©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2007; 13(34): 4560-4565
Published online Sep 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i34.4560
Published online Sep 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i34.4560
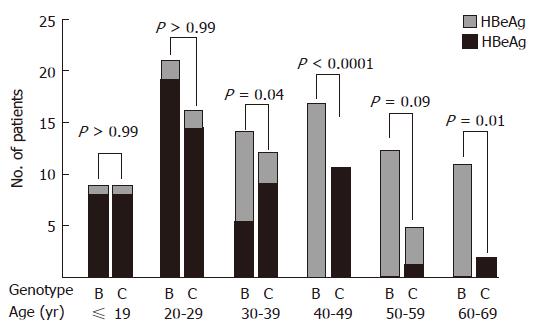
Figure 1 Age-specific HBeAg status at entry in the study in chronic hepatitis type B (CH-B)-infected patients with genotype B or C.
Black box, HBeAg-positive patients; gray box, HBeAg-negative patients. Among the ≥ 30 yr old group, there are significantly more HBeAg-negative patients of genotype B than those of genotype C. In contrast, there are more HBeAg-positive patients in both groups, among the < 30 yr old group.
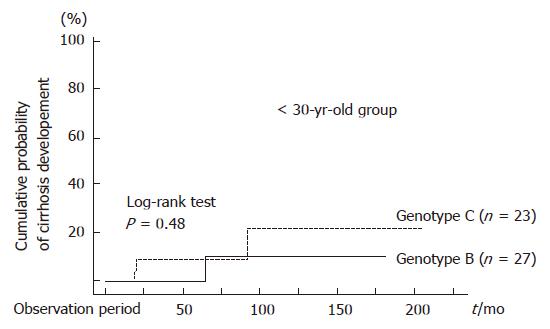
Figure 2 Comparison of cumulative probabilities of cirrhosis development between patients of genotypes B and C in the < 30 yr old group (P = 0.
48, log-rank test). Multivariate analysis identified no significant predictors.
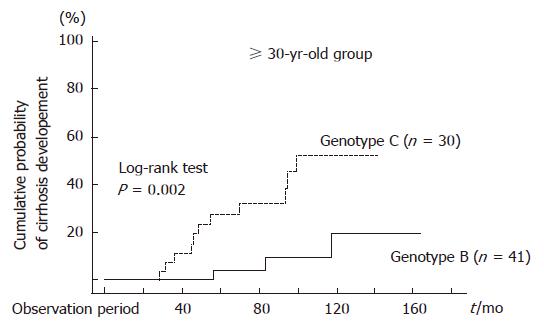
Figure 3 Comparison of cumulative probabilities of cirrhosis development between patients with genotypes B and C in the ≥ 30 yr old group (P = 0.
002; log-rank test). A Cox proportional hazards analysis also indicated that genotype C was the only significant predictor (relative risk 5.75; 95% confidence intervals: 0.033-0.916, P = 0.039).
- Citation: Maeshiro T, Arakaki S, Watanabe T, Aoyama H, Shiroma J, Yamashiro T, Hirata T, Hokama A, Kinjo F, Nakayoshi T, Nakayoshi T, Mizokami M, Fujita J, Sakugawa H. Different natural courses of chronic hepatitis B with genotypes B and C after the fourth decade of life. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(34): 4560-4565
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i34/4560.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i34.4560