©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2007; 13(34): 4655-4657
Published online Sep 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i34.4655
Published online Sep 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i34.4655
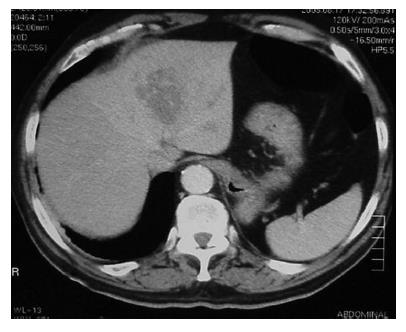
Figure 1 CT scan showing a hypodense lesion located in the left hepatic lobe of unclear etiology.
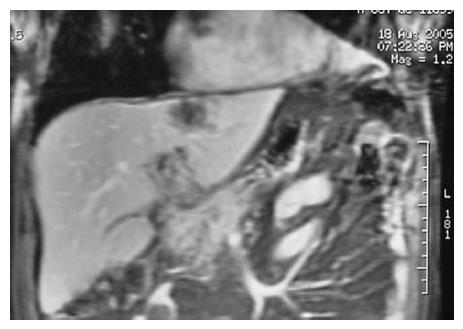
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance of the liver and bile duct showing a lesion in segments II and III and a normal common bile duct.
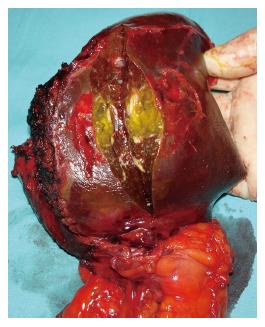
Figure 3 Left lobectomy demon-strating a lesion in segment III.
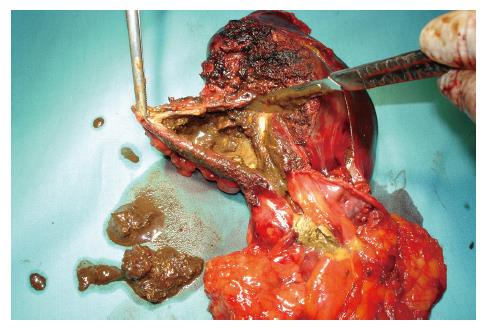
Figure 4 Cystic lesion in segment II showing the continuity with the lesser omentum and necrotic material from the pseudocyst.
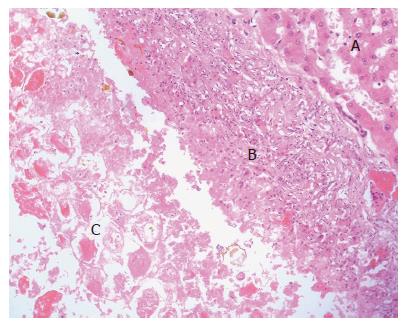
Figure 5 Microscopically the liver pseudocystic lesion is surrounded by a wall formed by macrophages and inflammatory cells (HE, x 20).
A: Normal liver tissue; B: Pseudocystic wall; C: Intracystic necrotic debris.
- Citation: Casado D, Sabater L, Calvete J, Mayordomo E, Aparisi L, Sastre J, Lledo S. Multiple intrahepatic pseudocysts in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(34): 4655-4657
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i34/4655.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i34.4655