©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2007; 13(29): 3932-3938
Published online Aug 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3932
Published online Aug 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3932
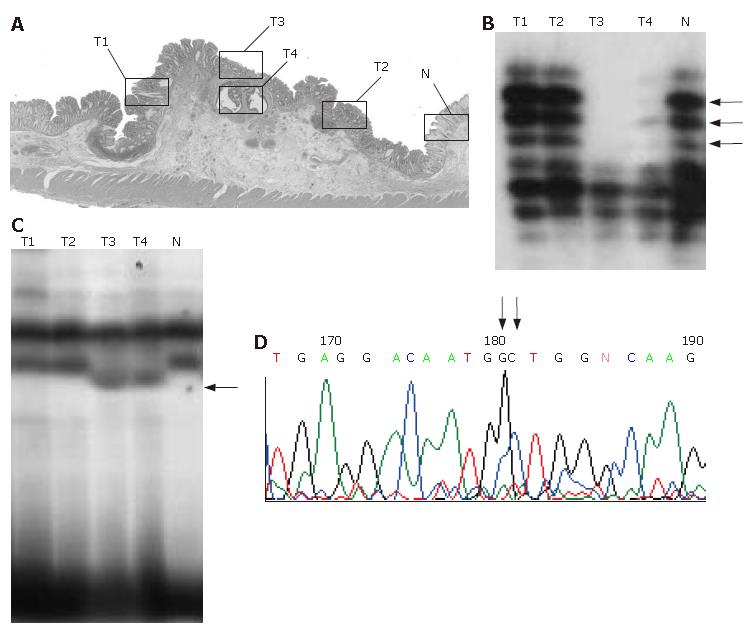
Figure 1 Representative example (case 22).
A: Histologic findings. Open squares indicate microdissected areas. T1-T4: tumor samples; N: normal sample. B: Microsatellite assay of D10S591. T3 and T4 show allelic loss of the locus (arrow). C:polymerase chain reaction-single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis of KLF6. T3 and T4 show mobility shift (arrow). D: Direct sequencing analysis of KLF6. A missense mutation at codon 735 (CTG to GCT) is confirmed.
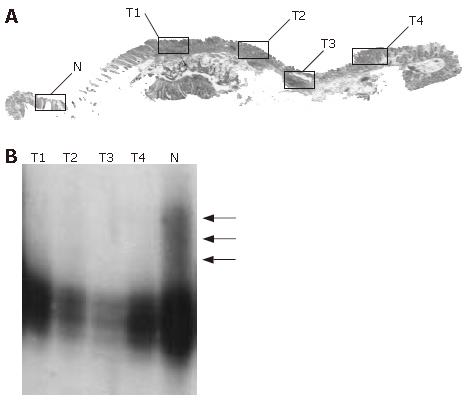
Figure 2 Representative example (case 38).
A: Histologic findings. T1-T4: tumor samples; N: normal sample. B: Microsatellite assay of TP53. All of the microdissected tumor foci (T1-T4) show allelic loss of the locus (arrow).
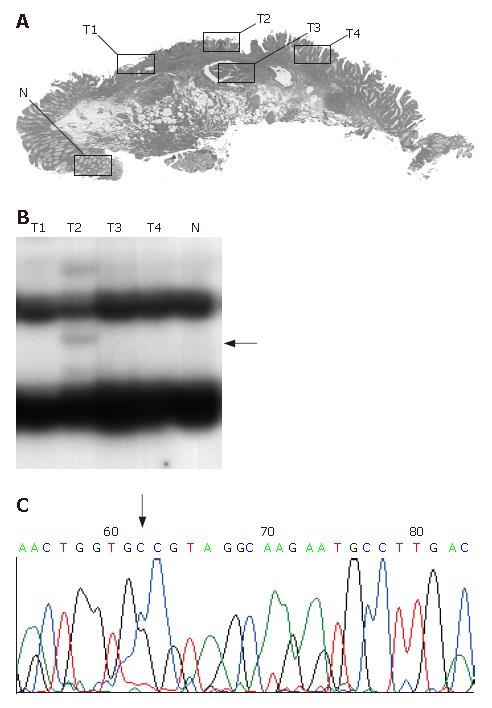
Figure 3 Representative example (case 20).
A: Histologic findings. T1-T4: tumor samples; N: normal sample. B: polymerase chain reaction-single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis of K-ras. T2 shows a mobility shift. C: Direct sequencing analysis of K-ras. A misssense mutation at codon 13 (GGC to GCC) is confirmed.
-
Citation: Mukai S, Hiyama T, Tanaka S, Yoshihara M, Arihiro K, Chayama K. Involvement of Krüppel-like factor 6 (
KLF6 ) mutation in the development of nonpolypoid colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(29): 3932-3938 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i29/3932.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3932