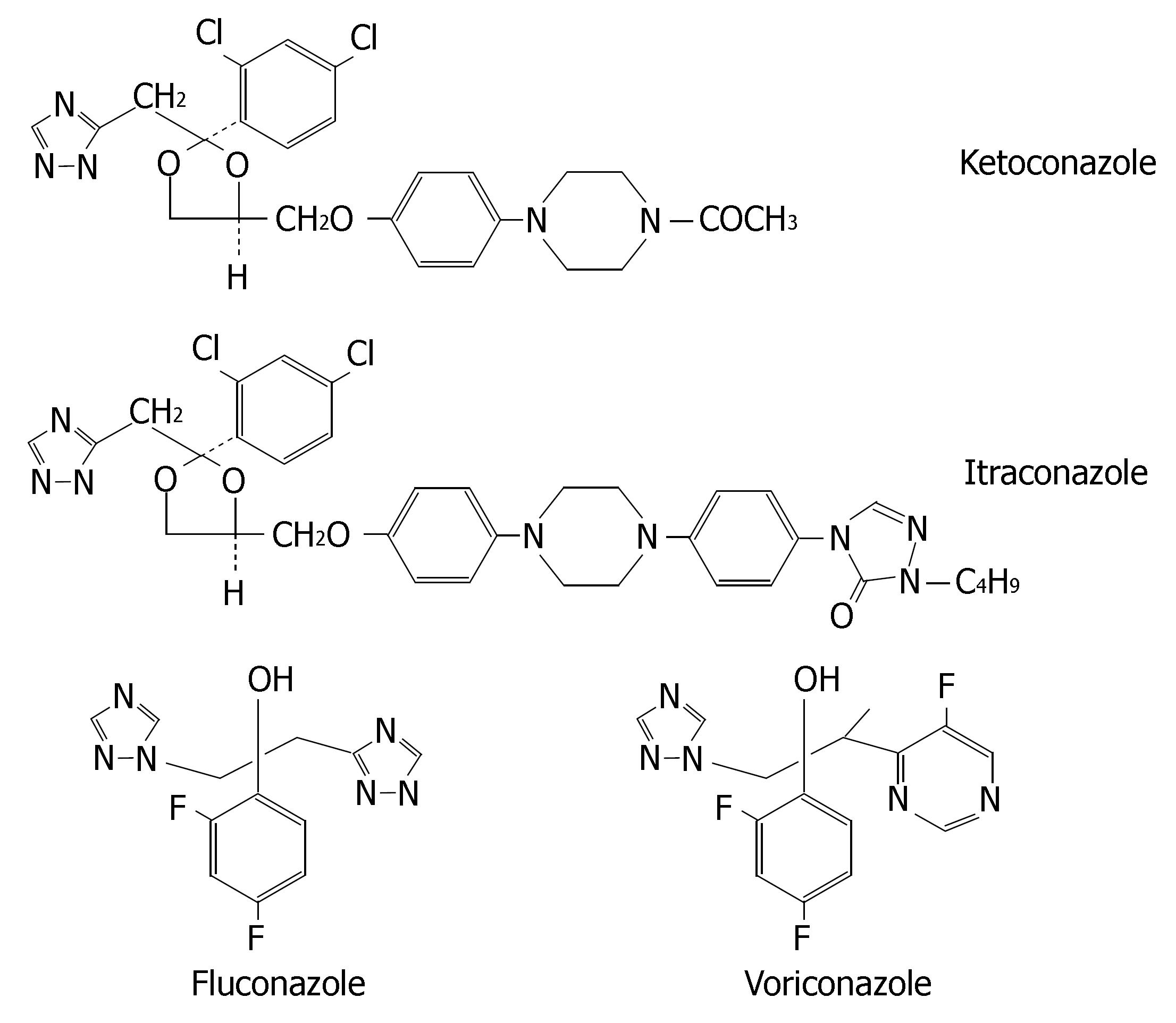
Figure 8 Chemical structures of four azole antifungals.
- Citation: Zhou Q, Yan XF, Zhang ZM, Pan WS, Zeng S. Rational prescription of drugs within similar therapeutic or structural class for gastrointestinal disease treatment: Drug metabolism and its related interactions. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(42): 5618-5628
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i42/5618.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i42.5618